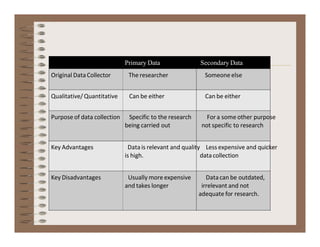
Here are some potential sources of secondary data that could help analyze this business problem:
- Industry reports on the retail sector that provide market size, growth trends and future projections at the state and national level. This can help assess expansion opportunities.
- Demographic data from census providing population stats, income levels etc. of potential target cities which impact retail spending.
- Economic indicators like GDP, disposable income figures of different states. This helps compare market potential of states.
- Competitor analysis studying expansion strategies of other retail chains operating in similar segments.
- Feasibility studies or reports conducted previously for other retailers exploring new markets.
Collecting and analyzing such secondary data sources can help get an overview