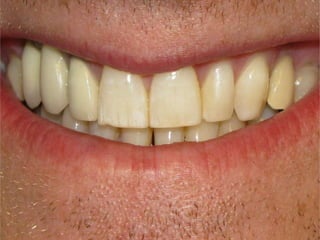
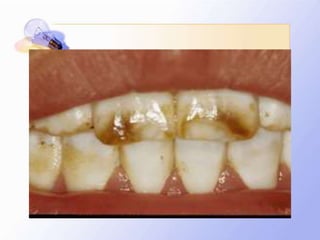
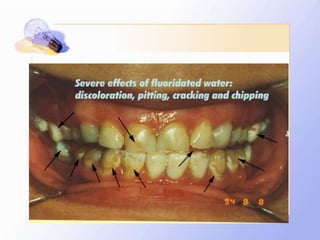
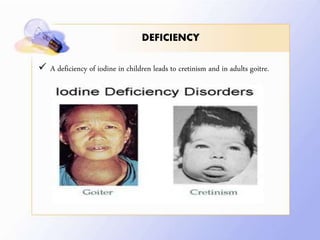
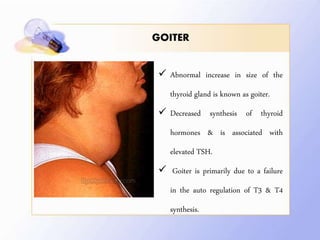
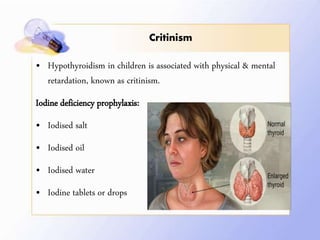
This document discusses human nutrition as it relates to iodine, fluoride, and magnesium. It provides information on the functions, sources, recommended daily amounts, and effects of deficiencies and toxicities for each mineral. Iodine is needed to make thyroid hormones which regulate metabolism. Sources include seafood, bread, and iodized salt. A deficiency can cause goiter or cretinism. Fluoride strengthens teeth and bones. It is found in drinking water and too much can cause dental or skeletal fluorosis. Magnesium is involved in many enzyme systems and is found in vegetables, grains, and dairy. Deficiencies or toxicities of any of these minerals can impact health.











![Toxicity
• Most people are very tolerant to excess iodine intake from food
with the exception of certain subgroups with autoimmune
thyroid disease and iodine deficiency.
• High intakes of iodine from food, water and supplements have
been associated with thyroiditus, goitre (due to increased thyroid
stimulating hormones [TSH] stimulation),hypothyroidism,
hyperthyroidism, sensitivity reactions, thyroid papillary cancer
and acute responses in some individuals.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microminerals-170925160812/85/Micro-minerals-16-320.jpg)