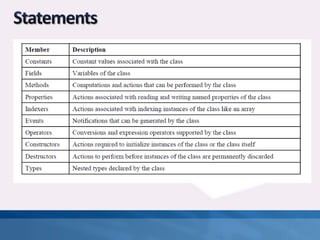
C# is a simple, modern, object-oriented, and type-safe programming language with a unified type system and support for versioning. It supports a variety of statements including blocks, declaration statements, expression statements, selection statements, iteration statements, jump statements, try-catch and try-finally statements, checked and unchecked statements, lock statements, and using statements. Classes are the most fundamental type in C# and combine state in the form of fields with actions in the form of methods and function members. Classes have both static and instance members.