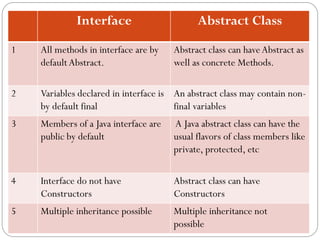
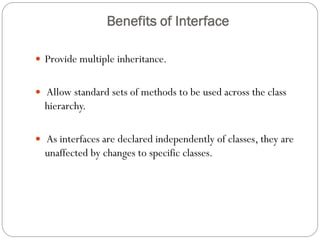
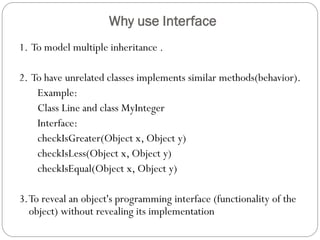
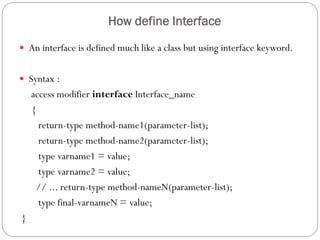
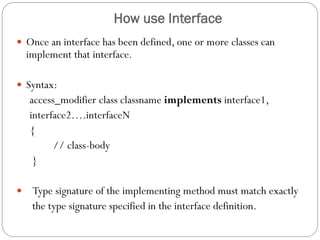
This document discusses interfaces in Java. It defines an interface as a collection of public abstract methods and public static final variables that defines a protocol for classes to implement but cannot be instantiated itself. Interfaces allow for multiple inheritance and reveal functionality without implementation details. The document explains how to define an interface with the interface keyword and how classes implement interfaces by matching method signatures. It also covers key properties of interfaces like default access modifiers and differences between interfaces and abstract classes. Benefits of interfaces include allowing standard method sets across hierarchies and resilience to class changes.




![Key Point Continued…
Variable names conflicts can be resolved by interface name
interface A
{
int x=10;
}
interface B
{
int x=100;
}
class Hello implement A,B
{
public static void Main(String arg[])
{
System.out.println(x); // reference to x is ambiguous both variables are x
System.out.println(A.x);
System.out.println(B.x);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interface-141208213059-conversion-gate02/85/Interface-8-320.jpg)