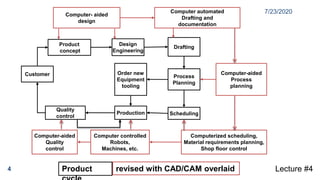
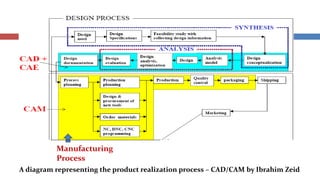
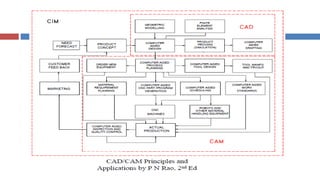
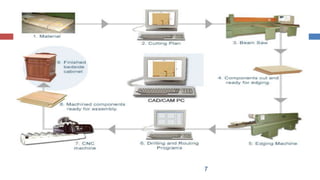
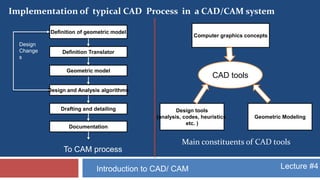
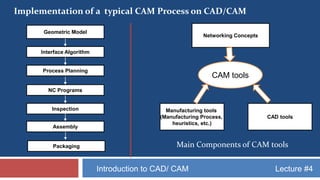
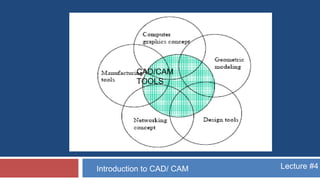
This document provides an overview of CAD/CAM systems and processes. It discusses the product cycle and how CAD/CAM is integrated at various stages from concept development to manufacturing. The key stages of a typical CAD process and CAM process within a CAD/CAM system are described. The achievements enabled by CAD/CAM technologies are listed. Product engineering is discussed as dealing with both the design and manufacturing aspects of a product while considering factors like cost, producibility and other specifications.