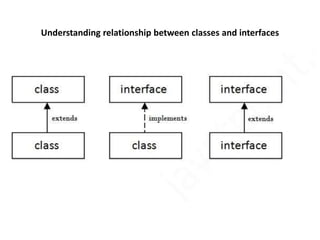
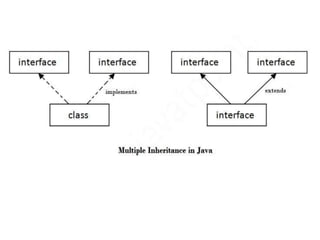
An interface in Java is like a class but contains only abstract methods and static constants. Interfaces are declared using the interface keyword and contain method signatures without implementations along with constant declarations. A class implements an interface by including the implements clause and must define implementations for all abstract methods defined in the interface.




![ To implement an interface
– include the implements clause in a class definition
access class classname [extends superclass] [implements interface
[,interface...]]
{
constant declarations ;
abstract method declarations;
}
The methods that implement an interface must be declared public.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javainterface-150203104422-conversion-gate01-170519042815/85/Javainterface-7-320.jpg)

![ An interface can be declared as member of a class or another
interface – called nested interface.
How can we define i/f inside a class and how can we access it.
class A
{
interface Message()
{
void msg();
}
}
Class test implements A.Message
{
Public void msg()
{
S.o.p(“Hello”);
}
Public static void main(String args[])
{
A.Message message=new test();
message.msg();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javainterface-150203104422-conversion-gate01-170519042815/85/Javainterface-9-320.jpg)

![interface Printable
{
void print();
}
interface Showable extends Printable
{
void show();
}
class A implements Showable
{
public void print()
{System.out.println("Hello");}
public void show()
{System.out.println("Welcome");}
public static void main(String args[])
{
A obj=new A();
obj.print();
obj.show();
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javainterface-150203104422-conversion-gate01-170519042815/85/Javainterface-11-320.jpg)