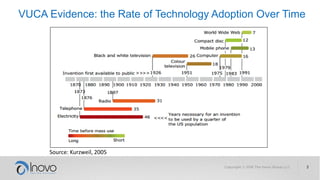
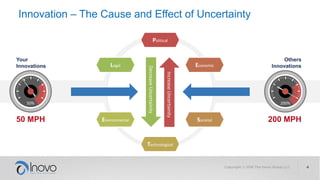
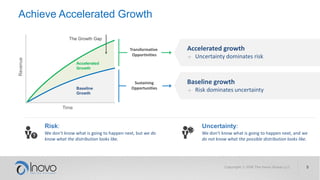
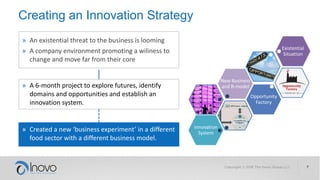
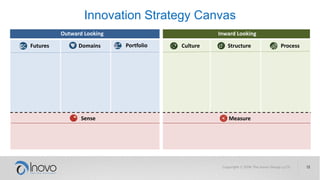
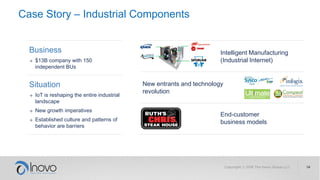
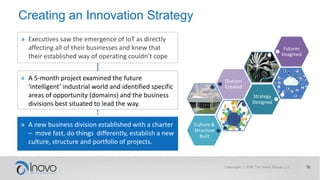
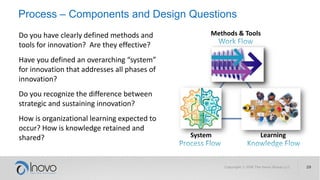
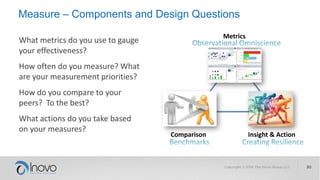
The document discusses the impact of a volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous (VUCA) world on innovation strategies, emphasizing the need for businesses to adapt in the face of technological and market changes. It outlines concepts like risk versus uncertainty, the importance of developing an innovation strategy canvas, and the necessity of fostering a culture of change and adaptation within organizations. Additionally, it provides practical guidance for assessing and enhancing a company's innovation strategy to better navigate future uncertainties.