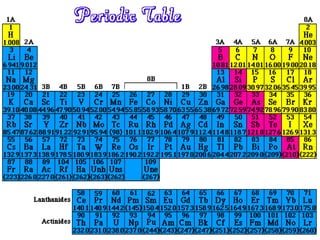
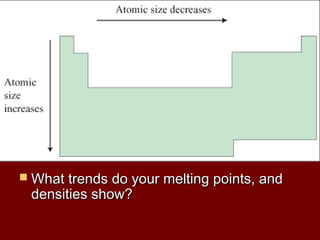
The document outlines the agenda and objectives for a chemistry lesson on the periodic table. It will include watching a Bill Nye video on atoms, taking notes on the periodic table, and completing homework problems from the textbook. The lesson will describe the structure and organization of the periodic table, distinguish between metals, nonmetals, and metalloids, and identify and describe the properties of halogens and noble gases.