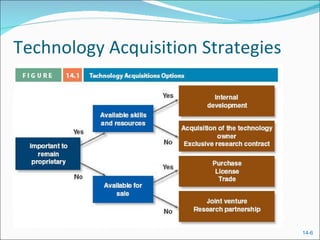
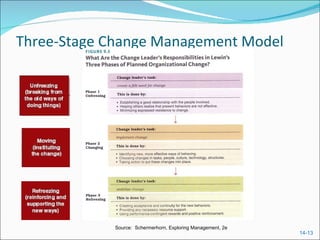
The document discusses assessing technology needs, acquiring new technologies, characteristics of innovative organizations, and managing change effectively. It provides learning objectives, forces driving technological development, ways to assess organizational needs and criteria for technology decisions. Methods of technology acquisition include internal development, licensing, and contracted development. The roles of a CIO/CTO and innovation team are described. Characteristics of innovative companies include an organizational culture that encourages creativity and learning from failures. Organizational development techniques and a three-stage change management model are also summarized.














![Wrap-up The Essence of Innovation – I have not failed. I’ve just found 10,000 ways that don’t work. -- Thomas Edison The Challenge of Change Almost everyone is more enthusiastic about change when [it’s] their idea, and less enthusiastic if they feel the change is being imposed on them. -- Maggie Bayless, managing partner, Zing Train](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap014modified2-110513212348-phpapp01/85/BUS137-Chapter-14-17-320.jpg)










