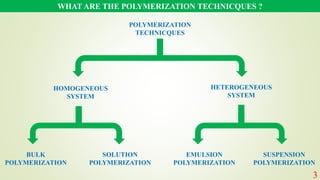
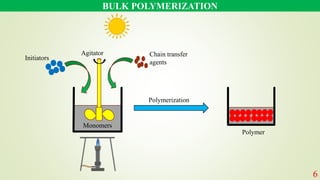
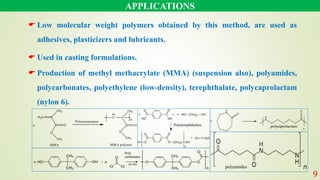
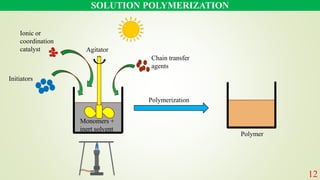
The document discusses various polymerization techniques, primarily focusing on bulk and solution polymerization. It describes their processes, advantages, disadvantages, and applications, highlighting that most commercial polymerizations occur in liquid states. Despite the challenges such as viscosity increase and contamination, these methods are used for producing a variety of polymers including adhesives and plastics.