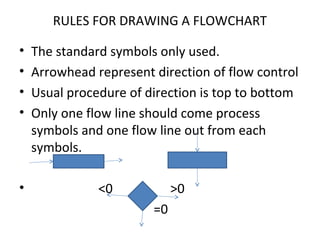
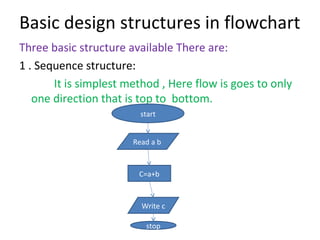
The document discusses algorithms and their characteristics. It defines an algorithm as a step-by-step procedure for solving a problem. Algorithms must have a finite number of unambiguous steps and result in the desired output. The document also discusses the building blocks of algorithms like statements, control flow, functions. It provides examples of different algorithm structures like sequence, selection, iteration. Finally, it discusses representations of algorithms using pseudocode, flowcharts and programming languages.








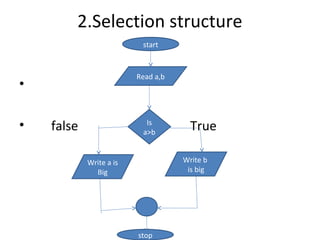
![2. Selection Structure:
• Selection control structures (or) Decision
structures allows the program to make a
choice between two alternate paths whether
it is true or false.
Eg: Step 1: start
Step 2:Input first number as A
Step 3: Input second number as B
Step 4: IF A=B
print “equal”
ELSE
print ”Not equal”
[End of IF]
step 5: stop](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1psp-181124055404/85/Unit-1-psp-10-320.jpg)



![3. Iteration(Loops):
Iterative structures are used when part of
the program is to be executed several times.
Eg:
Step 1: [initialize]set I=1,N=10
Step 2:Repeat steps 3 & 4 while I<=N
Step 3: Print I
Step 4: set I=I+1
[End of the loop]
Step 5: end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1psp-181124055404/85/Unit-1-psp-14-320.jpg)