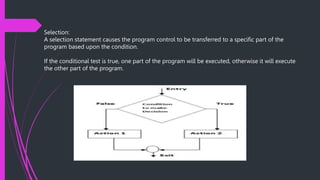
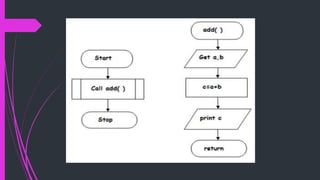
The document summarizes the basic building blocks of algorithms: sequence, selection, and iteration. It provides examples of each: sequence execution to add two numbers, selection execution to check voter eligibility based on age, and iteration execution to print all natural numbers up to n. It also discusses functions as a way to divide complex problems into smaller tasks, listing benefits of functions like code reuse and readability. An example algorithm adds two numbers using a function.