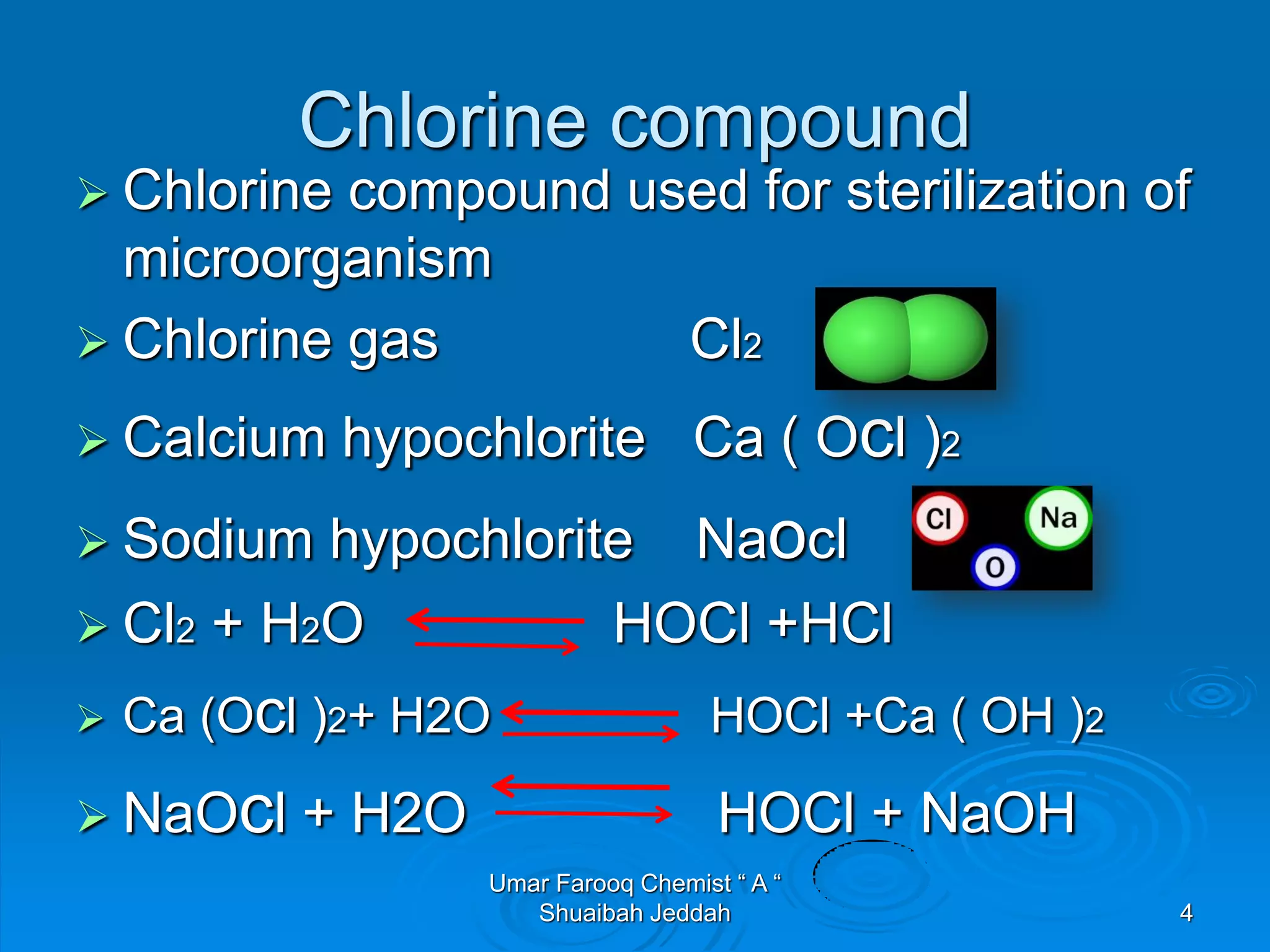
1. Chlorine is used as a disinfectant in power plant cooling water systems to kill microorganisms, maintaining a residual of 0.3-0.5 ppm.
2. Chlorine exists in water as hypochlorous acid and hypochlorite ions, which have sterilization effects. Hypochlorous acid is much more effective than hypochlorite ions.
3. Chlorine is a strong oxidizer that is corrosive and can cause burns, and safety precautions must be followed when handling or exposed to chlorine.