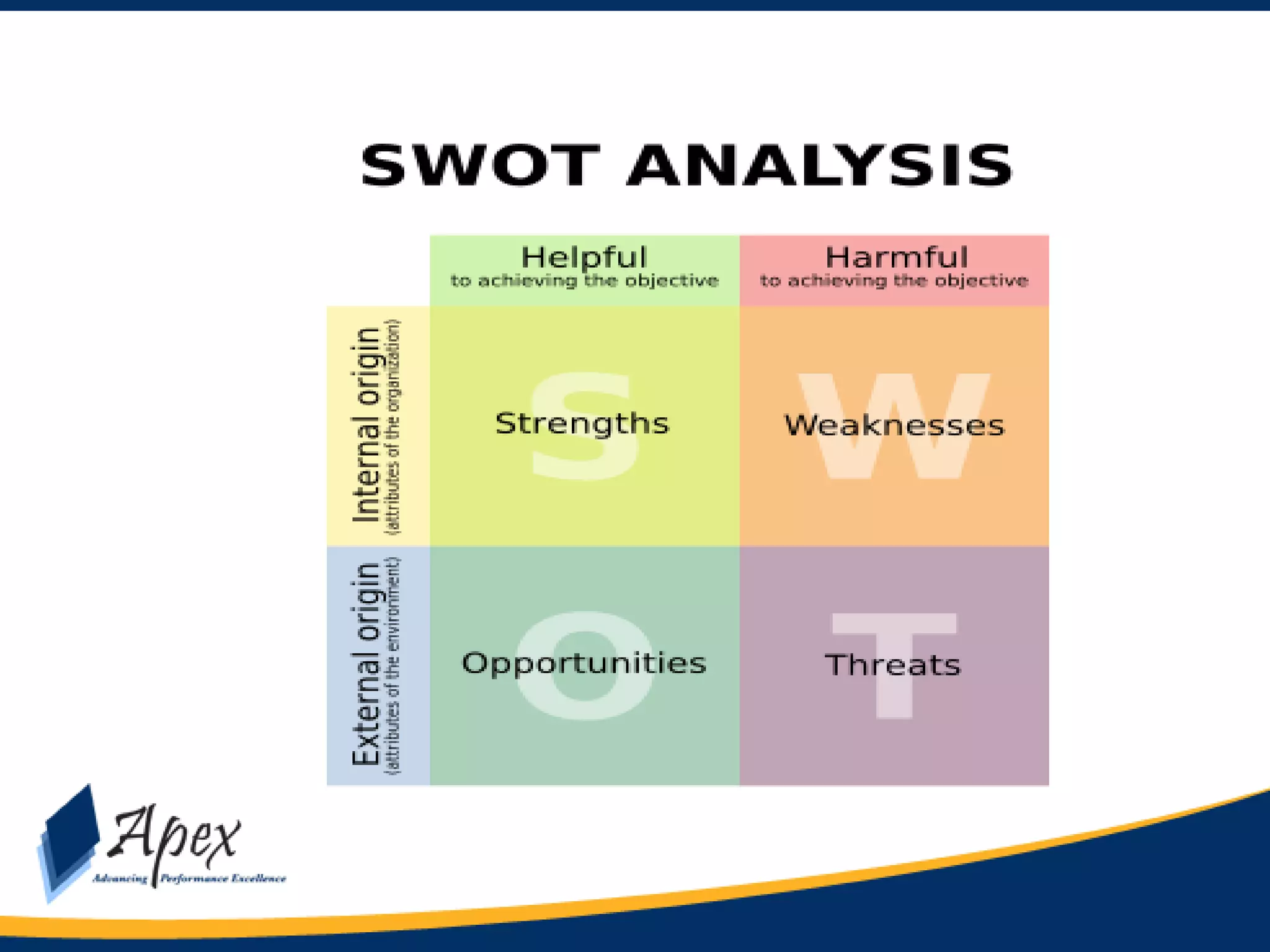
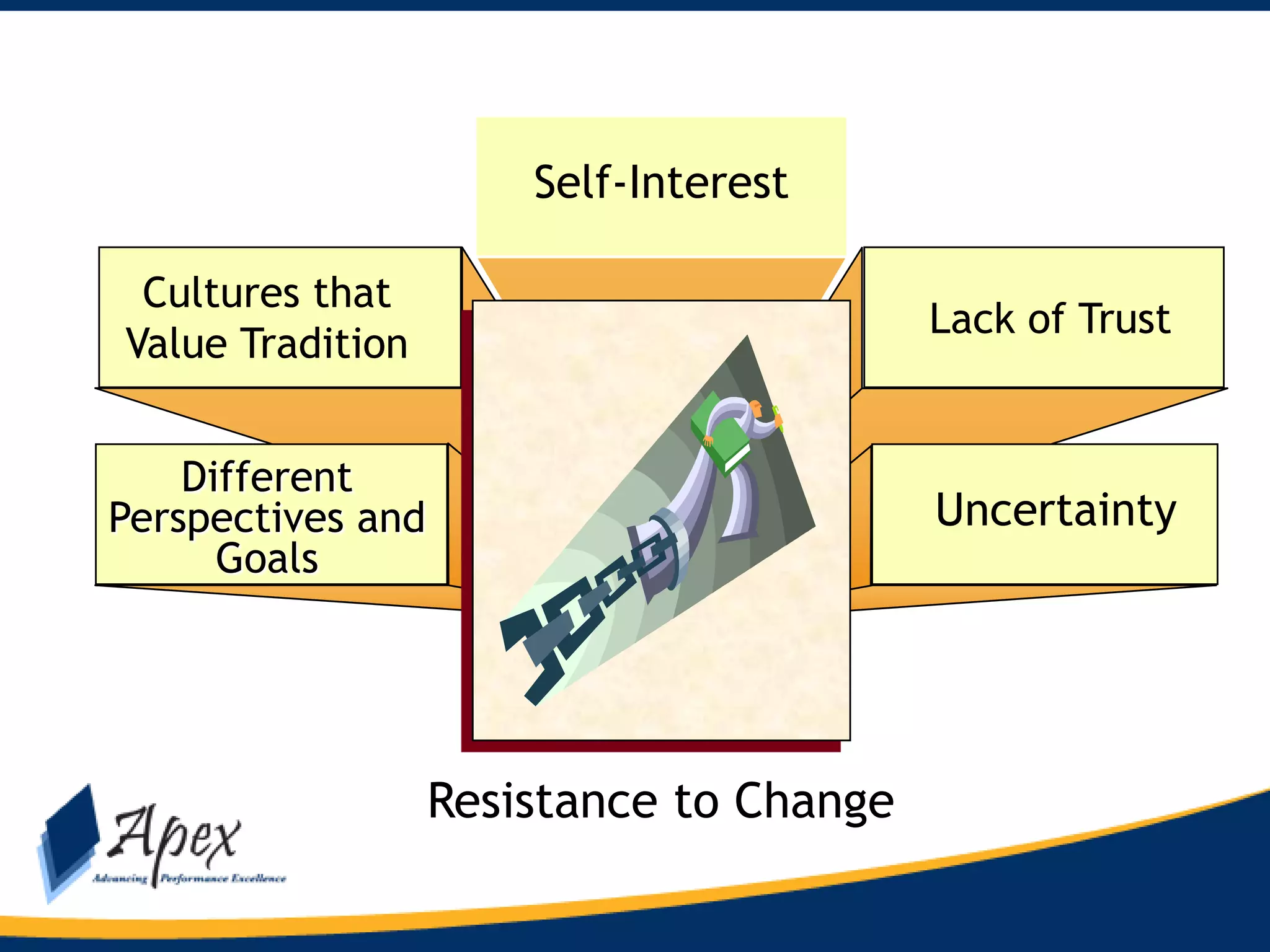
This document discusses building high performance teams. It covers establishing team rules at the beginning to ensure all members understand expectations. It discusses conducting a SWOT analysis to understand strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. The importance of communication, coordination, and cooperation ("The 3 C's") are explained. Developing trust, commitment, and loyalty in a team is also discussed. The document outlines how to introduce change and address resistance. It concludes with discussing the expectations a leader should have for team members, including being contributors, communicating, cooperating, problem solving, and continuous learning.