This document provides an overview of C# programming basics, including:
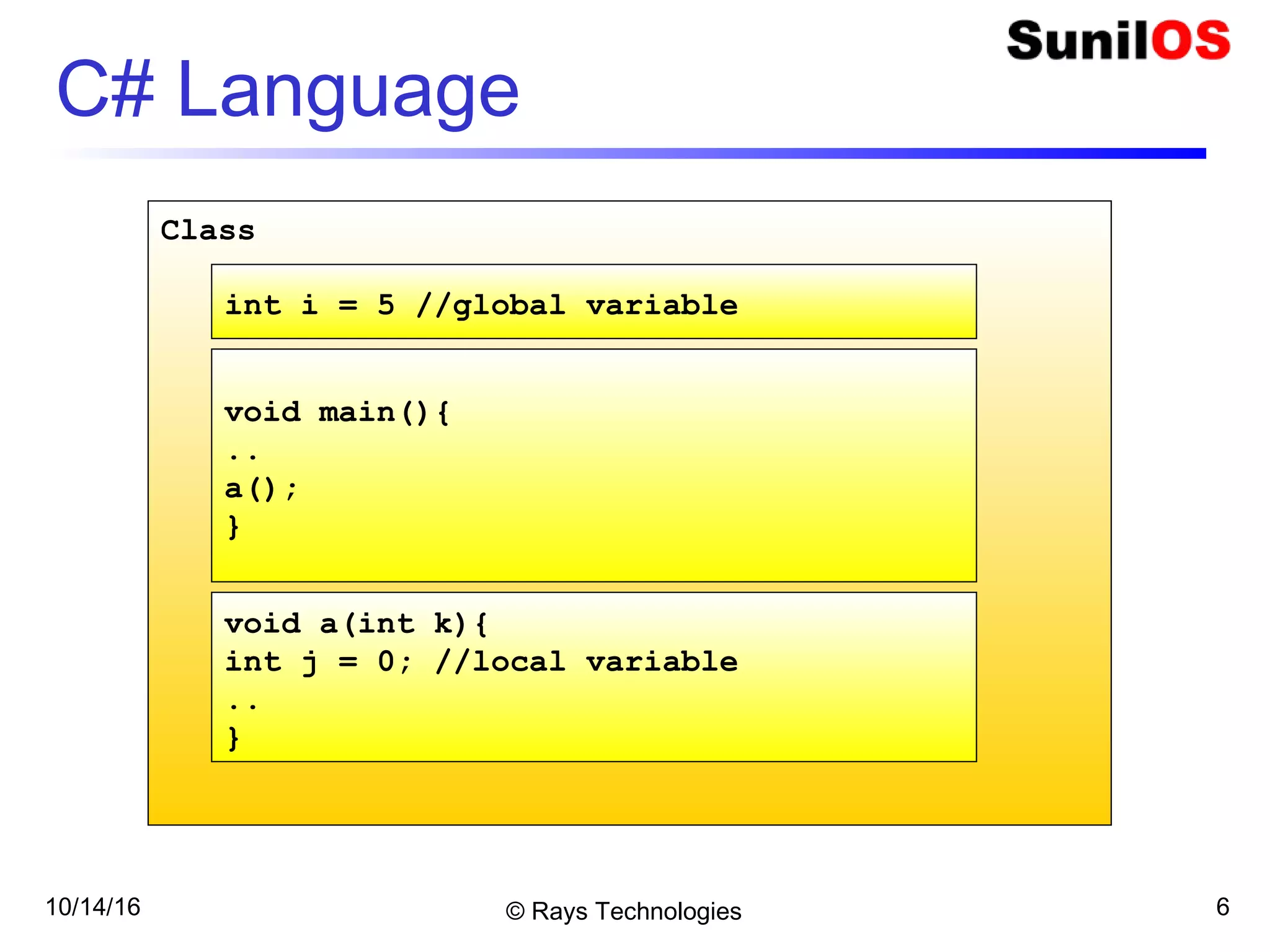
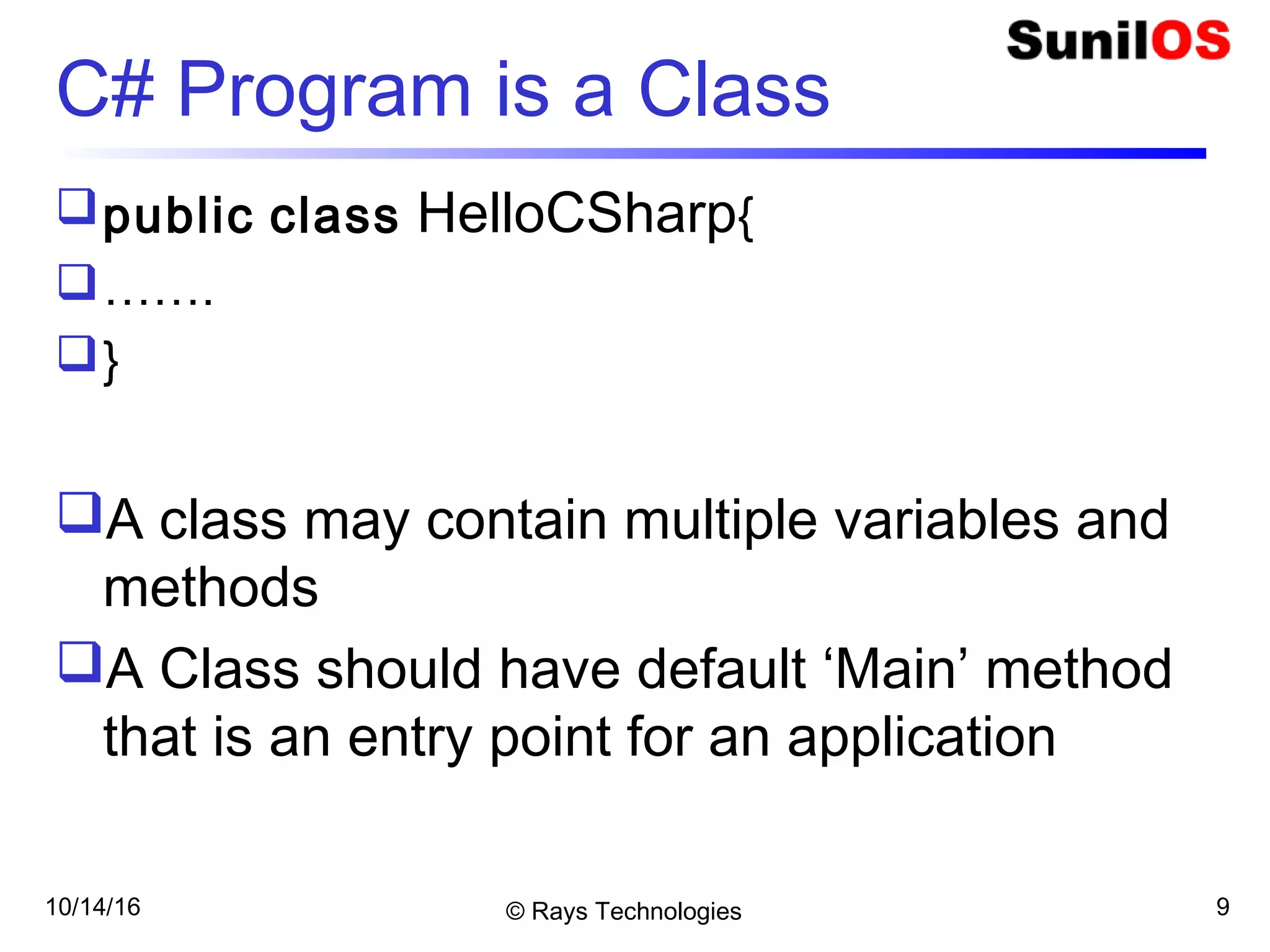
- C# is an object-oriented language where the basic unit is a class containing methods and variables.
- A C# program consists of at least one class that must contain a Main method, which acts as the program entry point.
- The document discusses basic C# concepts like variables, data types, operators, conditional statements, loops, methods, and arrays.
- It also covers how to compile and run a simple "Hello World" C# program, and provides examples of different programming constructs.




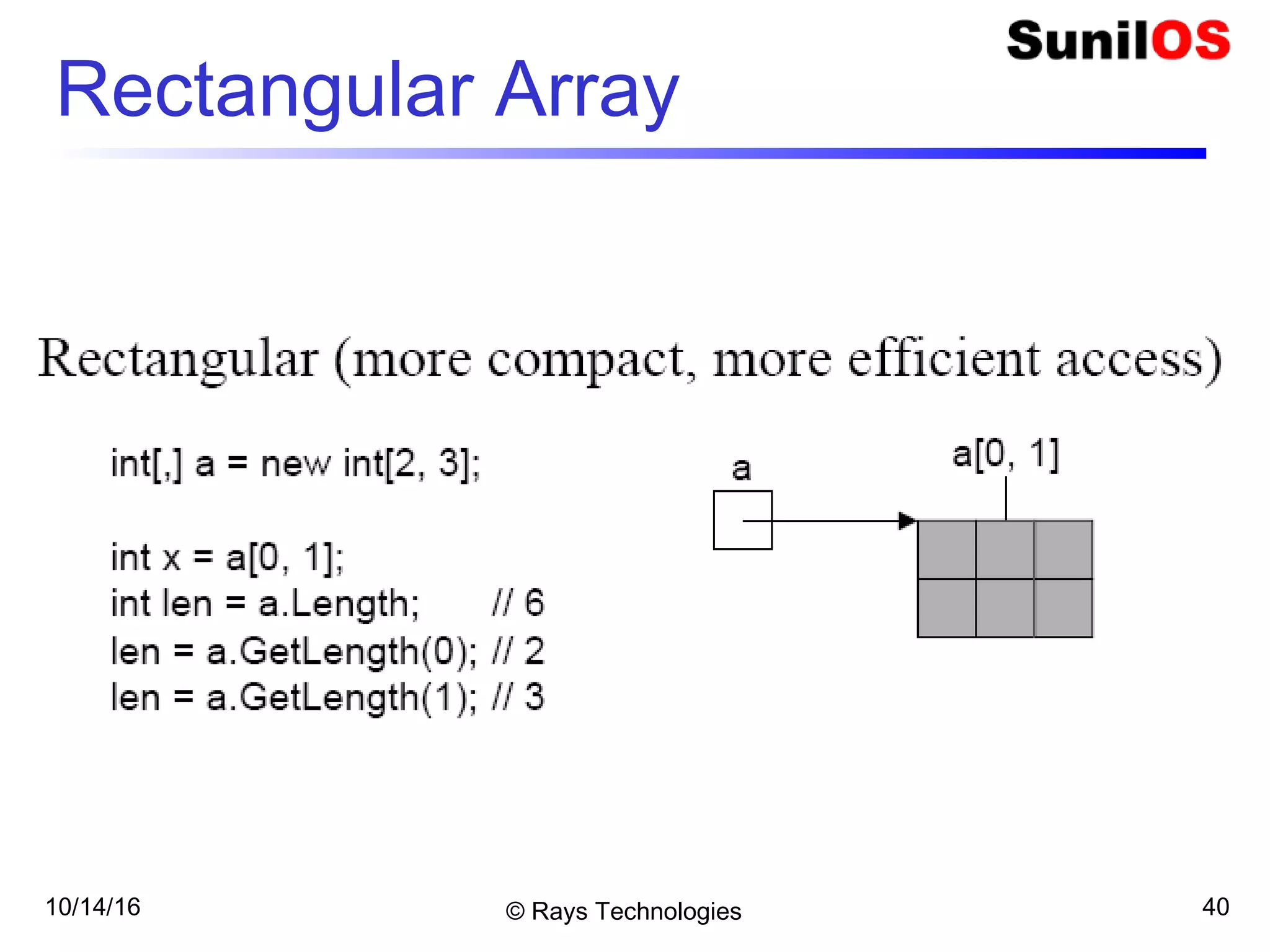
![10/14/16 © Rays Technologies 14
Main method
The Main method is sometimes called the application's
entry point.
Can be declared as
public static void Main(){}
OR
public static void Main(string args[]){}
OR
public static int Main()
{… return errorCode}
OR
public static int Main(string args[])
{… return errorCode}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbasicsdraftv2-161014073217/75/C-Basics-14-2048.jpg)

![10/14/16 © Rays Technologies 16
Print Hello C# 5 times - while
using System;
public class HelloWhile {
public static void Main(String[] args) {
o boolean isAlive = true;
o int round = 0;
o while (isAlive) {
o Console.WriteLine(“Basanti will dance");
o round++;
o If(round>500 )
isAlive =false;
o }
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbasicsdraftv2-161014073217/75/C-Basics-16-2048.jpg)

![10/14/16 © Rays Technologies 20
Add.java
using System;
public class Add {
public static void Main(String[] args) {
oint a = 5;
oint b = 10;
oint sum = a + b;
oConsole.WriteLine ("Sum is " + sum);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbasicsdraftv2-161014073217/75/C-Basics-20-2048.jpg)

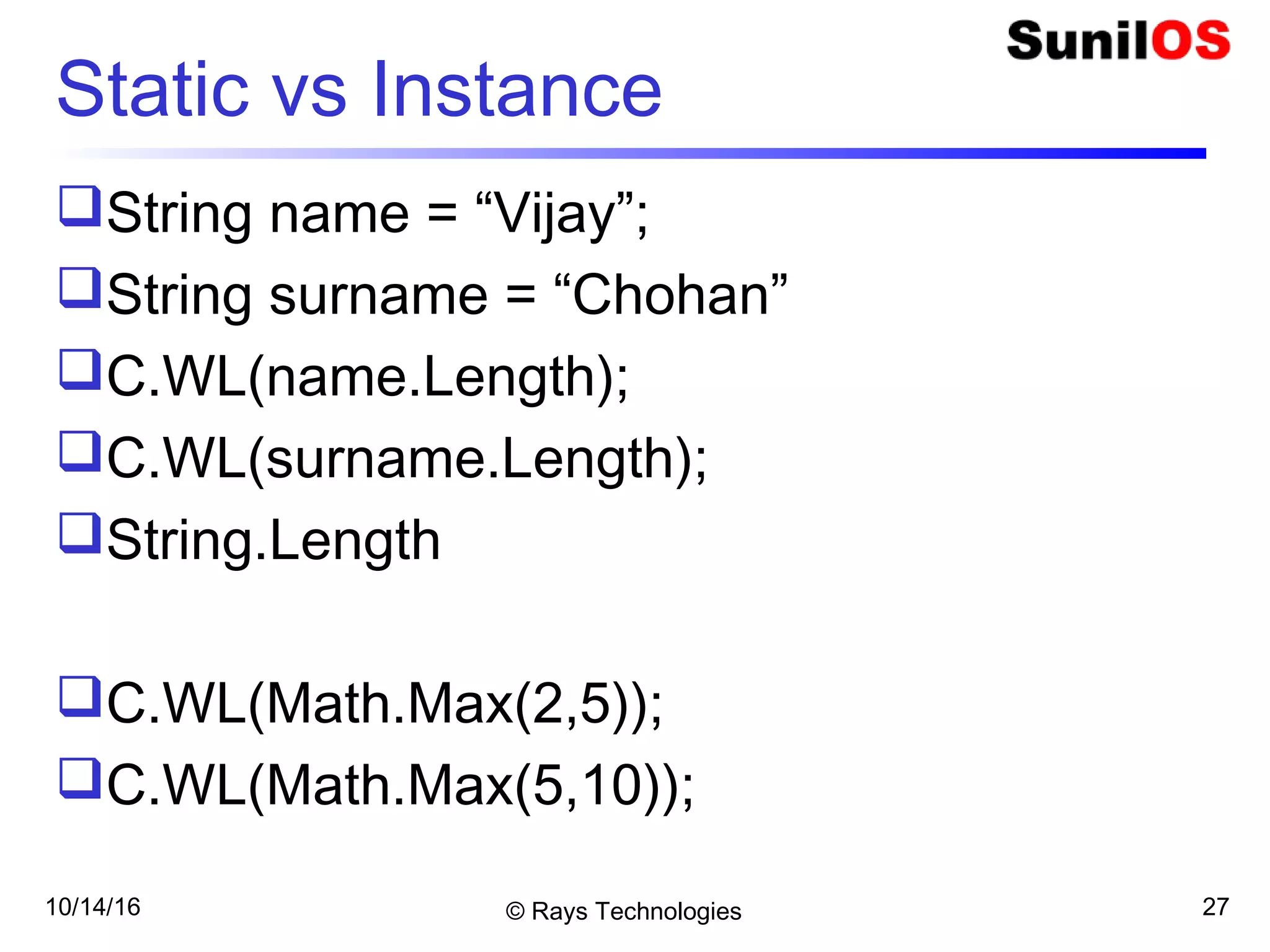
![10/14/16 © Rays Technologies 25
System.String class
public static void Main() {
String name = "Vijay Dinanth Chouhan";
Console.WriteLine(" String Length- " + name.Length);
Console.WriteLine(" 7 ths caharcter is- " + name[6]);
Console.WriteLine(" Dina index is- " + name.IndexOf("Dina"));
Console.WriteLine(" First i Position- " + name.IndexOf("i"));
Console.WriteLine(" Last i Position- " + name.LastIndexOf("i"));
Console.WriteLine(" a is replaced by b- " + name.Replace("a",
"b"));
Console.WriteLine(" Chota vijay- " + name.ToLower());
Console.WriteLine(" Bada vijay- " + name.ToUpper());
Console.WriteLine(" Starts With Vijay- " +
name.StartsWith("Vijay"));
Console.WriteLine(" Ends with han- " + name.EndsWith("han"));
Console.WriteLine(" Substring- " + name.Substring(6));
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbasicsdraftv2-161014073217/75/C-Basics-25-2048.jpg)
![10/14/16 © Rays Technologies 26
System.Math class
public static void main(String[] args) {
Console.WriteLine("Math functions");
Console.WriteLine(" Max 2,5 - " + Math.Max(2,5));
Console.WriteLine(" Min 2,5 - " + Math.Min(2,5));
Console.WriteLine(" Absolute 3.7 - " + Math.Abs(3.7));
Console.WriteLine(" Exp 10 - " + Math.Exp(10));
Console.WriteLine(" Square Root- " + Math.Sqrt(4));
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbasicsdraftv2-161014073217/75/C-Basics-26-2048.jpg)
![10/14/16 © Rays Technologies 28
Hello <Name>
public class HelloName {
public static void Main(String[] args) {
Console.WriteLine("Hello " + args[0]);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbasicsdraftv2-161014073217/75/C-Basics-28-2048.jpg)
![10/14/16 © Rays Technologies 29
Hello Name – if <condition>
public class HelloName{
public static void Main(String[] args) {
o if (args.Length == 1) {
Console.WriteLine("Hello " + args[0]);
o } else {
Console.WriteLine("Usage : HelloName <name>");
o }
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbasicsdraftv2-161014073217/75/C-Basics-29-2048.jpg)
![10/14/16 © Rays Technologies 30
Hello All
public class HelloAll {
public static void Main(String[] args) {
o for (int i = 0; i < args.Length; i++) {
Console.WriteLine(i + " = Hello " + args[i]);
o }
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbasicsdraftv2-161014073217/75/C-Basics-30-2048.jpg)
![10/14/16 © Rays Technologies 31
Hello All - define Method
public static void Main(String[] args) {
o PrintAll(args);
}// main
public static void PrintAll(String[] args) {
o int size = args.Length;
o for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Console.WriteLine((i + 1) + " = Hello " + args[i]);
o }
}//myMethod](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbasicsdraftv2-161014073217/75/C-Basics-31-2048.jpg)
![10/14/16 © Rays Technologies 32
Add.java
public class Add {
public static void Main(String[] args) {
o int a = Integer32.Parse(args[0]);
o int b = Integer32.Parse (args[1]);
o int sum = a + b;
o Console.WriteLine("Sum is " + sum);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbasicsdraftv2-161014073217/75/C-Basics-32-2048.jpg)
![10/14/16 © Rays Technologies 33
Division
public class Division {
public static void Main(String[] args) {
o int a = Integer32.Parse (args[0]);
o int b = Integer32.Parse (args[1]);
o double div = a/b;
o Console.WriteLine("Division is " + div);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbasicsdraftv2-161014073217/75/C-Basics-33-2048.jpg)
![10/14/16 © Rays Technologies 34
Return a Value
public class Division3 {
public static void Main(String[] args) {
o int a = Integer.Parse (args[0]);
o int b = Integer.Parse (args[1]);
o double div = getDivision(a, b);
o Console.WriteLine("Division is " + div);
}
public static double getDivision(int a, int b) {
o double div = a / b;
o return div;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbasicsdraftv2-161014073217/75/C-Basics-34-2048.jpg)
![10/14/16 © Rays Technologies 35
10
One Dimension Array
20
[0]
18
..
10
8
6
4
2
[1]
[8]
[9]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[n]
Length
int[] table = new int[10];
int a = table[4];
int a = table[2];
int size = table.Length](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbasicsdraftv2-161014073217/75/C-Basics-35-2048.jpg)
![10/14/16 © Rays Technologies 36
10
Initialize an Array
20
[0]
18
..
10
8
6
4
2
[1]
[8]
[9]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[n]
Length
int[] table = new int[10];
table[0] =2;
table[1] =4;
….
Or
int[] table =
{2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,
20};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbasicsdraftv2-161014073217/75/C-Basics-36-2048.jpg)
![10/14/16 © Rays Technologies 37
Other Data Type Arrays
char[] chList = new char[5];
chList[0] = ‘A’….
Or
char[] chList = {‘A’,’B’,’C’,’D’,’E’}
String[] strList = new String[5];
strList[0] = “A”
strList[1] = “Bee”
Console.WriteLine(strList[0]);
….
Or
String[] strList = {“A”,”Bee”,”Cee”,”Dee”,”E”}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbasicsdraftv2-161014073217/75/C-Basics-37-2048.jpg)
![10/14/16 © Rays Technologies 3810length
2D Array
[0]
20
18
..
10
8
6
4
2
[1]
[8]
[9]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[n]
30
27
..
15
12
9
6
3
40
36
..
20
16
12
8
4
90
81
..
45
36
27
18
9
100
90
..
50
40
30
20
10
…
[0] [1] [2] [7] [8]
9
9
..
9
9
9
9
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbasicsdraftv2-161014073217/75/C-Basics-38-2048.jpg)
![10/14/16 © Rays Technologies 39
int[][] table = new int[10][9];
table[1][5] = 5;
int size = table.Length;
int size = table[0].Length;
int[][] rows = new int[10][];
rows[0] = new int[9];
rows[1] = new int[19];
rows[2] = new int[29];
int xyz = new int[10][9][2];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbasicsdraftv2-161014073217/75/C-Basics-39-2048.jpg)
![10/14/16 © Rays Technologies 41
3D Array
20
[0]
18
..
10
8
6
4
2
[1]
[8]
[9]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[n]
30
27
..
15
12
9
6
3
40
36
..
20
16
12
8
4
90
81
..
45
36
27
18
9
100
90
..
50
40
30
20
10
[0] [1] [2] [8] [9]
20
18
..
10
8
6
4
2
30
27
..
15
12
9
6
3
40
36
..
20
16
12
8
4
20
18
..
10
8
6
4
30
27
..
15
12
9
6
20
18
..
10
8
6
4
2
30
27
..
15
12
9
6
3
40
36
..
20
16
12
8
4
90
81
..
45
36
27
18
9
100
90
..
50
40
30
20
10
90
81
..
45
36
27
18
9
100
90
..
50
40
30
20
10
…
[0]
[1]
[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbasicsdraftv2-161014073217/75/C-Basics-41-2048.jpg)