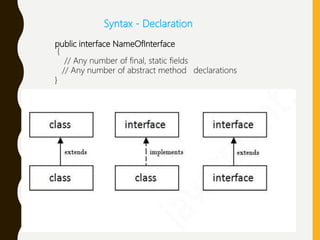
Interfaces in Java define behaviors and abstract methods that classes can implement. An interface is a blueprint of a class that defines constants and method signatures but not method bodies. When a class implements an interface, it must implement all the interface's abstract methods. Interfaces allow for abstraction and multiple inheritance in Java. Some key points about interfaces are that interface methods must be public and abstract, fields must be public and final, and interfaces cannot be instantiated - objects must be of a class that implements the interface.

![interface Printable
{
void print();
}
interface Showable extends Printable
{
void show();
}
class TestInterface4 implements Showable
{
public void print() { System.out.println("Hello"); }
public void show() { System.out.println("Welcome"); }
public static void main(String args[])
{
TestInterface4 obj = new TestInterface4();
obj.print();
obj.show();
}
}
Example - Interface extends interface](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4interface-210516073706/85/Java-Interface-4-320.jpg)
![interface printable
{
void print();
}
class A6 implements printable
{
public void print()
{
System.out.println("Hello");
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
A6 obj = new A6();
obj.print();
}
}
Example - Class implements interface](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4interface-210516073706/85/Java-Interface-5-320.jpg)
![interface A
{
int x=10;
}
interface B
{
int x=100;
}
class Hello implements A,B
{
public static void Main(String args[])
{
// reference to x is ambiguous both variables are
x
System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(A.x);
System.out.println(B.x);
}
Example –Accessing Interface Variable](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4interface-210516073706/85/Java-Interface-6-320.jpg)


