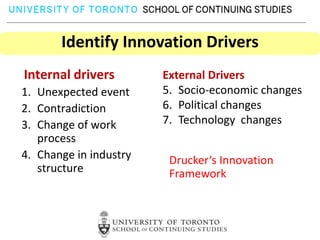
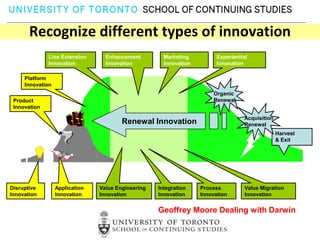
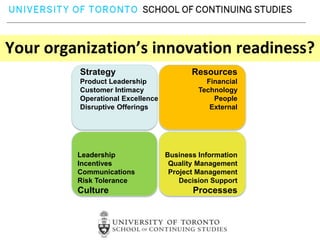
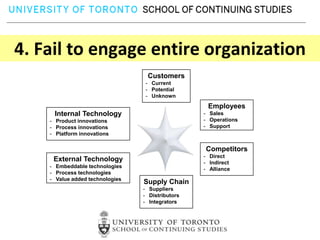
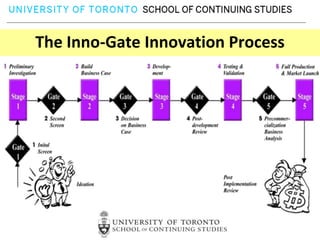
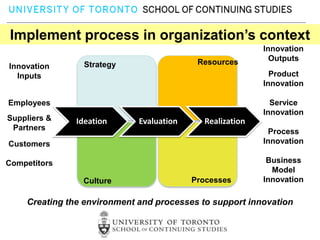
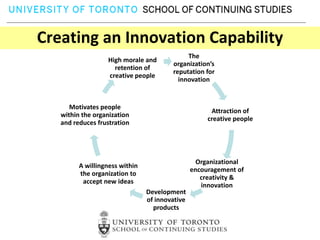
This document provides an overview of key reasons for failure to innovate within organizations. It identifies the top ten causes of failure to innovate as: confusing the role of innovation, failing to clarify innovation goals, not recognizing innovation barriers, failing to engage the entire organization, lack of recognition of the importance of communication, underestimating the need for innovation resources, having an unclear process for selecting innovation projects, failure to create an innovation culture, and treating innovation as a destination rather than a journey. The document stresses that innovation is essential for success and provides frameworks to help organizations better foster innovation.