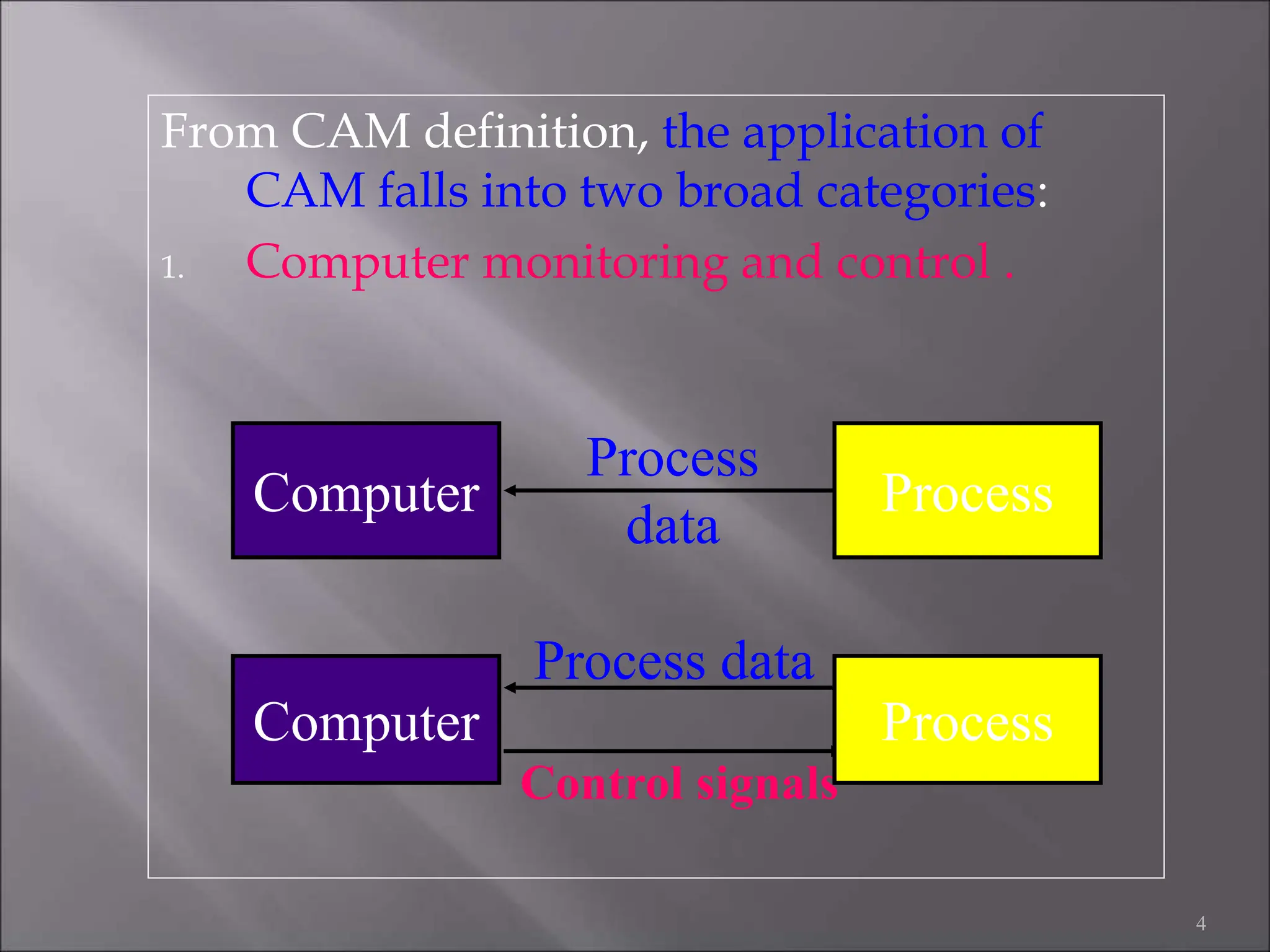
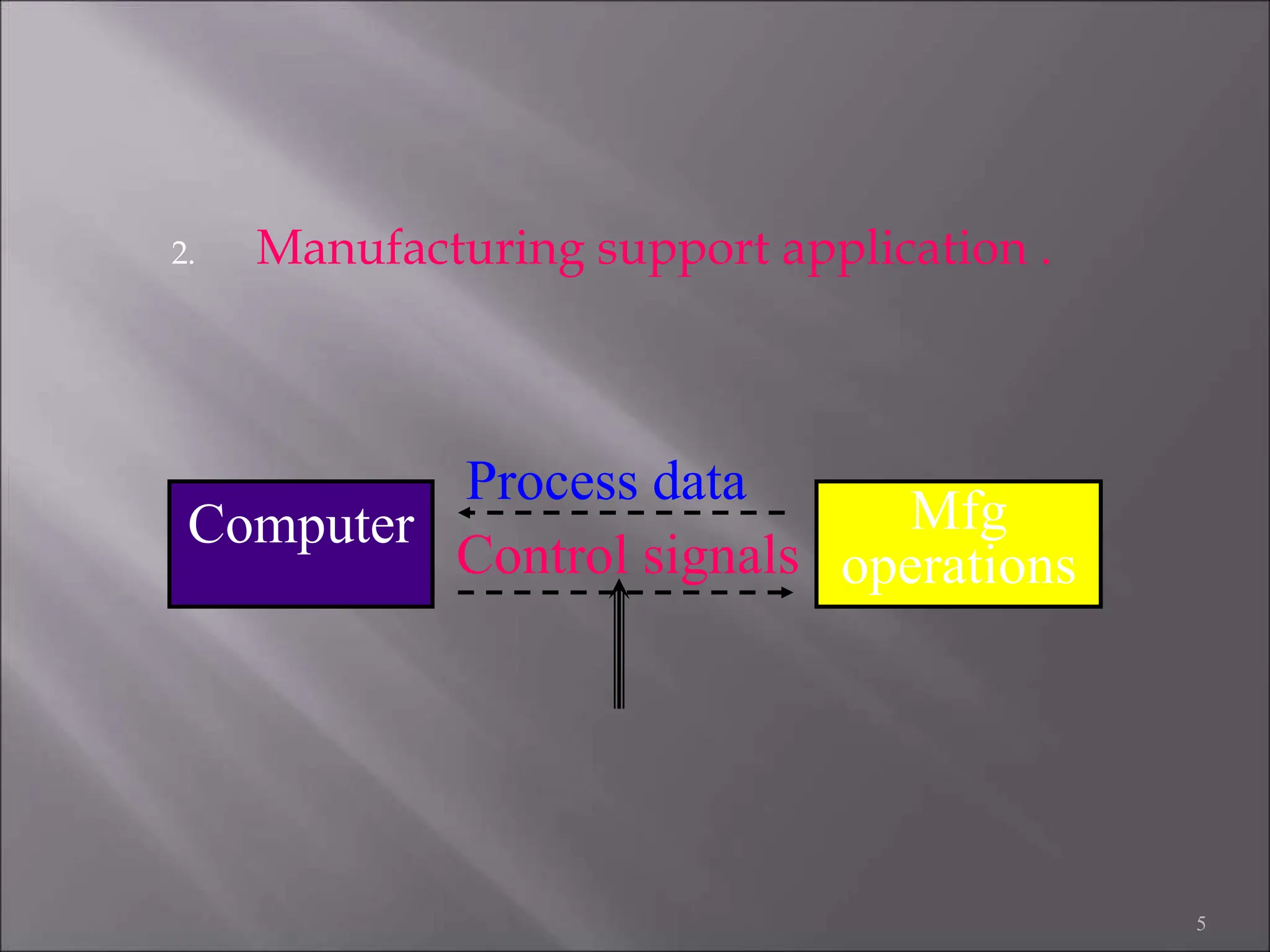
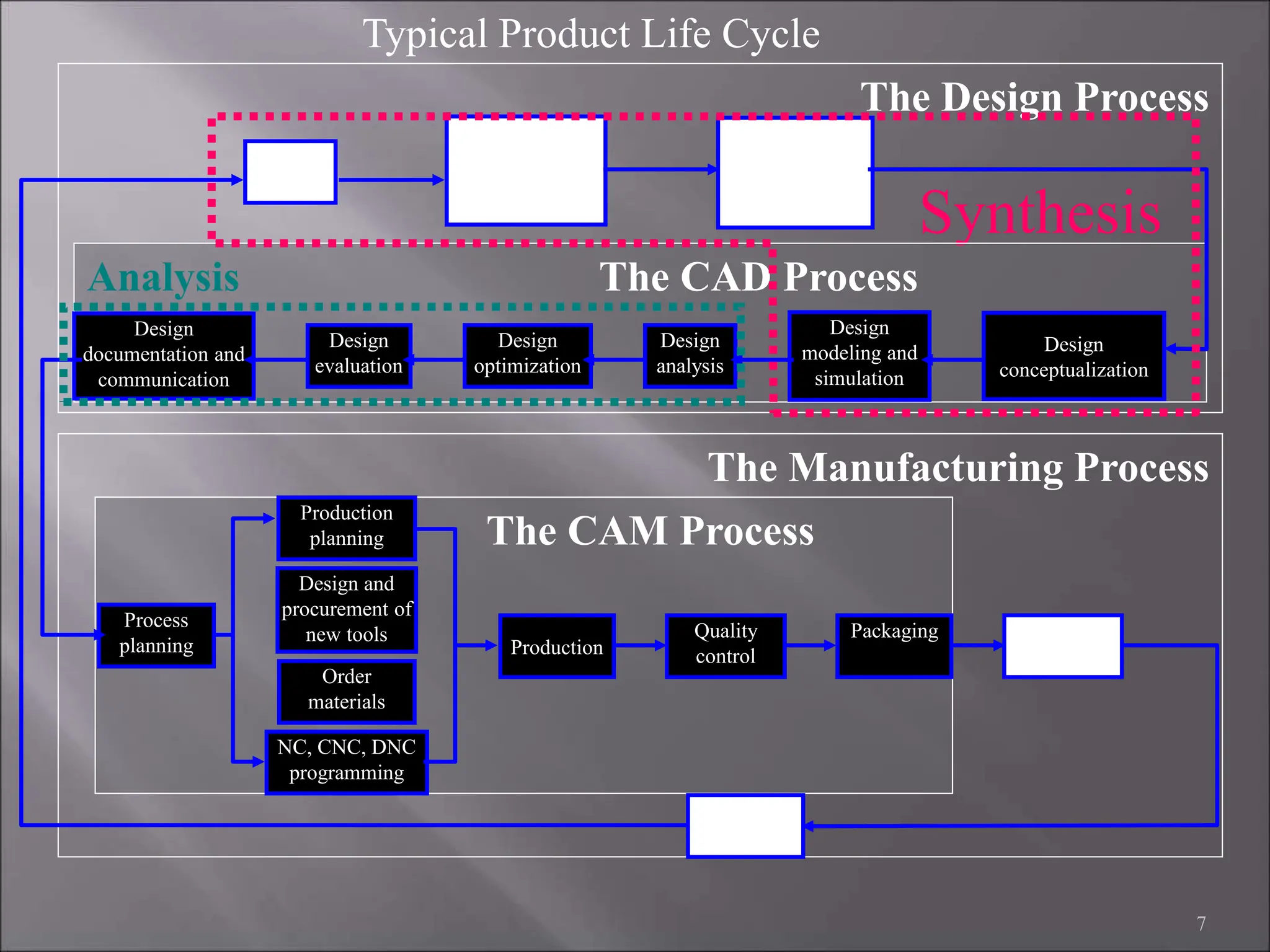
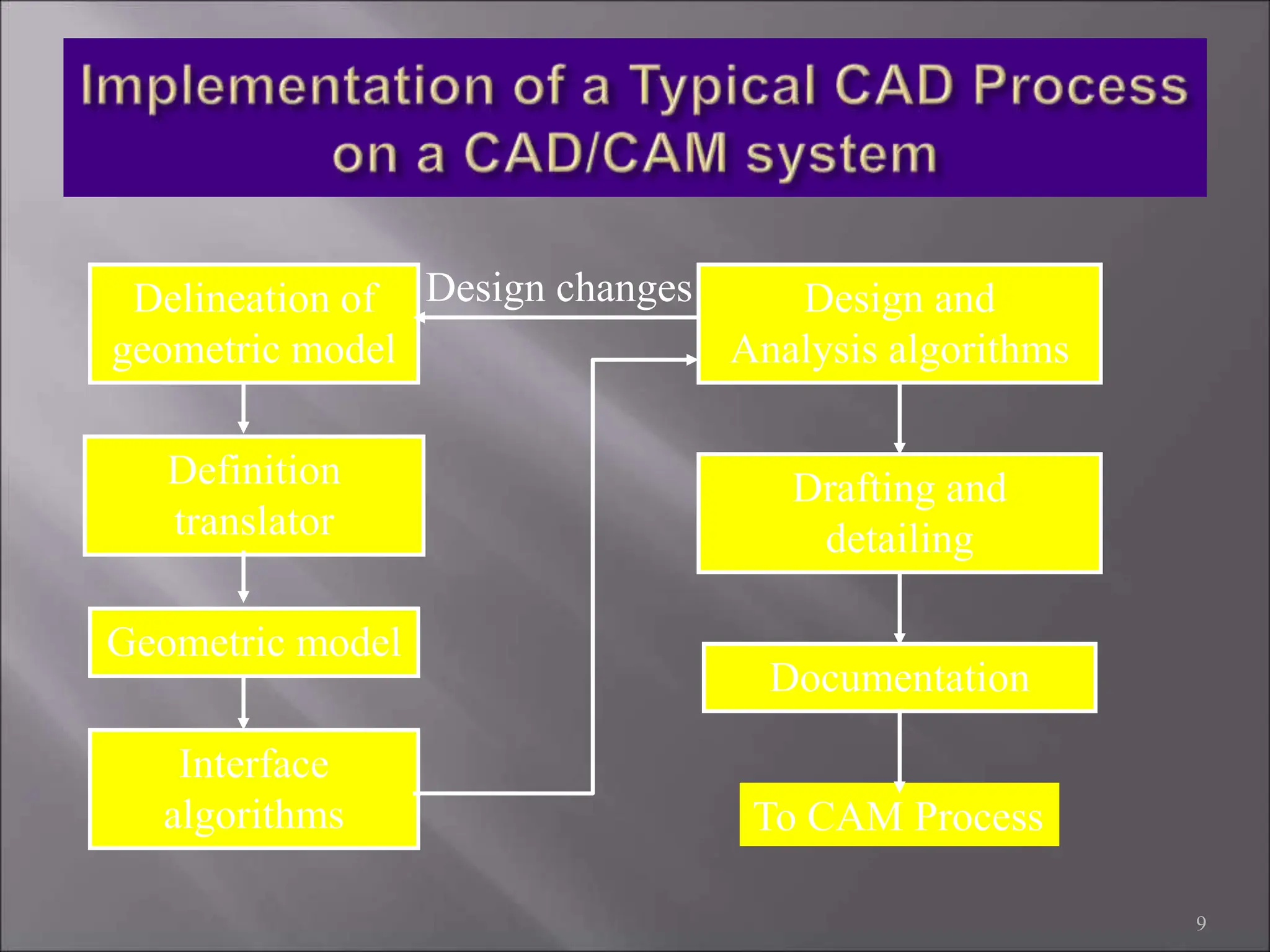
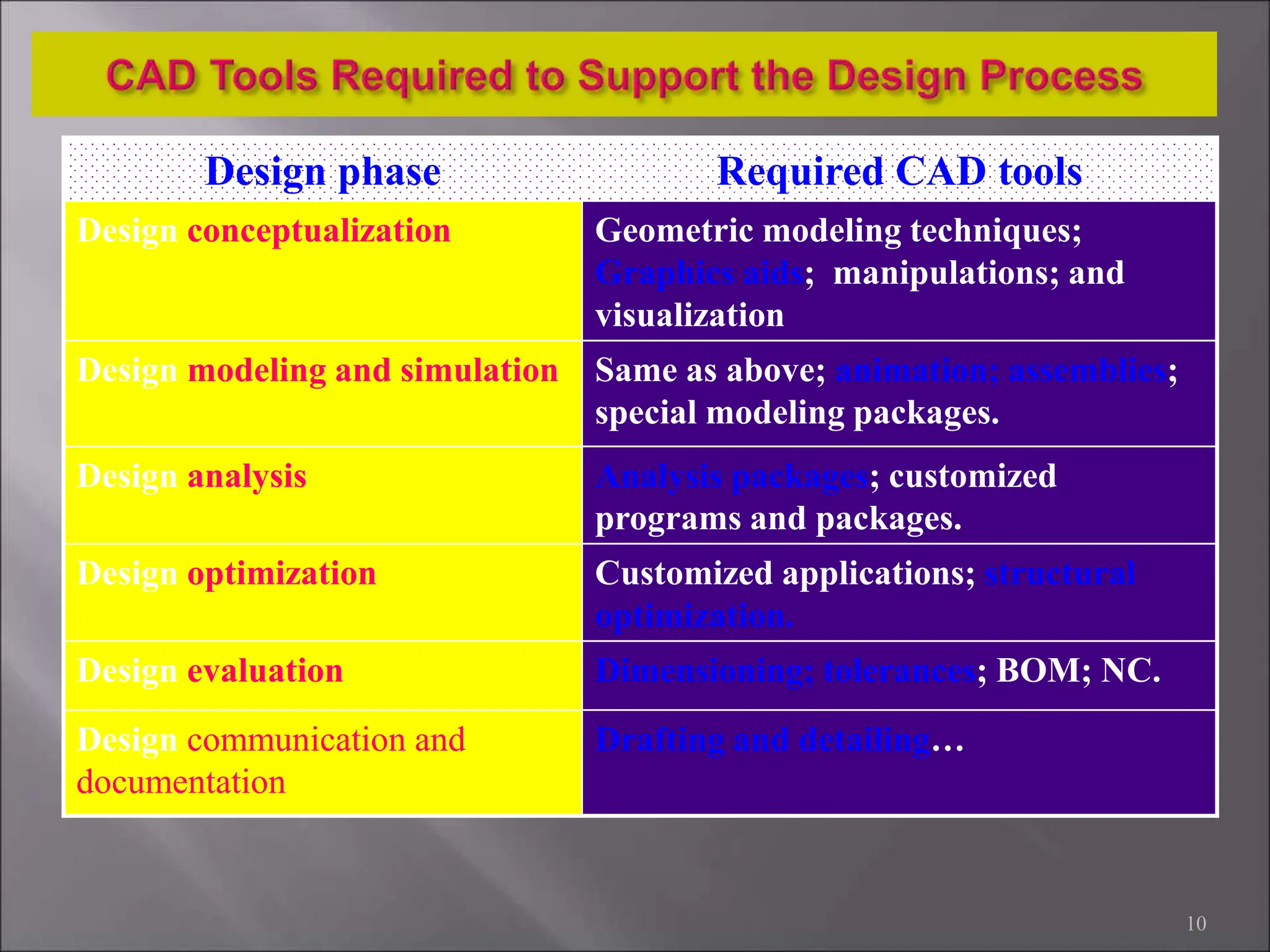
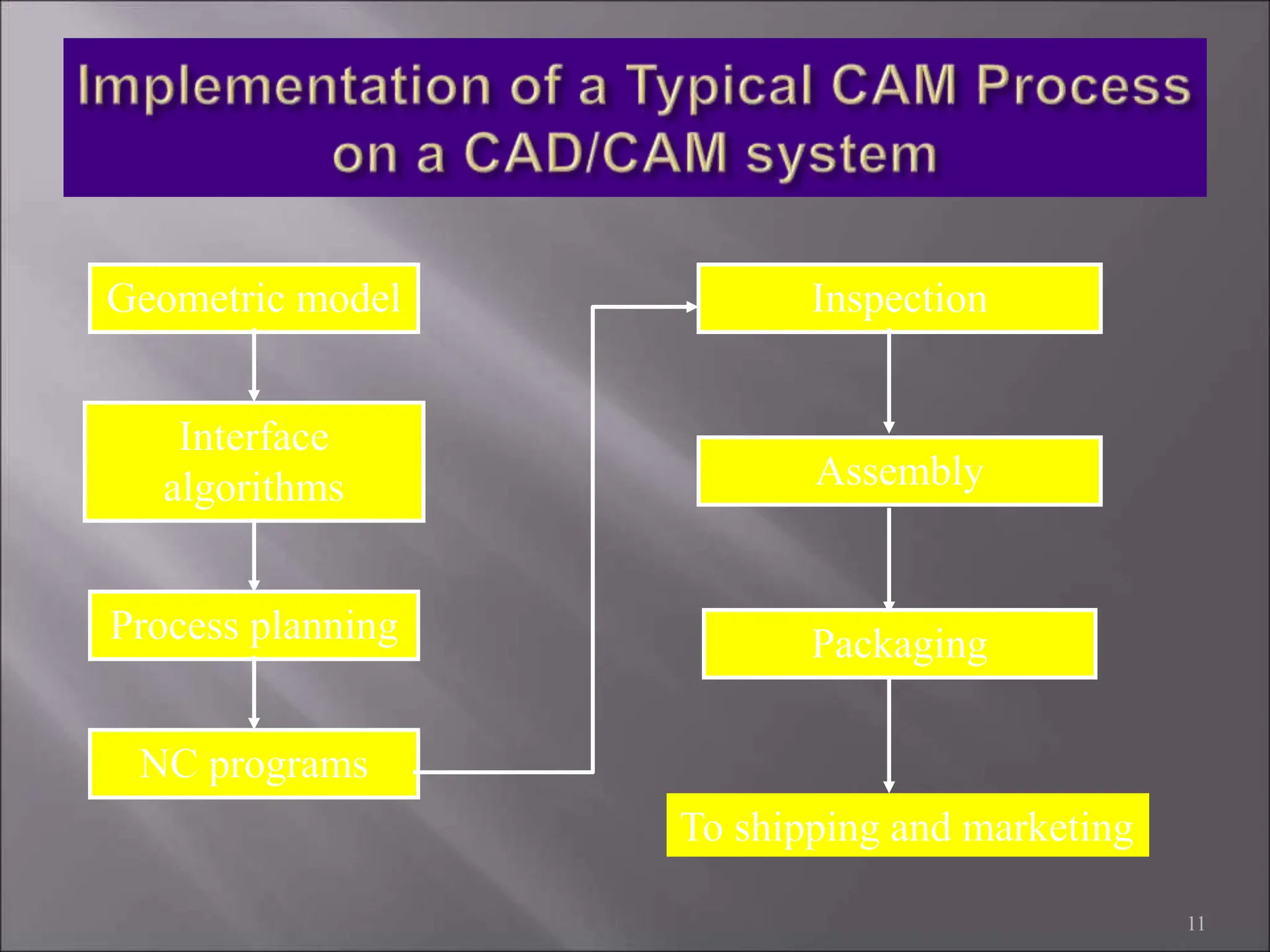
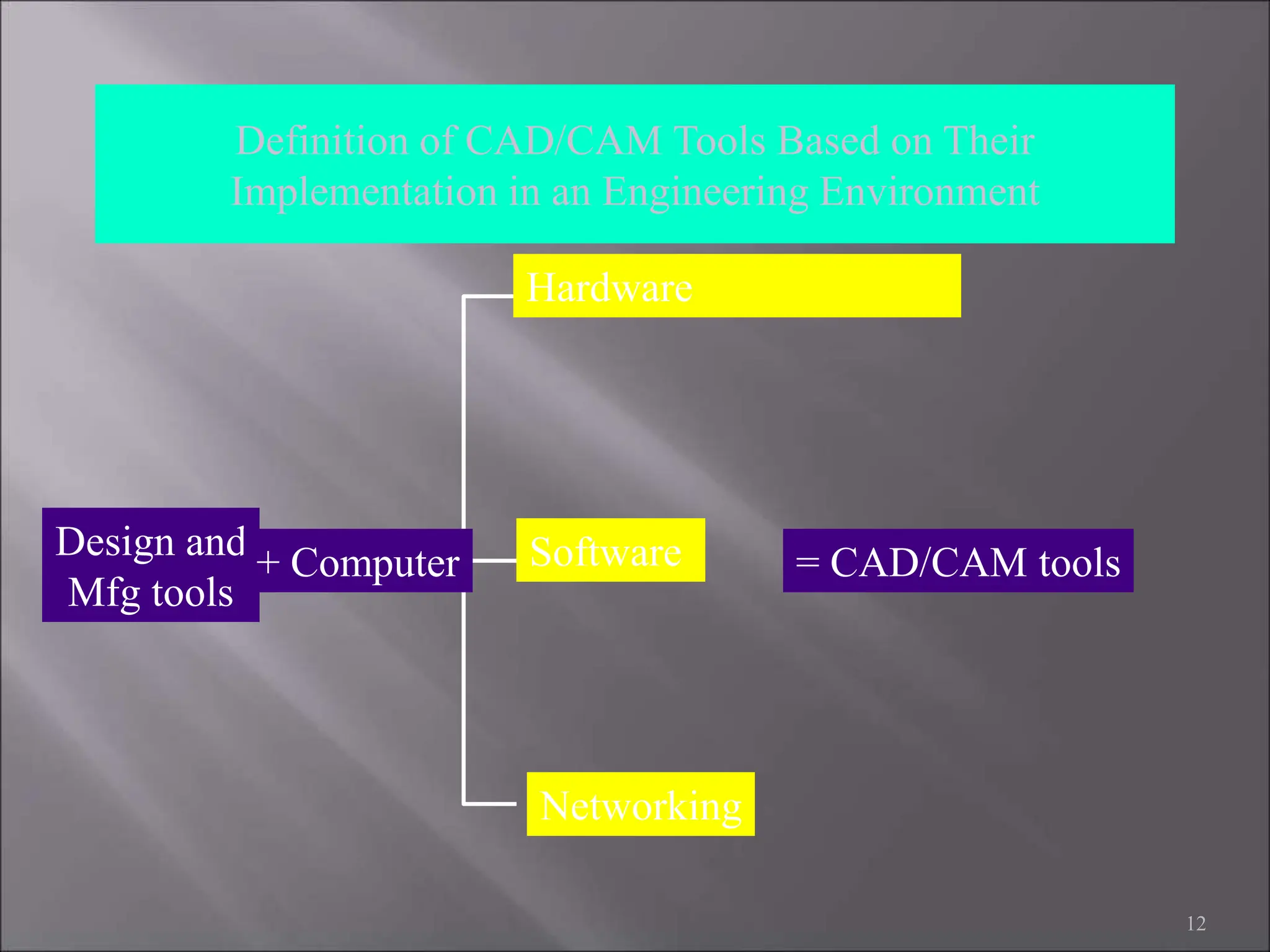
CAD/CAM refers to the use of computer systems in design and manufacturing functions, with CAD focusing on design processes and CAM on the management of manufacturing operations. The product life cycle consists of identification, design, and manufacturing processes, including synthesis and analysis. CAD/CAM tools are essential for modern engineering environments, enhancing productivity, flexibility, and quality while integrating design and manufacturing functions.