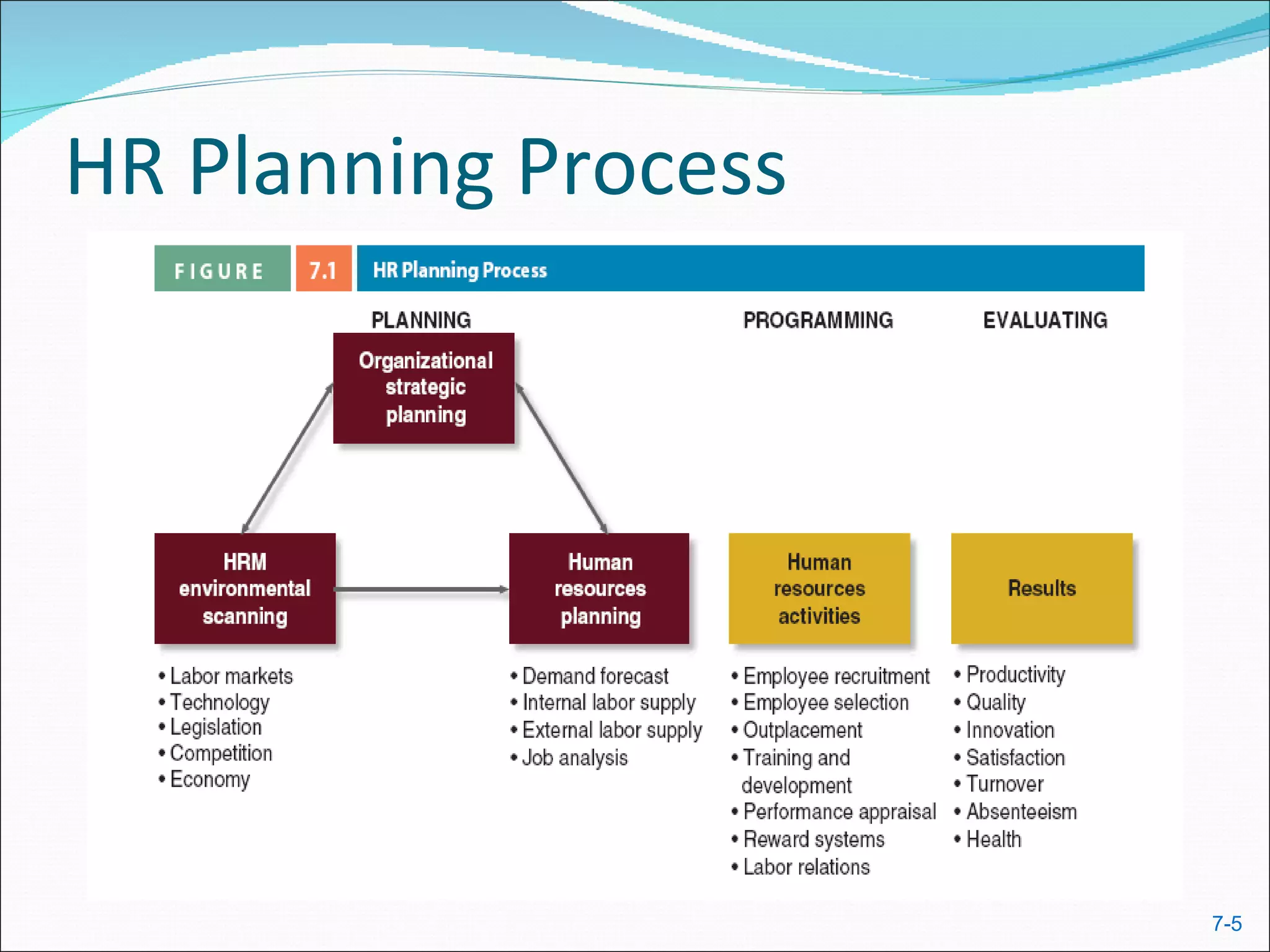
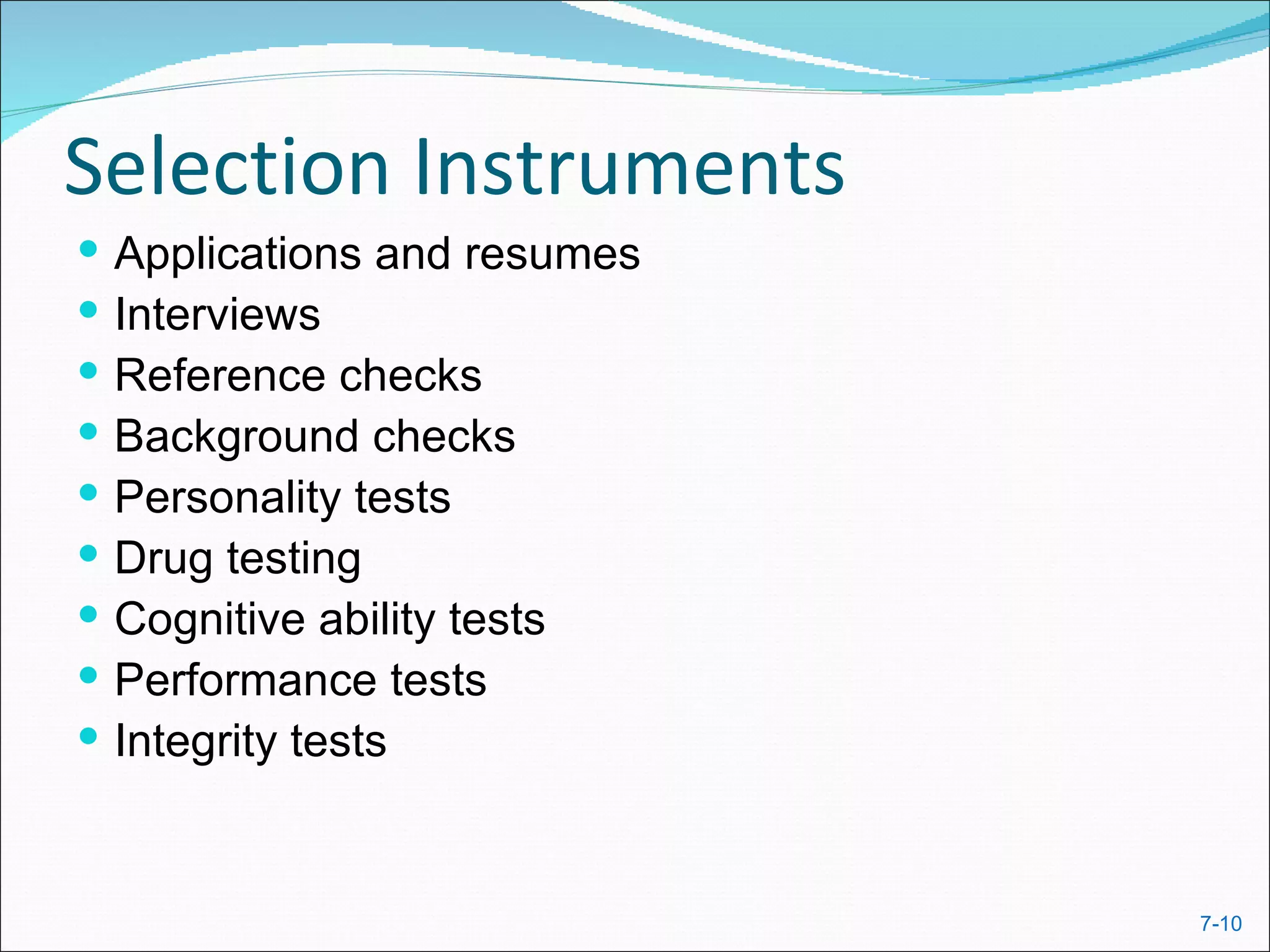
The document discusses strategic human resource management and how attracting, developing, and retaining talent provides a competitive advantage. It covers HR processes like recruitment, selection, training, performance management, compensation and benefits. Unions and labor laws also influence these areas through collective bargaining and legislation regarding issues like discrimination, wages, and workplace safety.