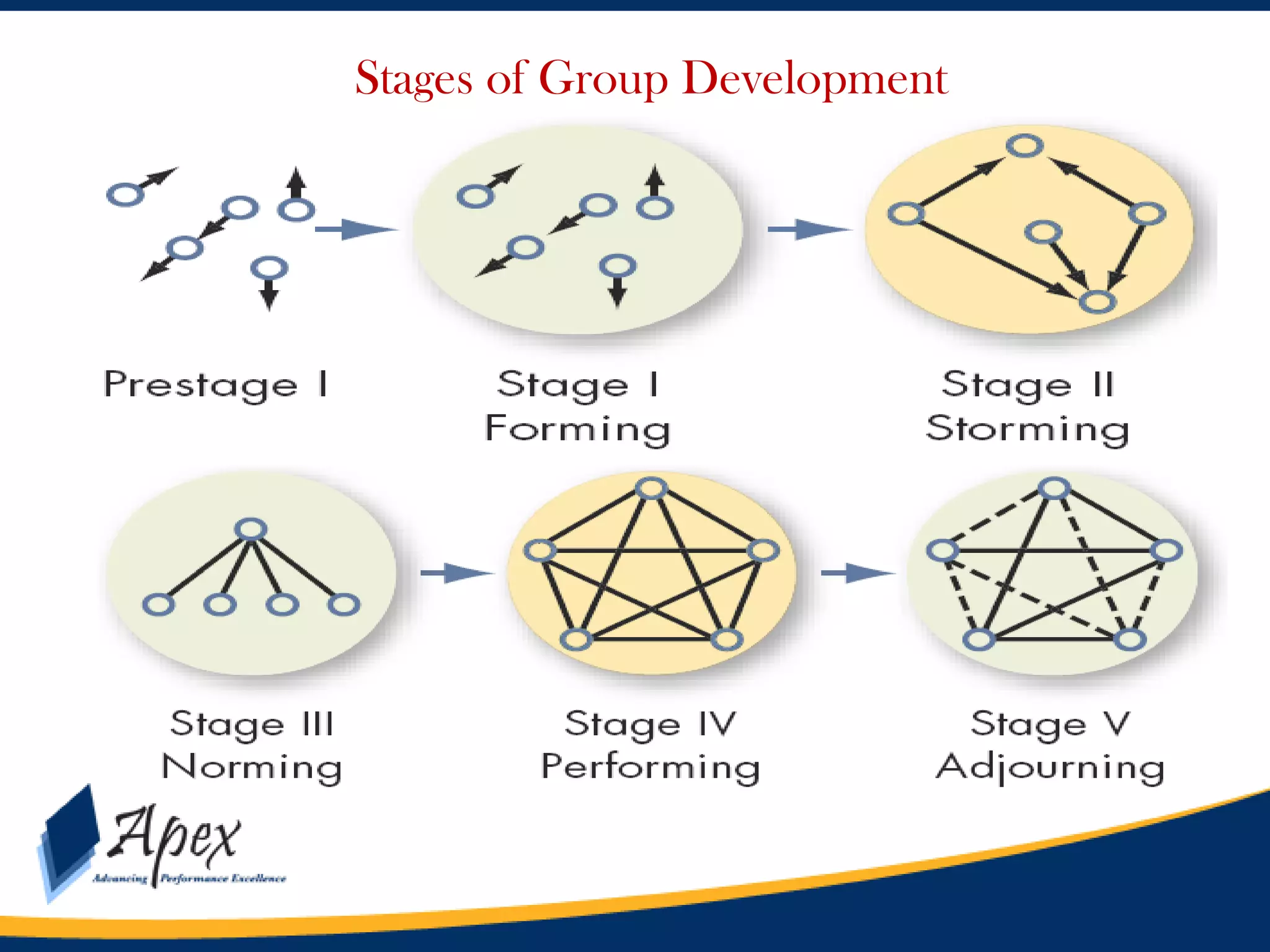
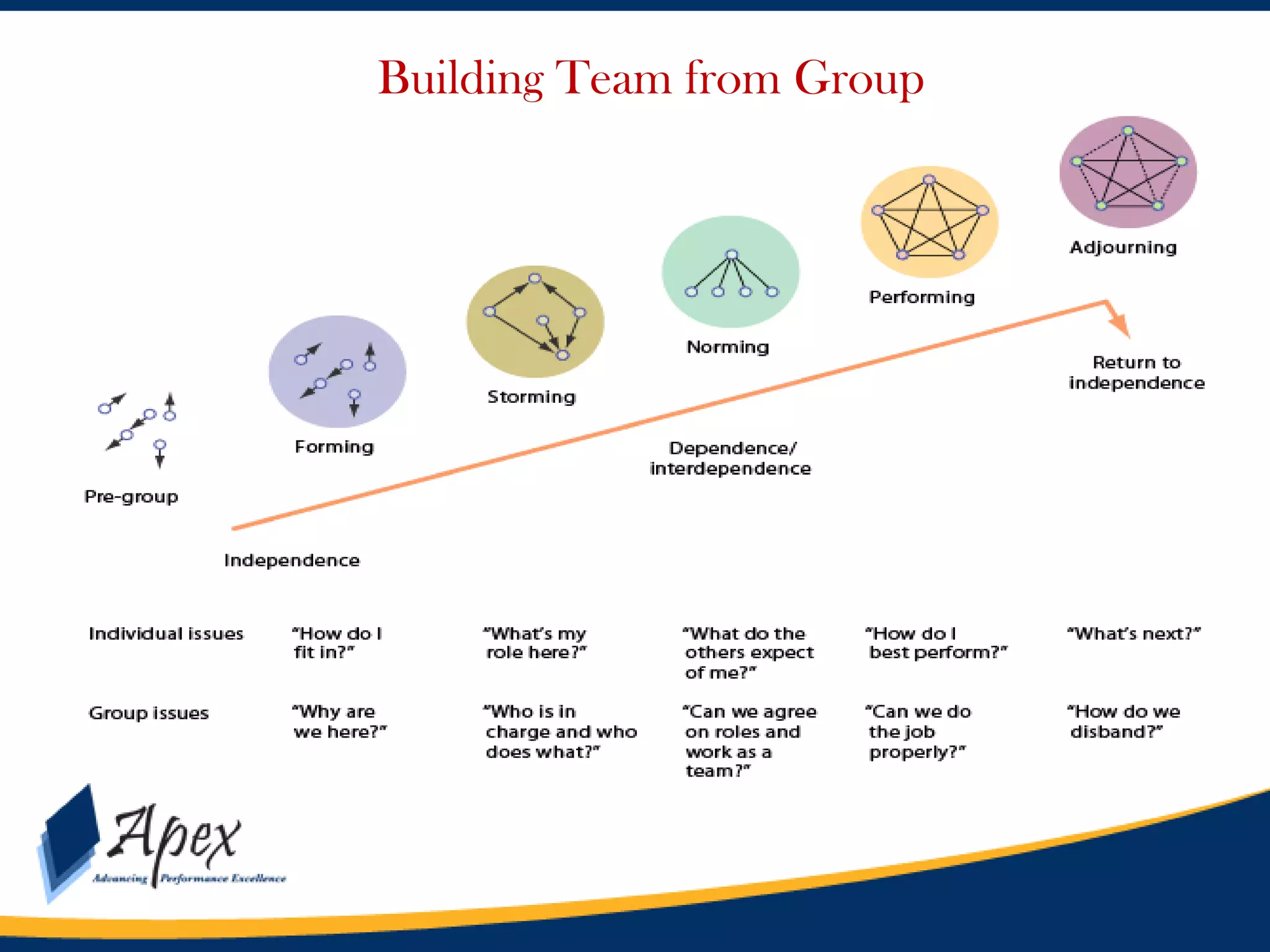
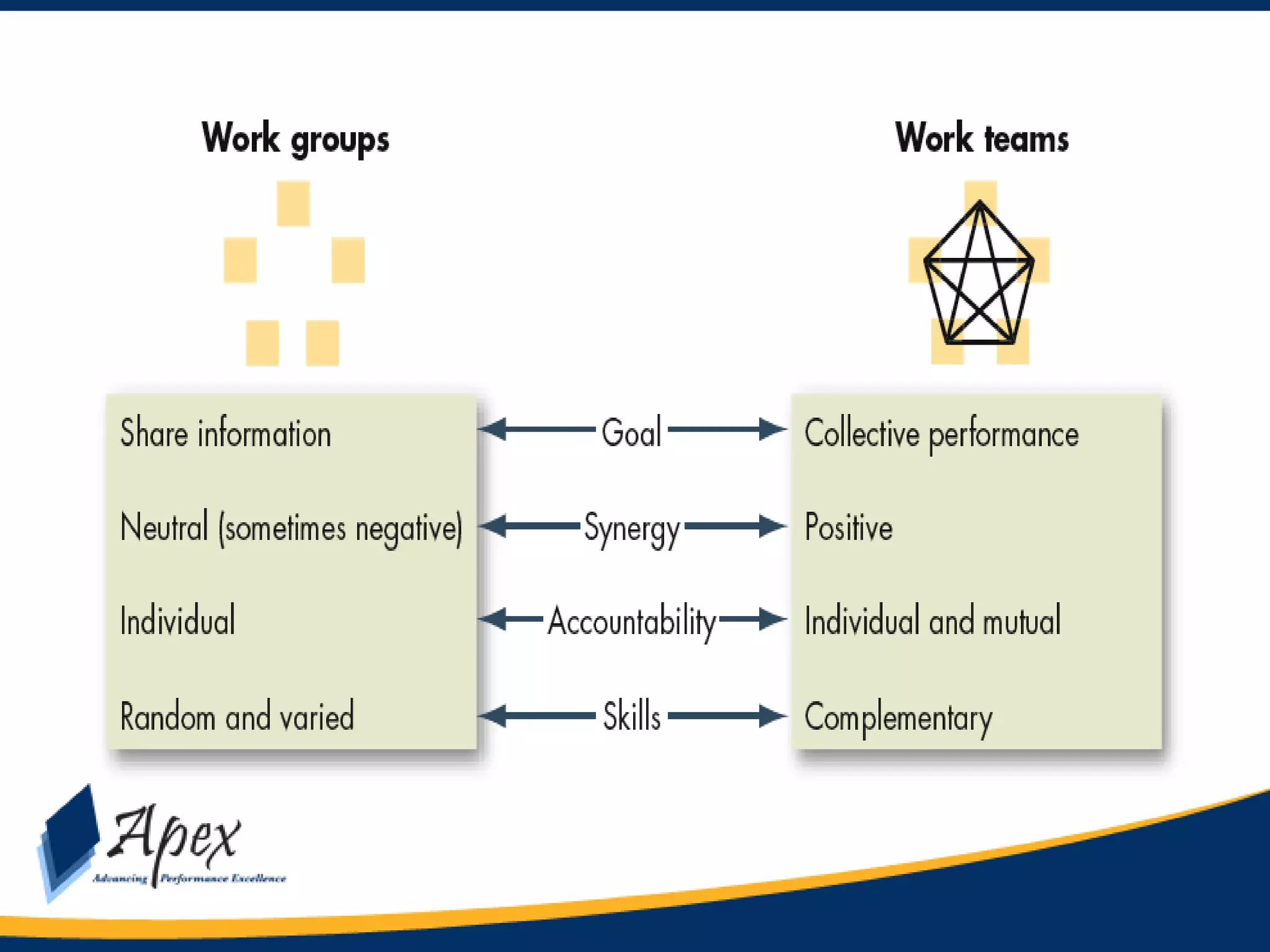
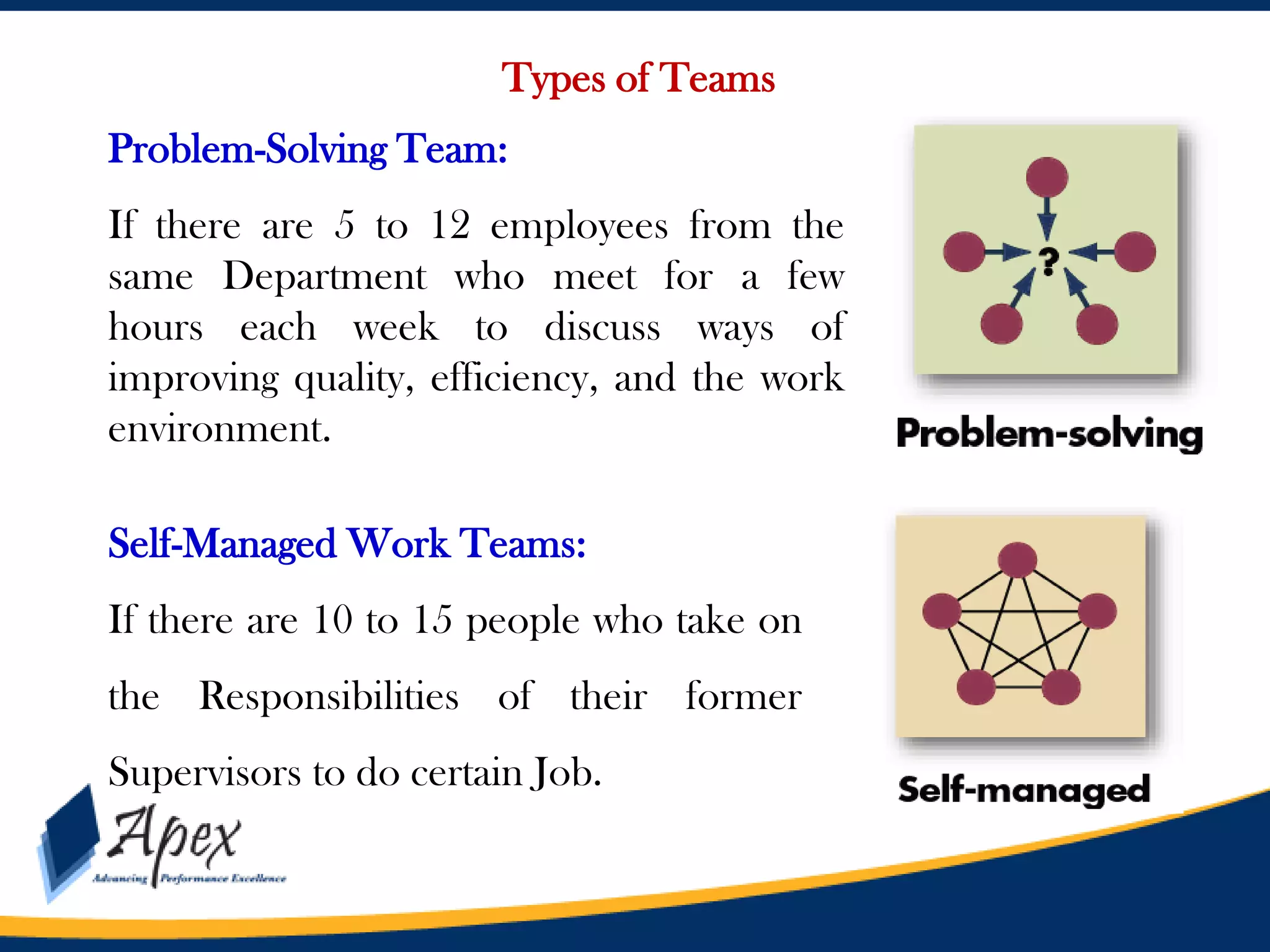
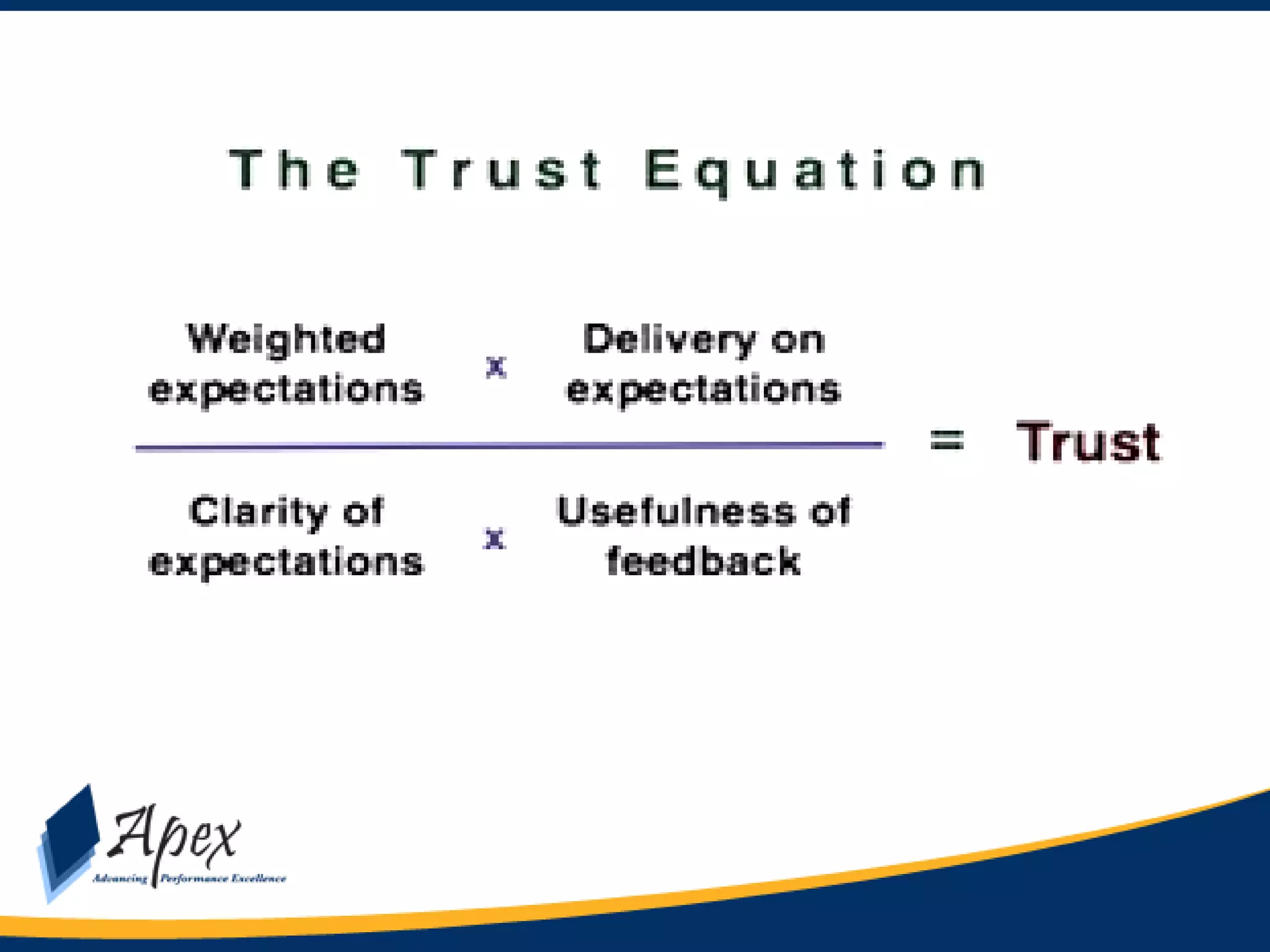
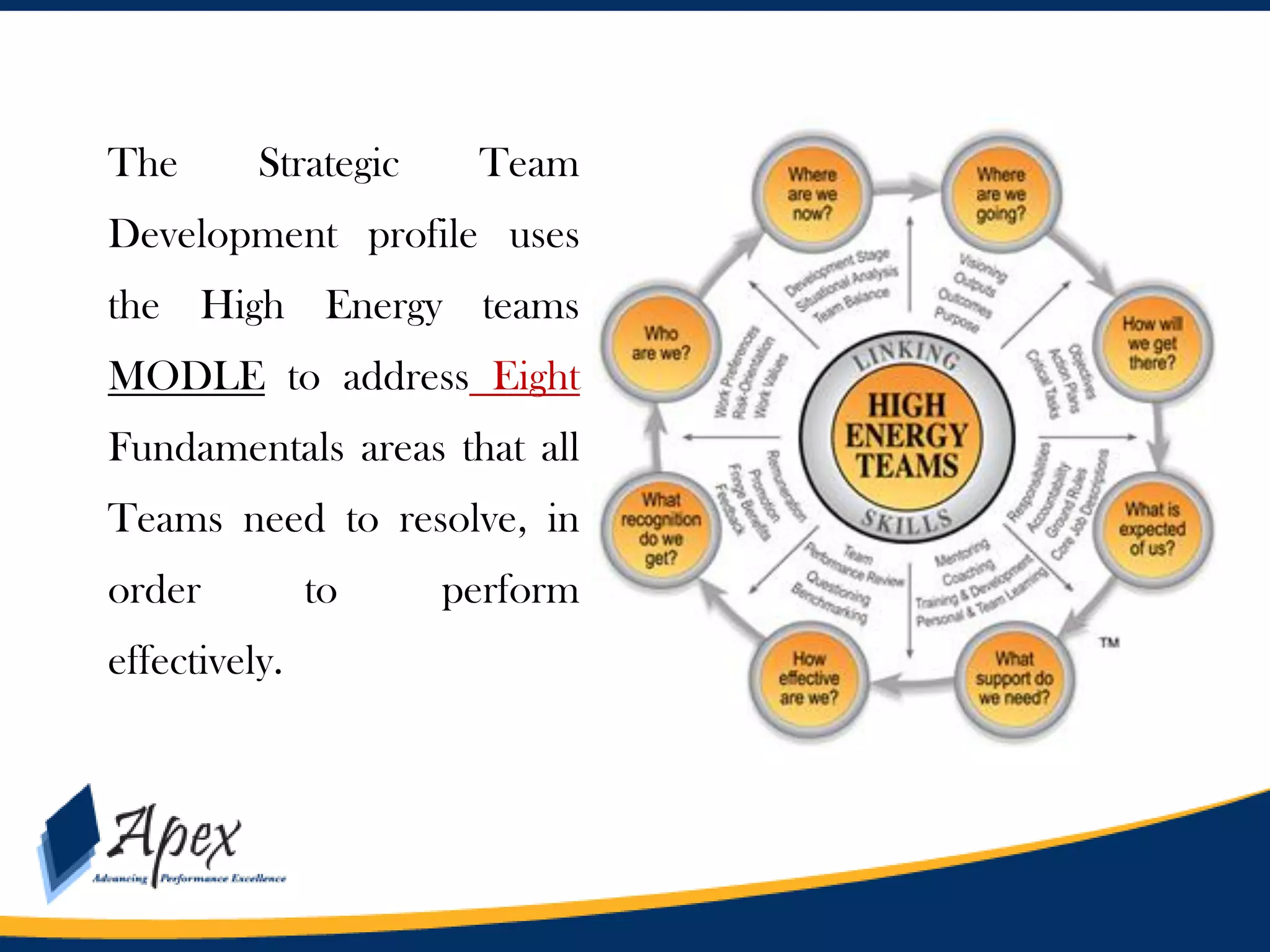
This document discusses building high performance teams. It covers topics like work groups versus teams, building trust and believability within teams, dealing with inter-team conflicts, and characteristics of effective teams. An effective team is defined as having five functions: trusting one another, engaging in constructive conflict, committing to decisions, holding each other accountable, and focusing on collective results. High performance leadership is also discussed, along with strategies like applying influence-based versus control-based leadership and integrating organizational change strategies with improvement tools. The final section covers styles of behaving toward team members in a way that lessens stress and gets the best out of the team.