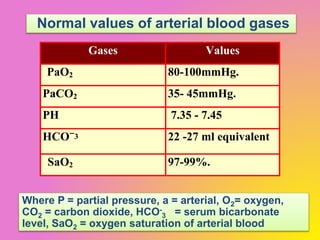
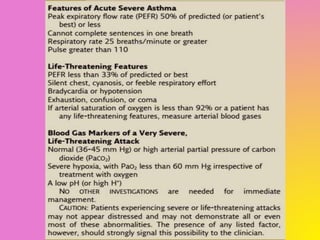
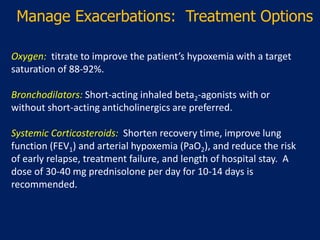
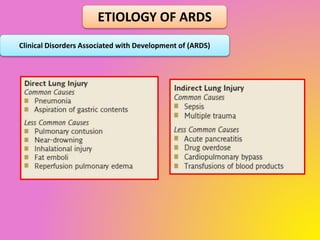
1) Respiratory failure is a condition where the lungs cannot properly oxygenate the blood and remove carbon dioxide, classified as Type I (hypoxemic) or Type II (hypercapnic).
2) It can result from problems affecting gas exchange in the lungs, respiratory control centers in the brain, or the chest wall muscles.
3) Common causes of Type I respiratory failure include pneumonia, ARDS, and severe asthma, while Type II is often due to conditions that decrease breathing, such as COPD.