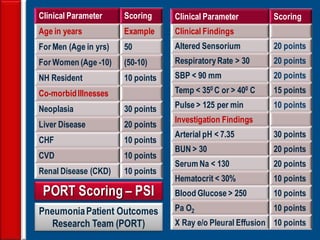
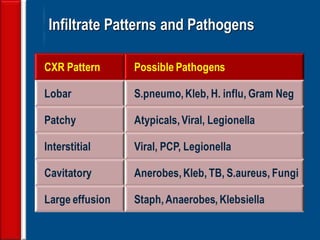
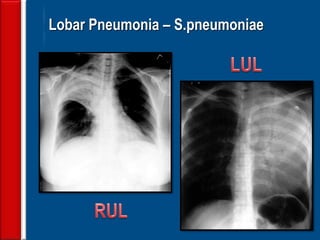
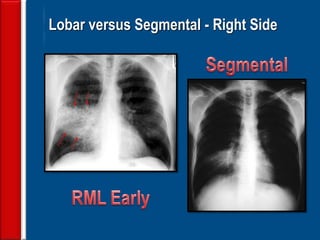
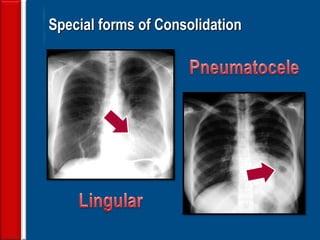
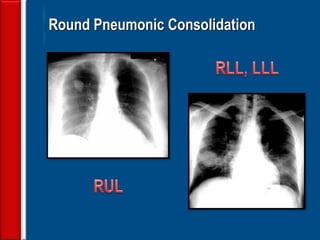
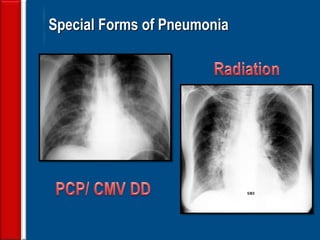
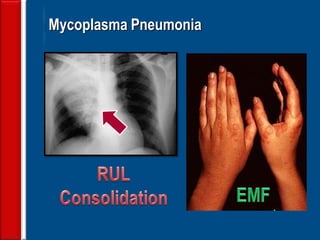
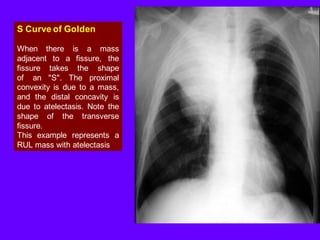
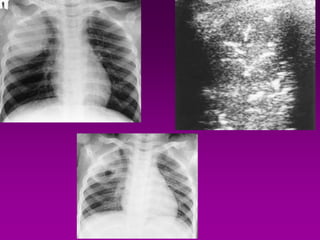
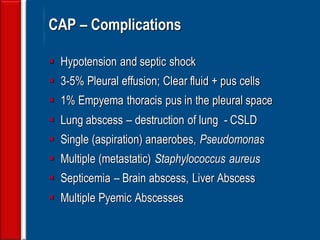
Community acquired pneumonia (CAP) is caused by pathogens acquired outside of a hospital setting. It is classified based on location and timing of acquisition. Empirical antibiotic treatment is recommended and should not be delayed. Severity is assessed using scoring systems like PORT and CURB-65 to determine treatment setting. Common pathogens include Streptococcus pneumoniae and atypical bacteria. Radiography can help establish diagnosis and prognosis. Outpatient treatment involves oral antibiotics while inpatient may require IV antibiotics. Duration of treatment and prevention strategies like vaccination are also discussed.