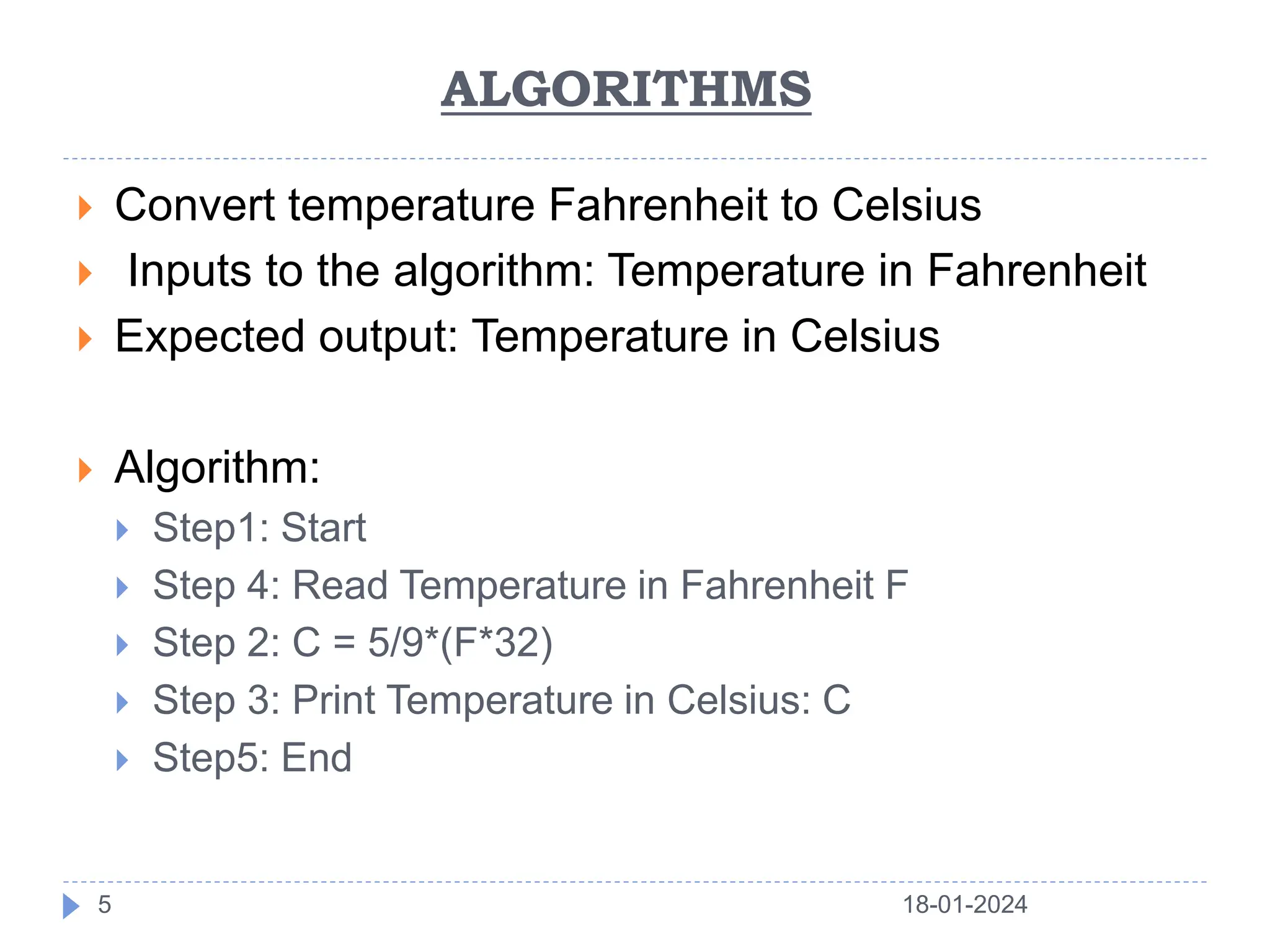
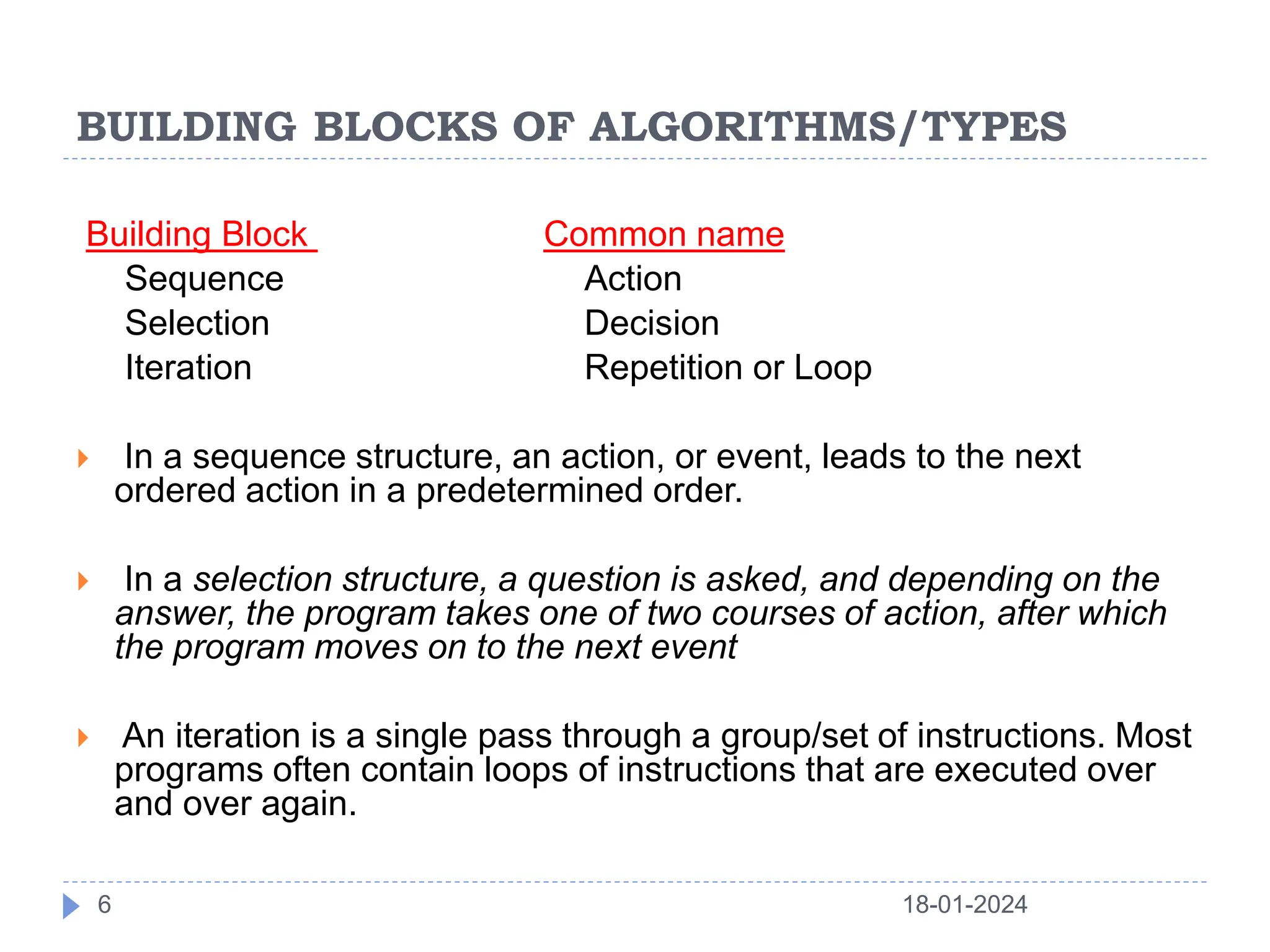
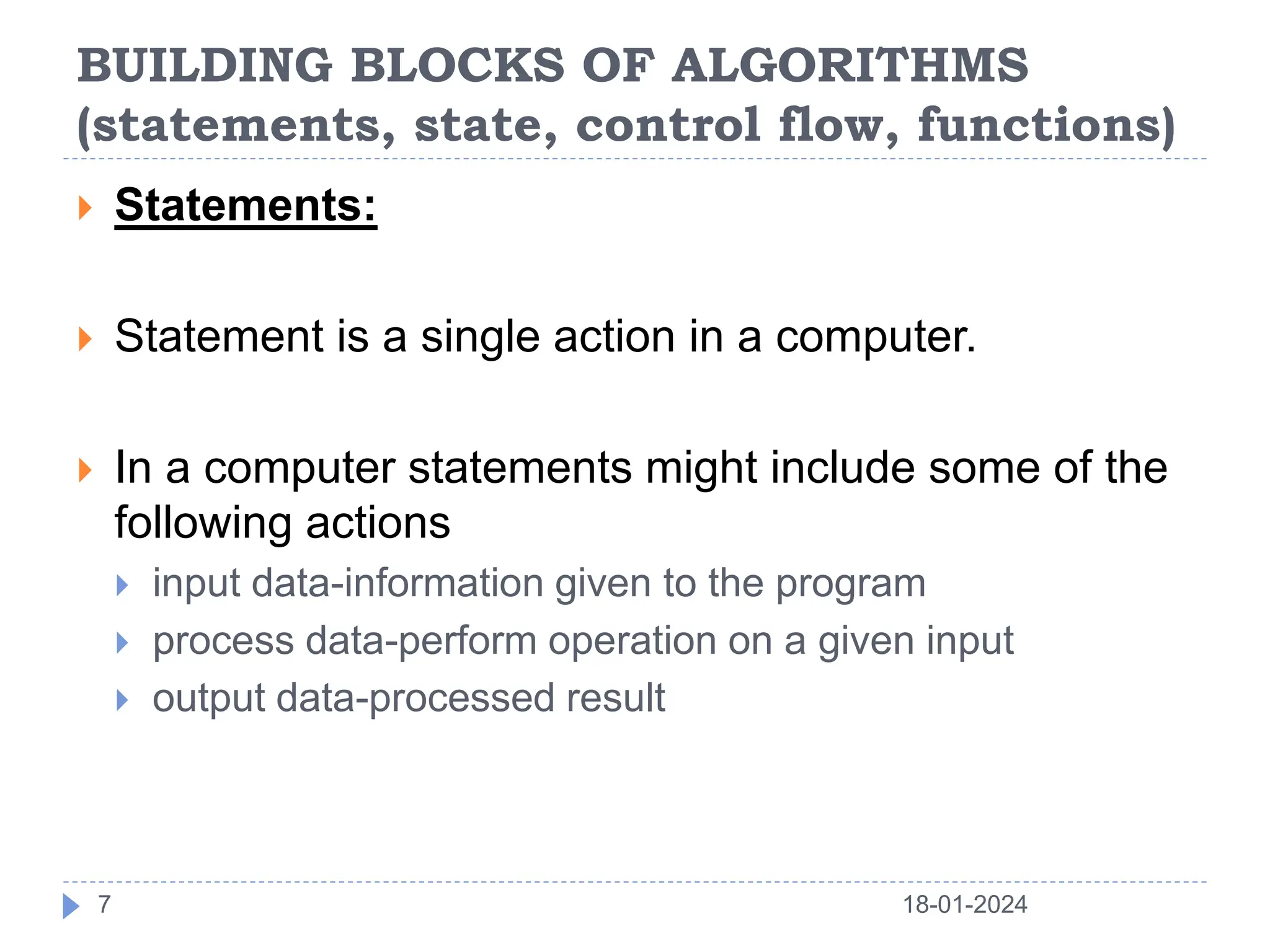
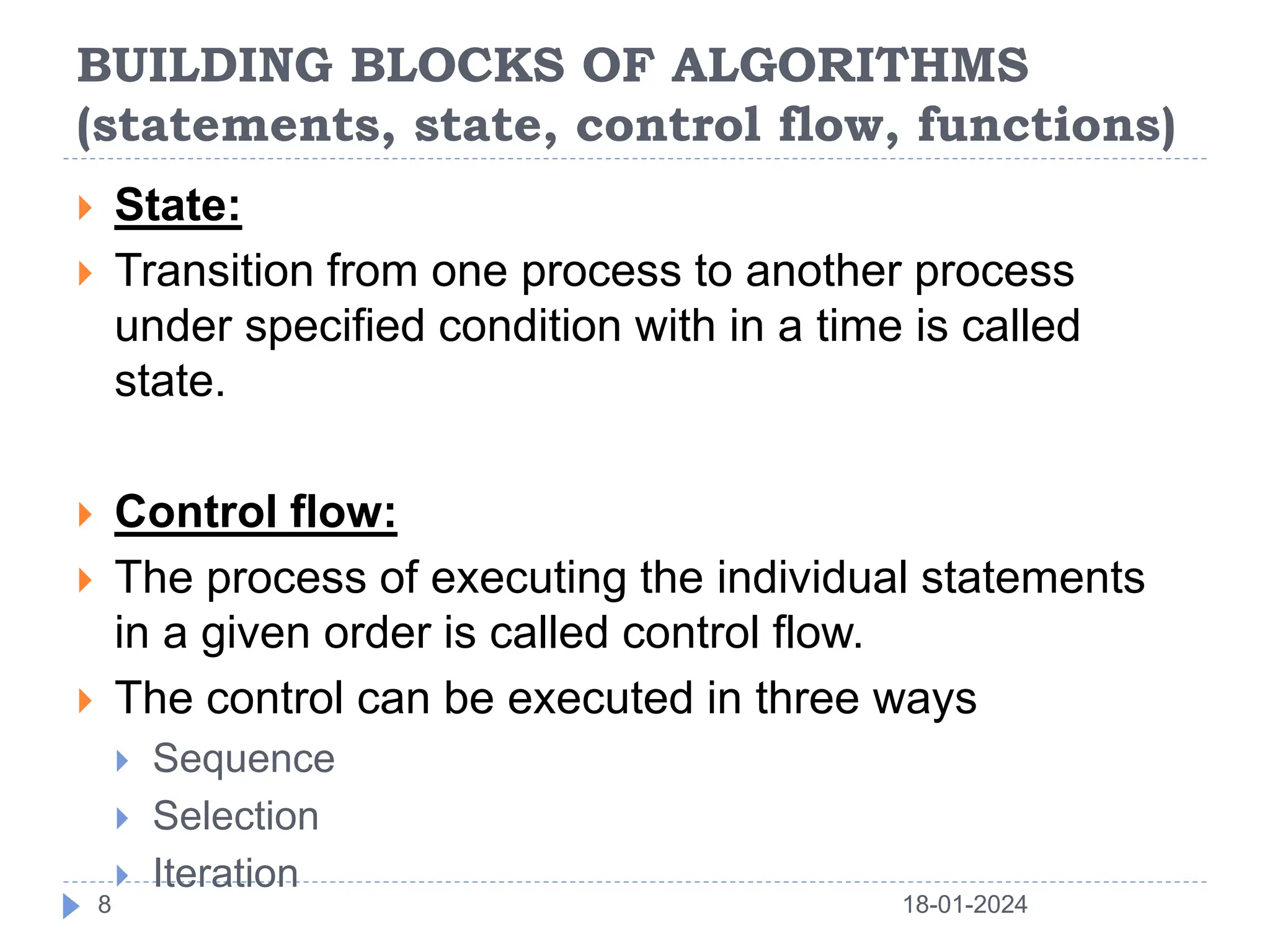
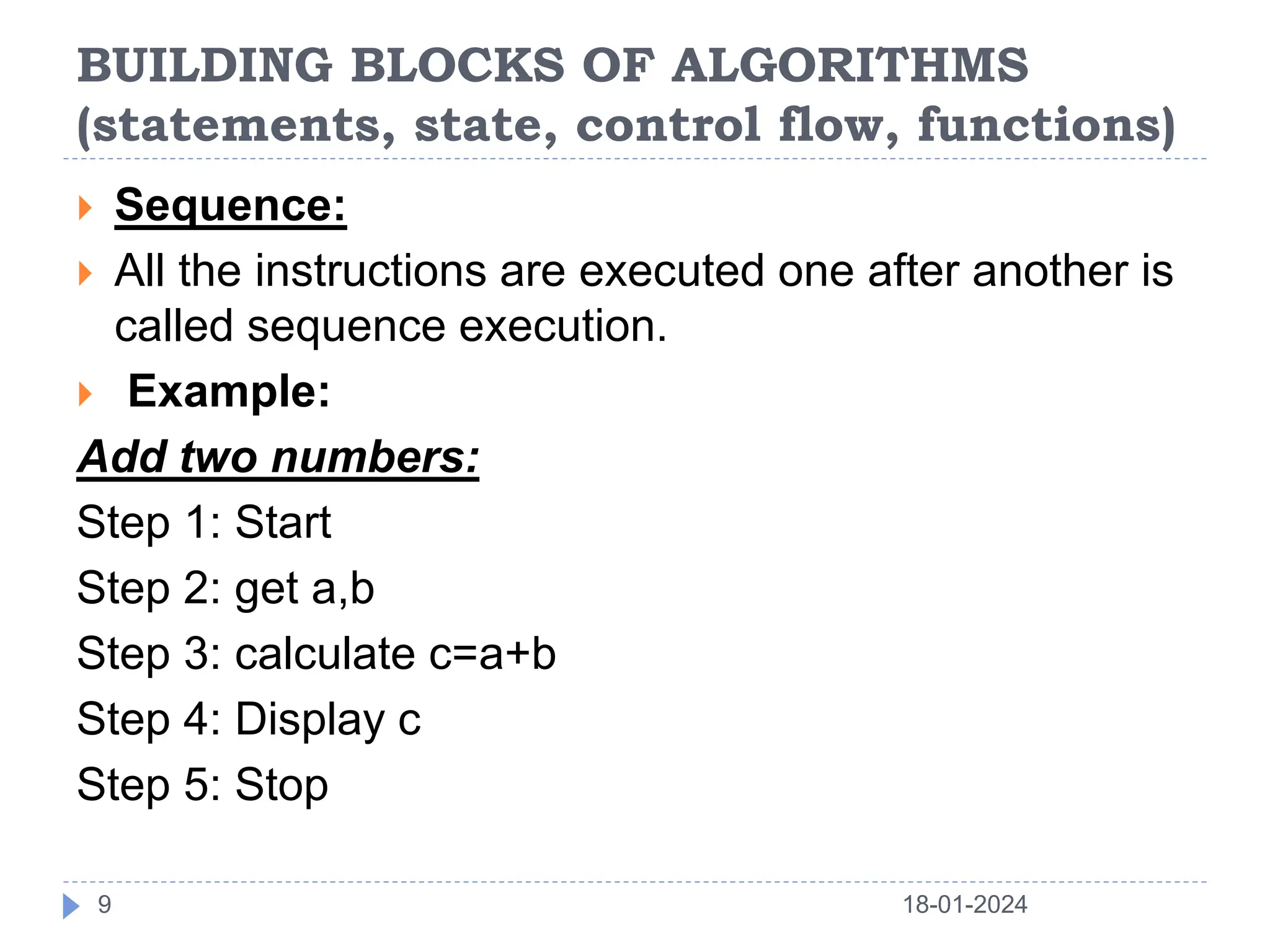
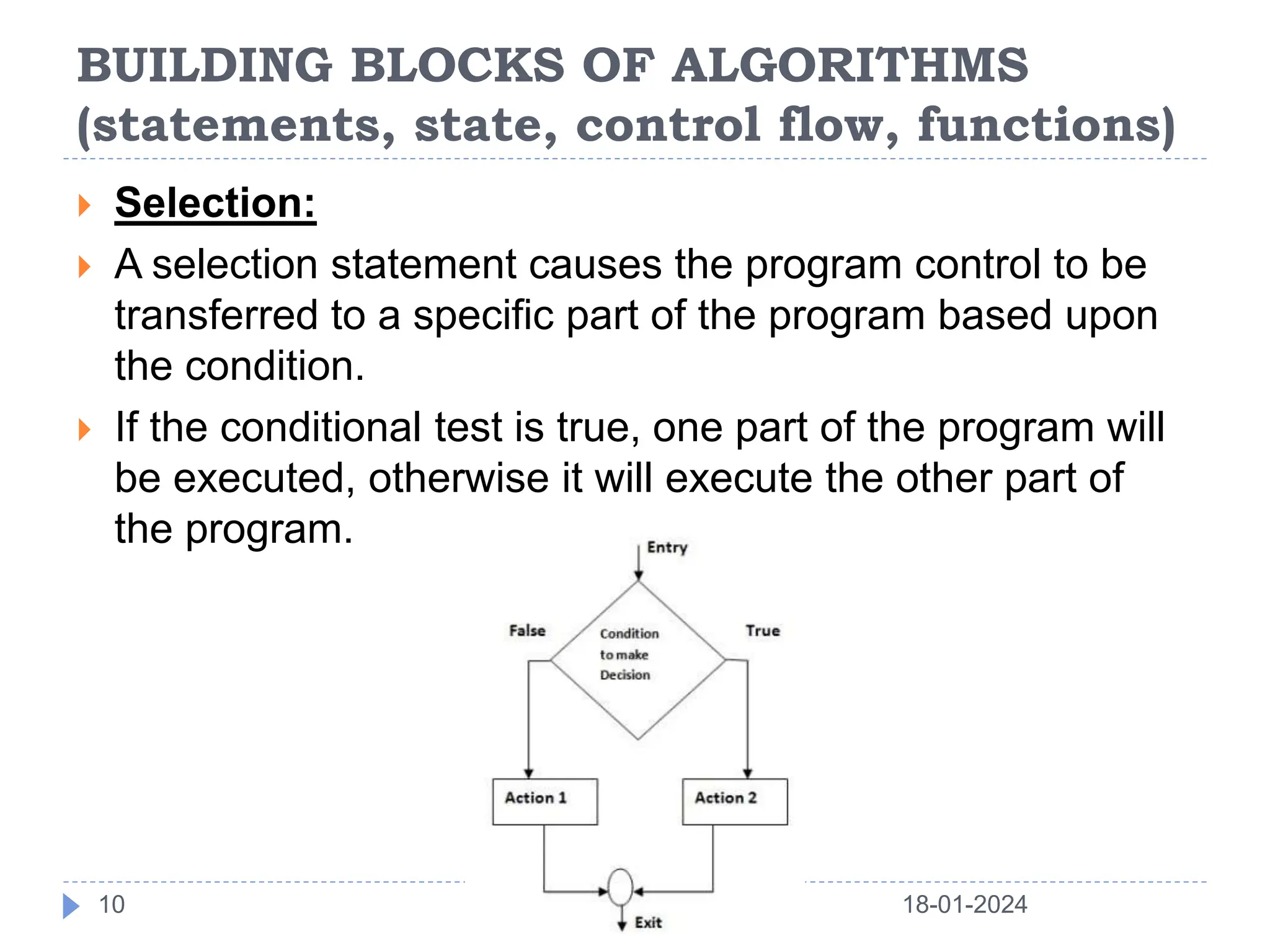
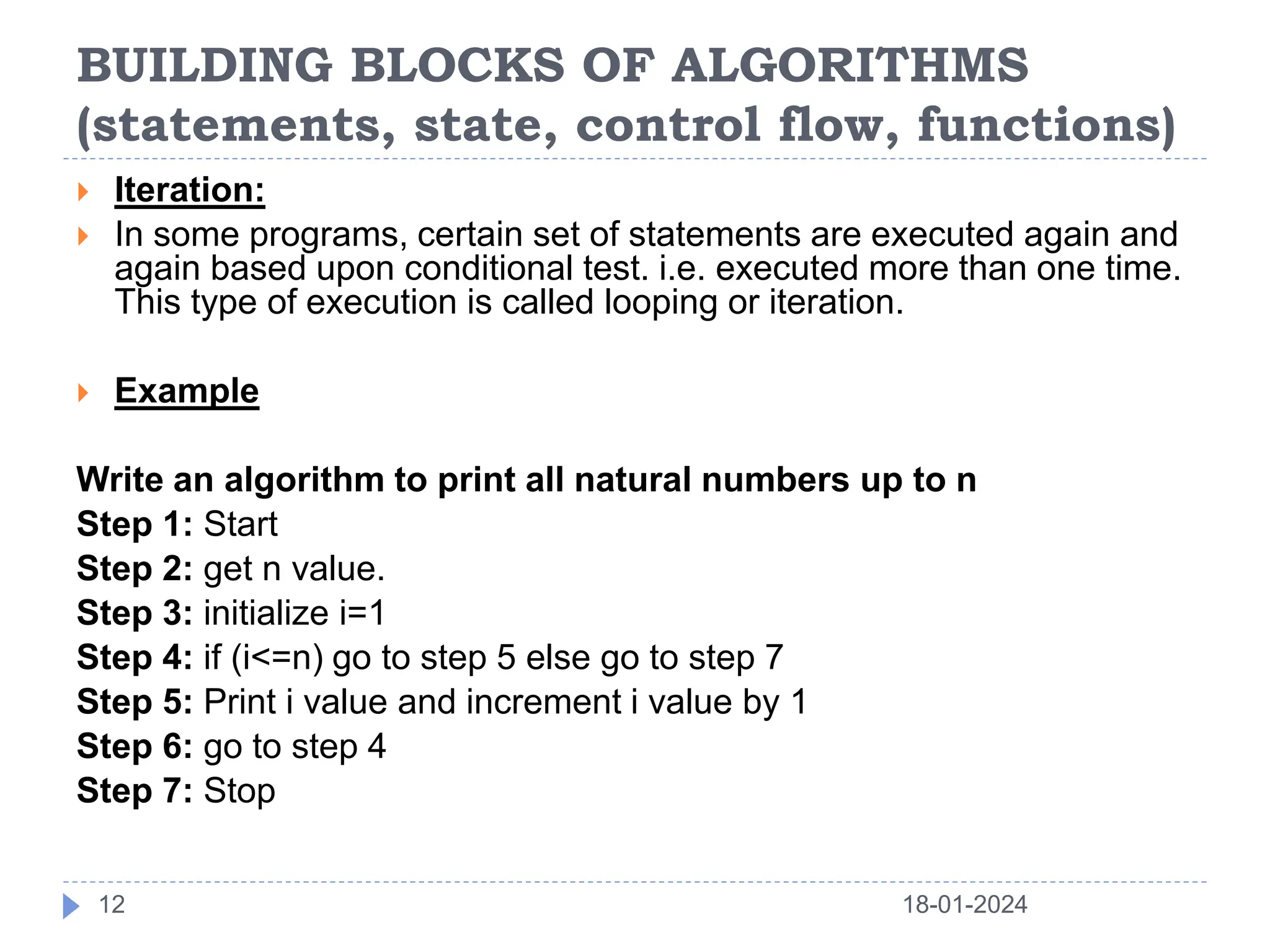
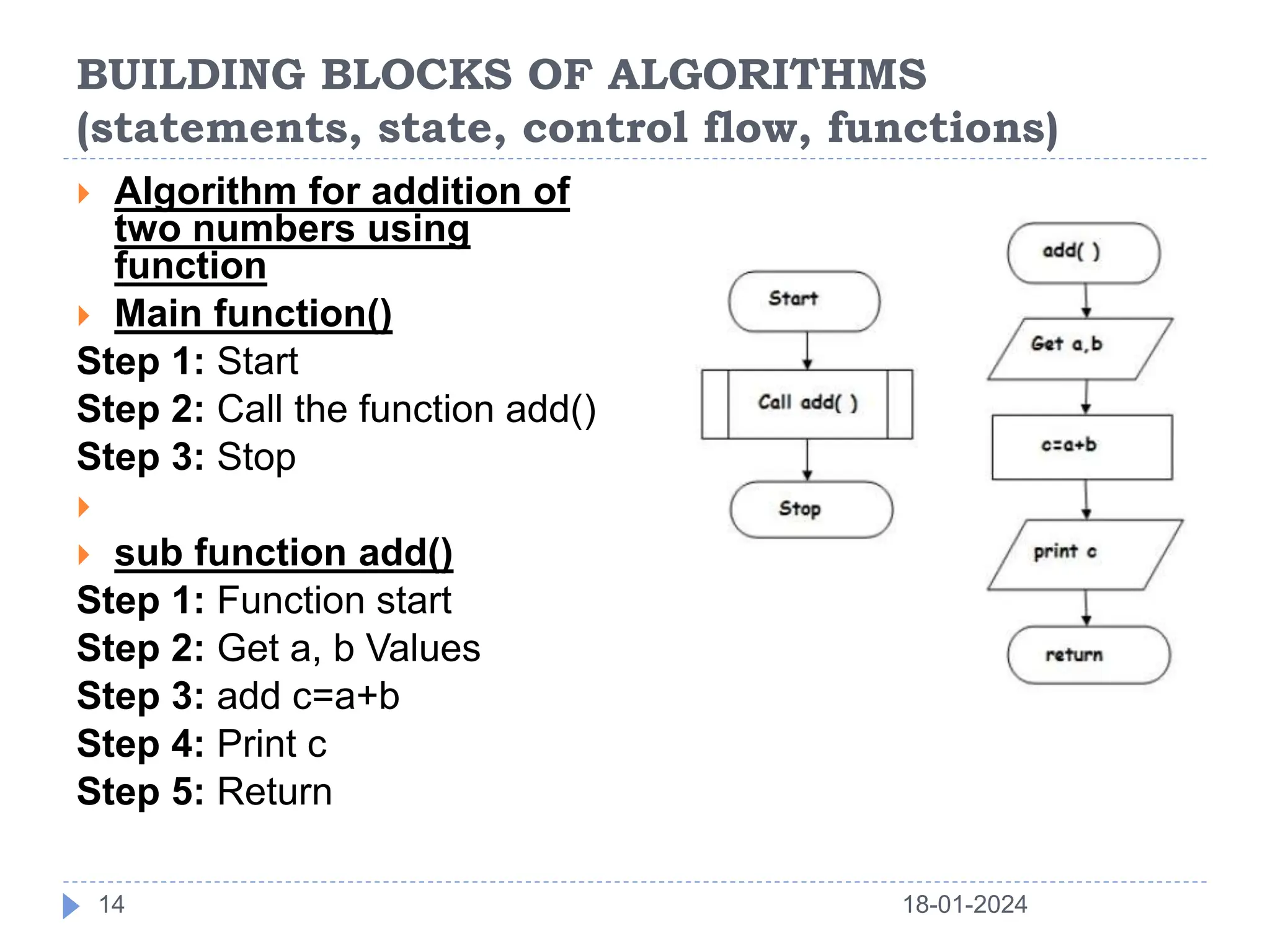
This document discusses the key building blocks of algorithms, including problem solving techniques, the problem solving process, and common algorithm structures. It describes algorithms as step-by-step procedures to solve problems and introduces common algorithm structures like sequences, selections, and iterations. It also discusses the basic components of algorithms, such as statements, state, control flow, and functions. Functions are described as reusable blocks of code that perform specific tasks to simplify complex problems.