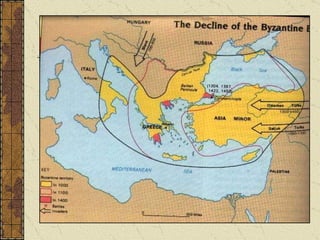
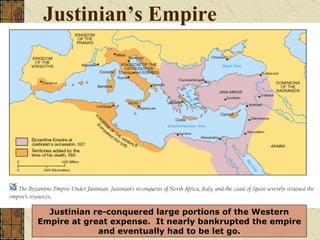
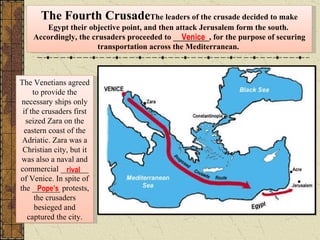
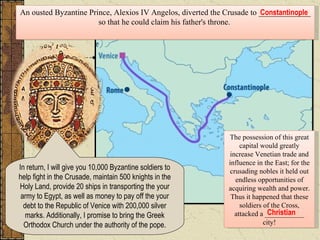
Byzantine art expressed the values of Byzantine culture through religious imagery in a conventionalized style. Artists followed strict rules and used symbolic rather than realistic representations. Mosaics and icons in churches depicted Jesus and Mary in standardized poses and features to convey devotion. The Byzantine Empire declined due to overextension of resources on borders, growing Islamic power, and the sacking of Constantinople by Catholic crusaders in 1204, which devastated the empire.


























![Primary Sources No one was without a share in the grief. In the alleys, in the streets, in the temples, complaints, weeping, lamentations, grief, the groaning of men, the shrieks of women, wounds, rape, captivity, the separation of those most closely united. Nobles wandered about ignominiously [shamefully], those of venerable age in tears, the rich in poverty. Thus it was in the streets, on the corners, in the temple, in the dens, for no place remained unassailed or defended the suppliants. All places everywhere were filled full of all kinds of crime. Oh, immortal God, how great the afflictions of the men, how great the distress! Below is a Byzantine account of the sack of Constantinople by Nicetas Chroniates. Then the bishops preached to the army, … and they showed to the pilgrims that the war was a righteous one; for the Greeks were traitors and murderers, and also disloyal, since they had murdered their rightful lord. Moreover, the bishops said that, by the authority of God and in the name of the pope, they would absolve all who attacked the Greeks. Then the bishops commanded the pilgrims to confess their sins and receive the communion devoutly; and said that they ought not to hesitate to attack the Greeks, for the latter were enemies of God. Robert of Clari of the sermons given by the Latin bishops before the final attack on Constantinople Document #1 Document #2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thebyzantineempireglobal9-120213200742-phpapp01/85/Byzantine-Empire-35-320.jpg)