Embed presentation
Downloaded 161 times


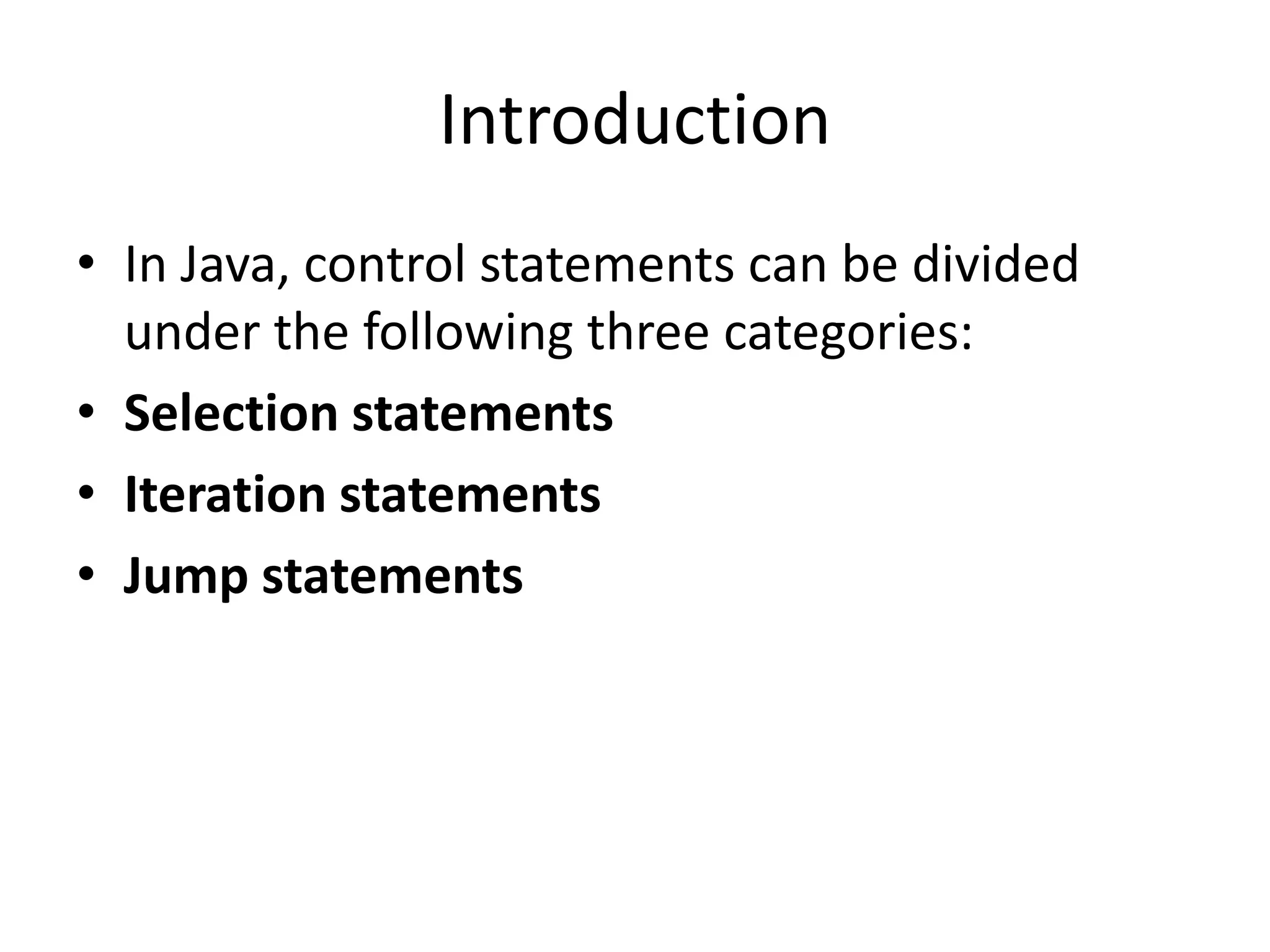






![Solution
public class Grades{
public static void main (String [] args){
int grade;
grade = 10;
if(grade >=75) {
System.out.println(“PASSED”);
}
else if(grade < 75){
System.out.println(“FAILED”);
}
else{
System.out.println(“ ”);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlstatements-131008052703-phpapp02/75/Control-statements-in-Java-10-2048.jpg)

Control statements are used in programming languages to control program flow based on conditions. In Java, there are three types of control statements: selection statements, iteration statements, and jump statements. Selection statements like if and if-else are used to choose different code paths based on boolean expressions or variable states. An if statement executes code if the expression is true, while if-else executes one block if true and another if false. The example program uses an if-else statement to display "PASSED" if a grade is above 75 and "FAILED" if below.









![Solution
public class Grades{
public static void main (String [] args){
int grade;
grade = 10;
if(grade >=75) {
System.out.println(“PASSED”);
}
else if(grade < 75){
System.out.println(“FAILED”);
}
else{
System.out.println(“ ”);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlstatements-131008052703-phpapp02/75/Control-statements-in-Java-10-2048.jpg)