This document discusses calcium, including its history, functions, absorption, metabolism, and sources. It provides the following key points:
- Calcium is essential for bone formation, muscle and nerve function, and plays a role in many biochemical reactions in the body.
- It is absorbed in the small intestine through both passive and active transport, and its levels are regulated by parathyroid hormone, vitamin D, and calcitonin.
- Good dietary sources include dairy products like milk and cheese, as well as green leafy vegetables. Calcium supplements may be recommended for some groups.
- Disorders can include osteoporosis, rickets, and hypocalcemia or hypercalcemia if levels


![Introduction -
calcium is a major mineral in human body.
Almost 99% of calcium is present in the hard
tissues of the body –namely the bones and
teeth.
The rest is distributed in blood and soft tissues ,
such as muscles , the liver and the heart.
Normal blood plasma calcium is 9 – 11mg/dl.
Calcium is stored in the form of hydroxyapatite
Ca10[PO4]6[OH]2.
Men accumulate more skeletal calcium
[1200mg] than women [1000mg].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calcium-180223062324/85/Calcium-3-320.jpg)
![Functions :
BONE FORMATION : calcium comprises 39.9 %
of the weight of bone mineral .there is about
1kg of calcium in the adult skeleton as a
complex crystalline material with phosphate
.the mineral is laid down on an organic matrix
– collagen.
There are two types of bones –dense cortical
bone [80%of skeleton ] and spongy trabecular
bone [20%of skeleton ].
The turnover of bone is controlled by the
activities of its bone cells –
1 Osteoclasts – resorption of bone.
2 osteoblasts – bone formation.
3 osteocytes – communication with each other.
Skeleton is constantly being resorbed and
replaced.
The peak bone mass is achieved during 18 -20
yrs. of age.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calcium-180223062324/85/Calcium-4-320.jpg)





![Metabolism
Once calcium is absorbed , it is transported to the blood and released
into the fluids of body tissues. This is taken up by cells from the
extracellular fluid.
As blood is filtered through kidneys about 99% of calcium is
reabsorbed into blood. 1% excreted in urine [normally 100-200mg
/day]
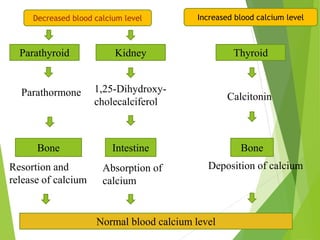
Hormonal control : The balance of calcium is controlled by the
action of parathyroid hormone,1,25,dihydroxy cholecalciferol and
calcitonin.
Parathyroid hormone –decreased plasma free calcium triggers the
release of parathyroid hormone. It helps in many ways in maintaining
normal calcium levels.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calcium-180223062324/85/Calcium-10-320.jpg)

![Calcitonin - Elevated plasma calcium levels ,release calcitonin
from the thyroid glands. It inhibits the release of calcium and
phosphorus into the blood from bones.
Vitamin D - In calcium deficiency, the most active form of vitamin
D – 1-25,[OH]2 D3 causes enhanced intestinal absorption and renal
reabsorption.
Cytokines - May have a central role in normal bone remodeling.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calcium-180223062324/85/Calcium-12-320.jpg)

![Abnormality :-
Osteoporosis
It is a condition associated with loss in bone density and bone mass,
primarily found in middle age and elderly women .
According to NIN studies, women of low socio-economic group have
thinner bones due to their poor nutritional status and poor reproductive
health.
Risk factors- gender, body size, family history, disease, effect of drugs,
alcohol, smoking, sedentary lifestyle, inappropriate diet etc.
Diagnosis – duel energy X –ray absorptiometer [DEXA] measures the
bone density.
The test is not expensive and not invasive.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calcium-180223062324/85/Calcium-14-320.jpg)

![BONE DISORDERS :
Children with vitamin D deficiency develop rickets ,and adults
osteomalecia.
They do not calcify bone normally and their bones contain
osteoid [unmineralised bone].
HYPOCALCEMIA : When ionic calcium is reduced ,nerve and
muscles become readily excitable leading to a clinical condition
– TETANY.
Also associated with premenstrual syndrome – low calcium diets
exhibit increased negative effects ,greater pain ,more water
retention and poorer concentration.
Recent studies show that low calcium intake [100mg/day] is
associated with increased blood pressure.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calcium-180223062324/85/Calcium-16-320.jpg)
![HYPERCALCEMIA :
Elevated plasma calcium levels occur in adults due to
hyperparathyroidism or excessive doses of vit D. Gastrointestinal
symptoms like anorexia, nausea, vomiting, constipation,
abdominal pain occur.
Hardening of soft tissues especially of kidneys is fatal .
BIOCHEMICAL TESTS FOR CALCIUM DETECTION :
1 Plasma calcium level
2 vitamin D level
3 Recent studies by cardiologists suggest coronary calcium scans,
to check calcium in arteries of heart .It looks for calcium in
plaques of the coronary artery [cardiac calcium score ].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calcium-180223062324/85/Calcium-17-320.jpg)




![RECENT HEALTH PROBLEMS IN INDIA :
Include maternal and neonatal morbidity and mortality due to
calcium deficiency
preeclampsia [low socioeconomic group]
Osteoporosis in elderly women.
Hypertension and cardiac disorders.
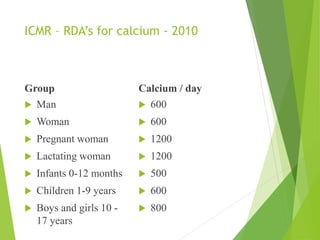
SUPPLEMENTS : are prescribed for women above the age of
40 yrs. [along with exercise ], men above 55yrs and pregnant
and lactating women.
NATIONAL INSTISTUTE OF HEALTH suggests not more
than 600 mg calcium supplement per day along with meals.
Different combinations are used depending upon health
conditions – calcium carbonate, calcium citrate, calcium
phosphate, calcium lactate etc.
If any iron or thyroxin supplements are taken , calcium
supplements to deliberately be taken separately.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calcium-180223062324/85/Calcium-23-320.jpg)