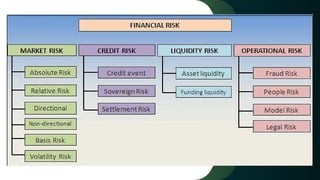
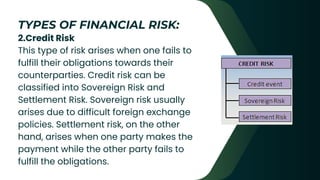
Financial risk management involves identifying risks an organization faces, assessing and quantifying those risks, defining strategies to manage them, implementing risk management strategies, and monitoring their effectiveness. Financial risks can arise from market exposures, transactions with other organizations, and internal failures. Key types of financial risk include market, credit, liquidity, and operational risk. Organizations manage financial risk through various strategies and products, often involving derivatives whose values are based on underlying assets.