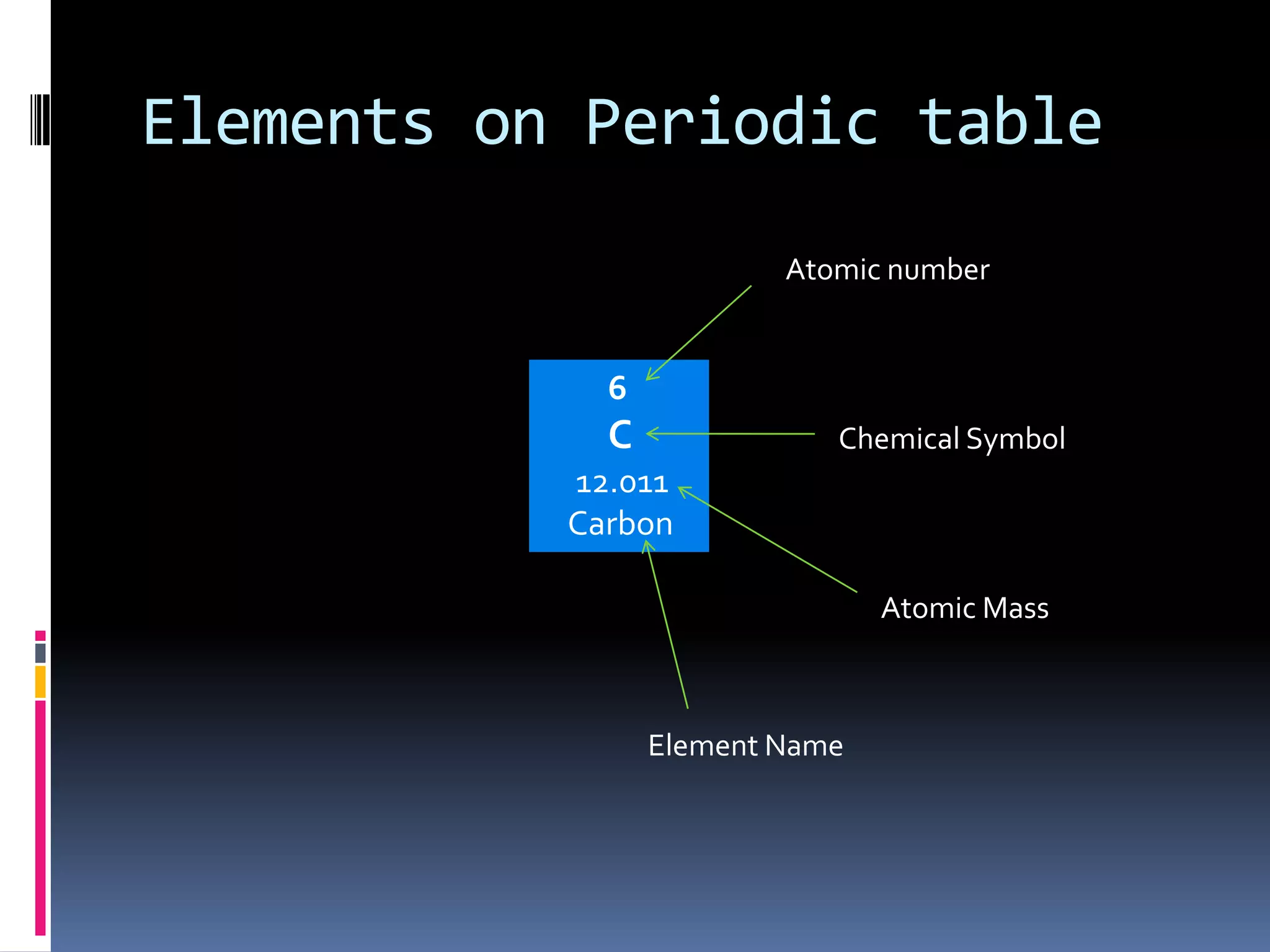
1. The document describes elements and their organization on the periodic table. It defines elements as pure substances that cannot be decomposed and discusses their characteristic properties.
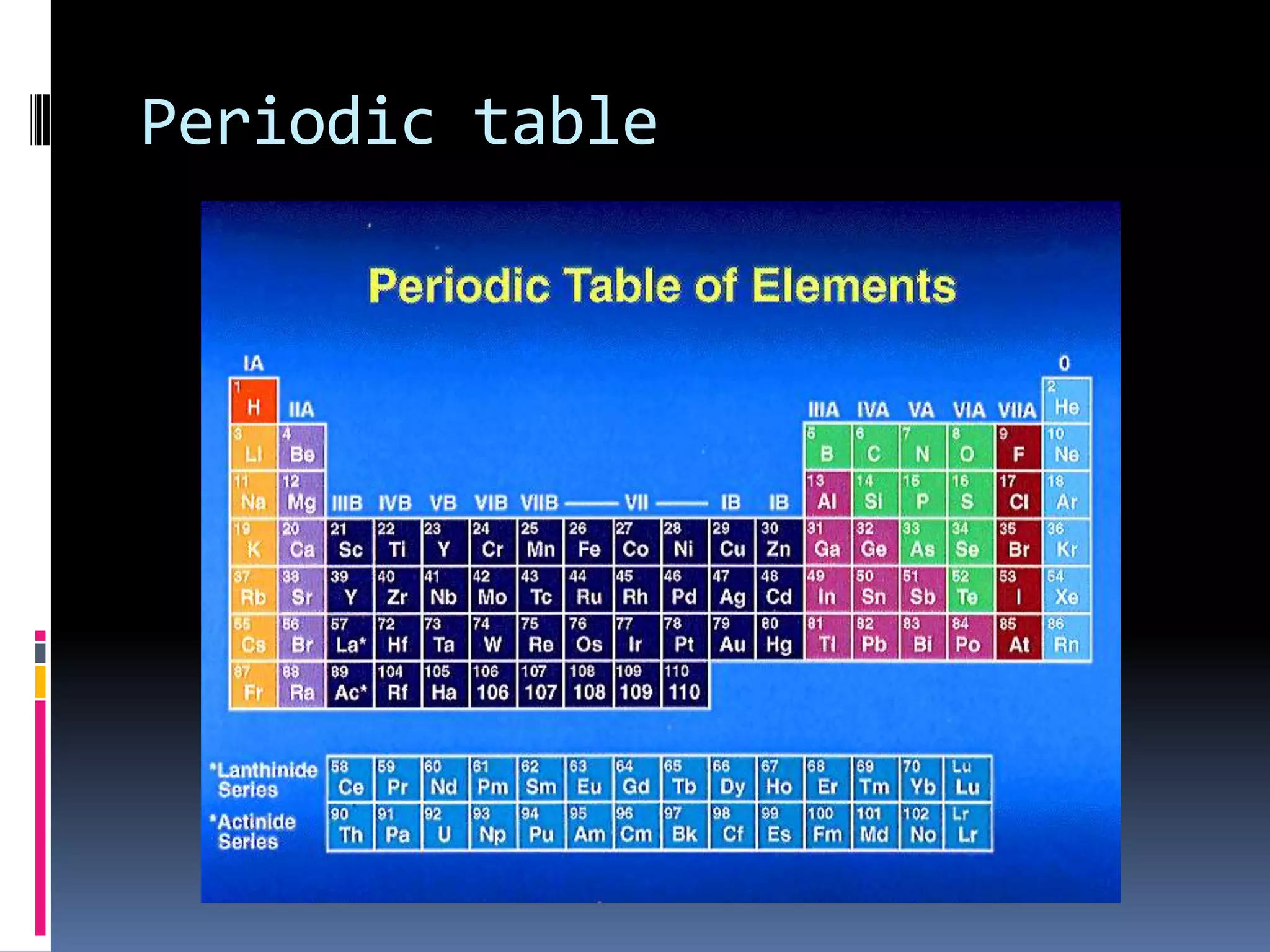
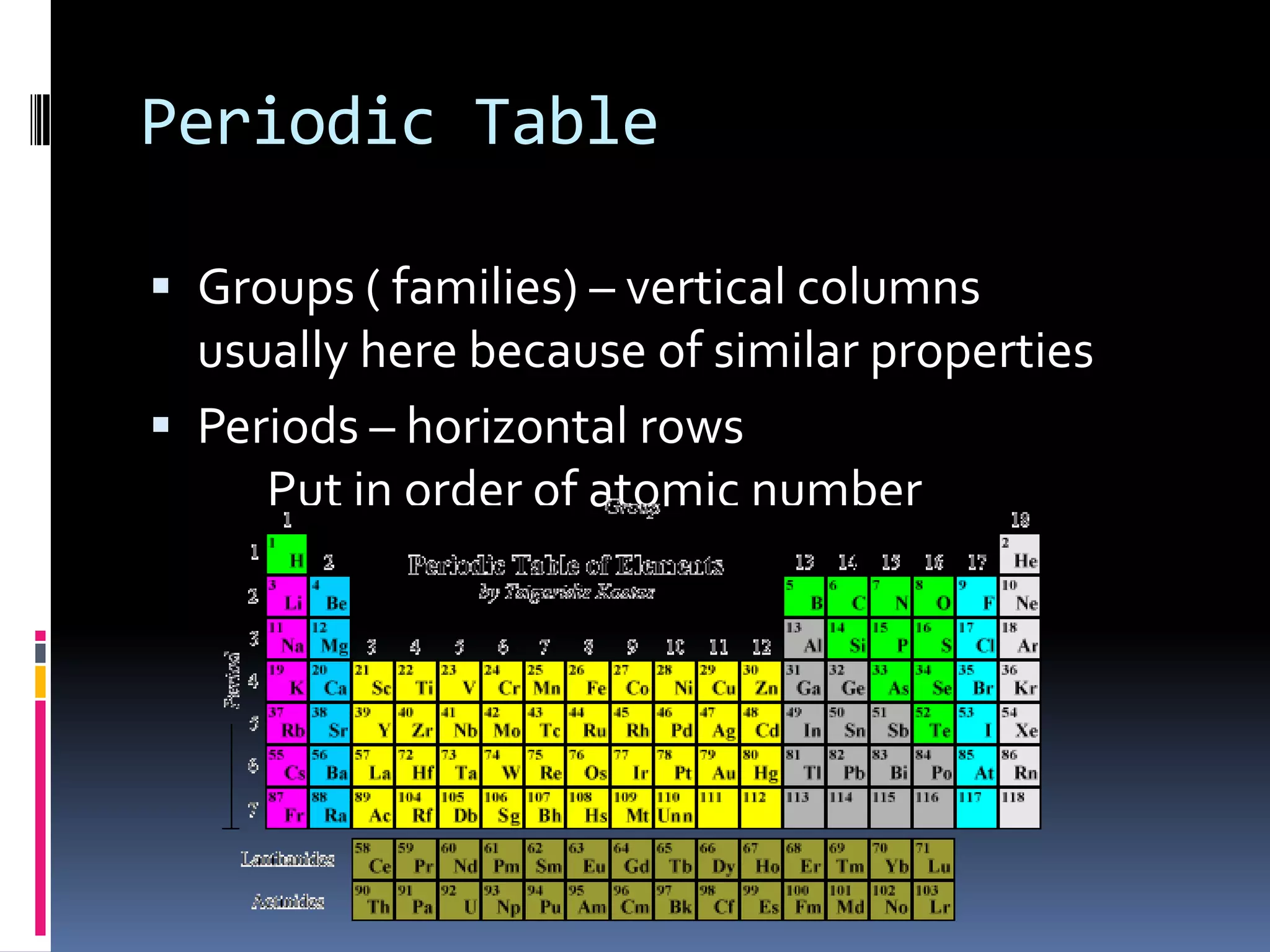
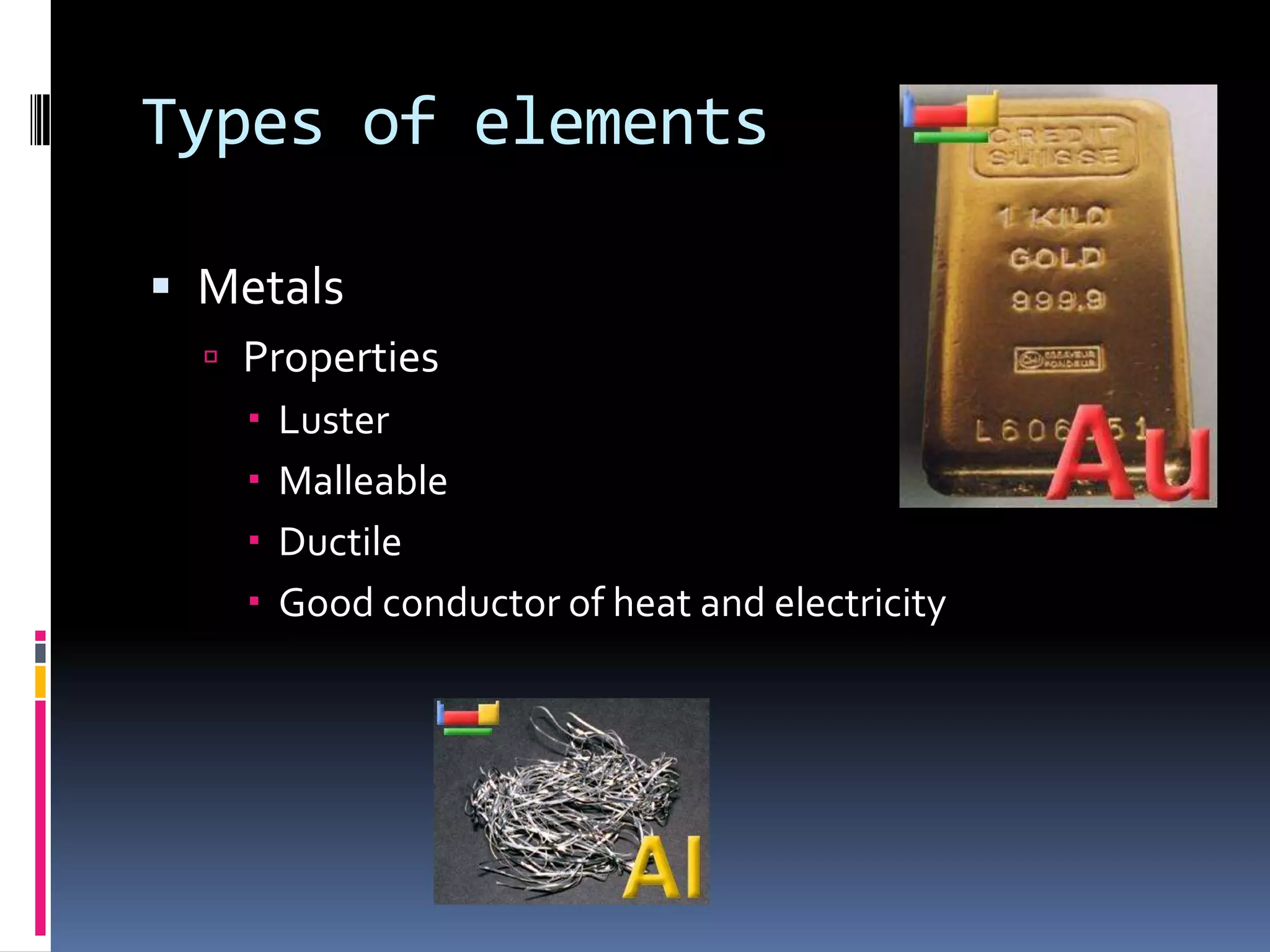
2. The periodic table arranges elements in groups and periods based on atomic number and similar properties. It distinguishes metals, nonmetals, and metalloids based on their physical properties like luster and conductivity.
3. Copper and phosphorus are used as examples of a metal and nonmetal, respectively, to illustrate their characteristic properties. Metalloids and noble gases are also described in terms of their placement and reactivity on the periodic table.