Embed presentation
Download to read offline

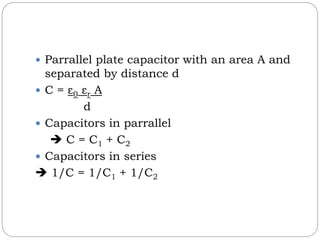







Capacitors store electric charge and their capacitance is measured in Farads. The capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor depends on the surface area of the plates, the distance between them, and the dielectric material between the plates. Capacitors can be connected in parallel, in which case the total capacitance is the sum of individual capacitances, or in series, in which case the reciprocal of the total capacitance is the sum of the reciprocals of the individual capacitances. Energy is stored in a charged capacitor and can be calculated using the formula of one-half the capacitance times the voltage squared. Capacitors have various uses including in radios, switches, charge storage, power supplies, and ampl









