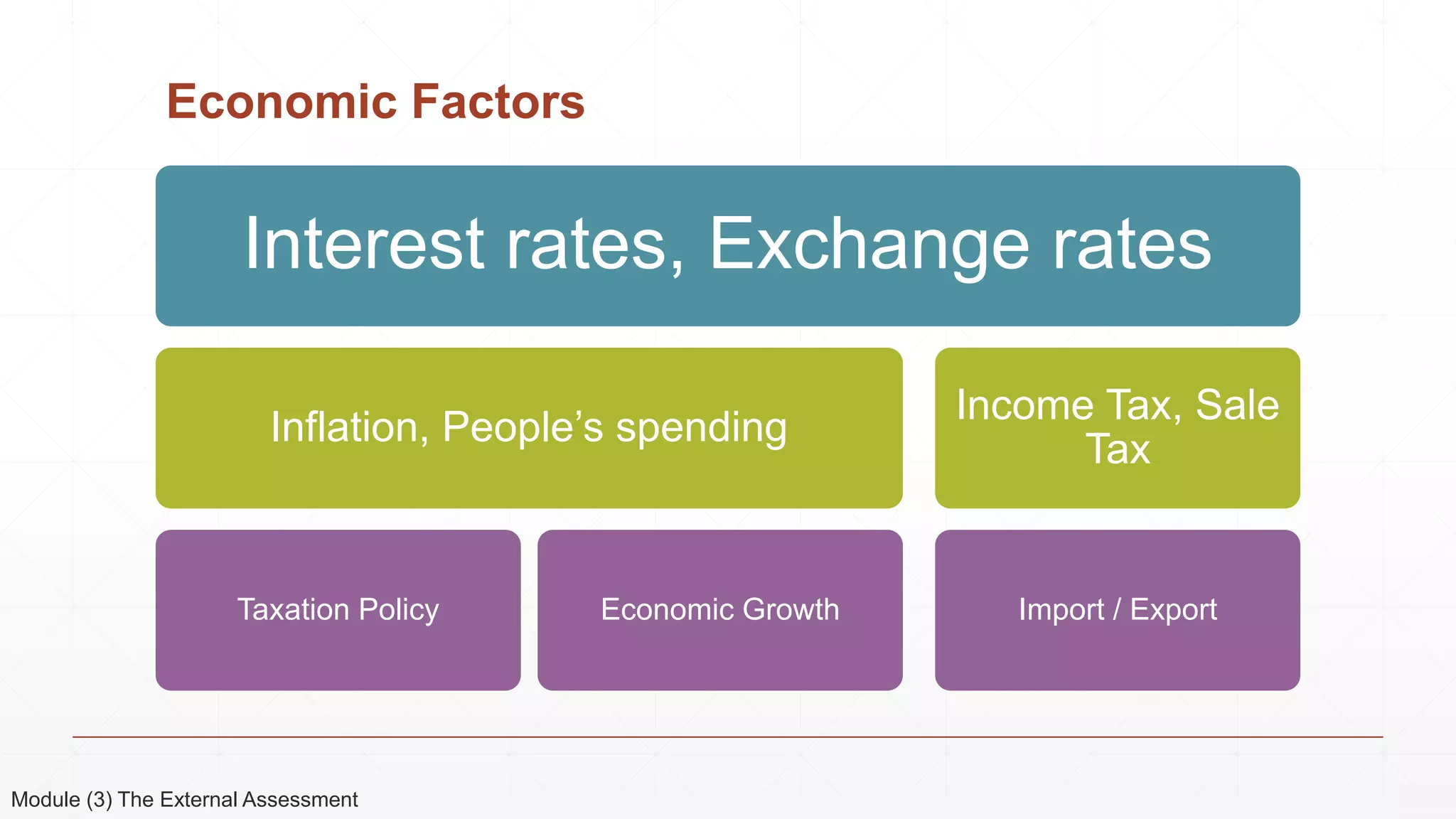
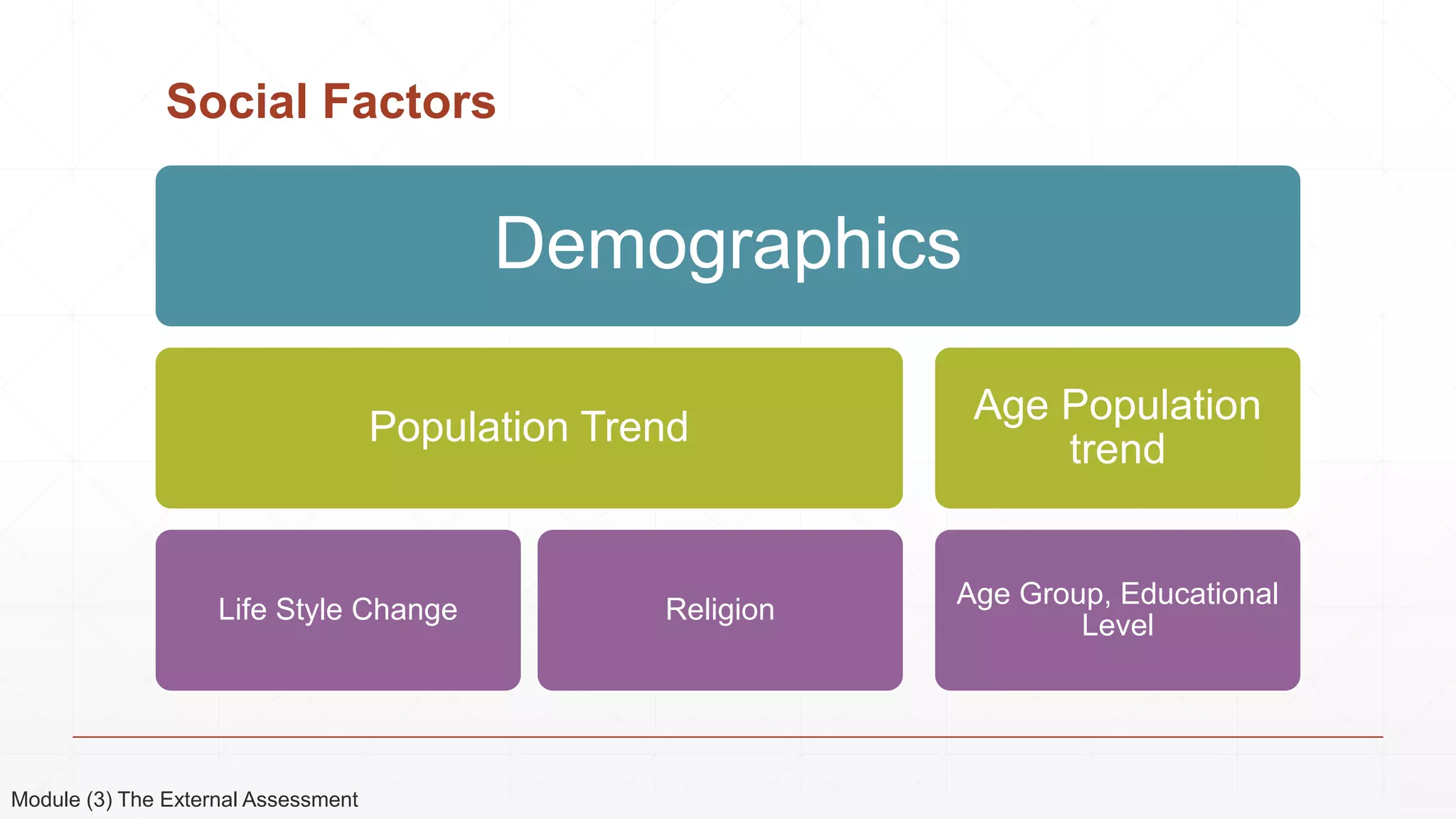
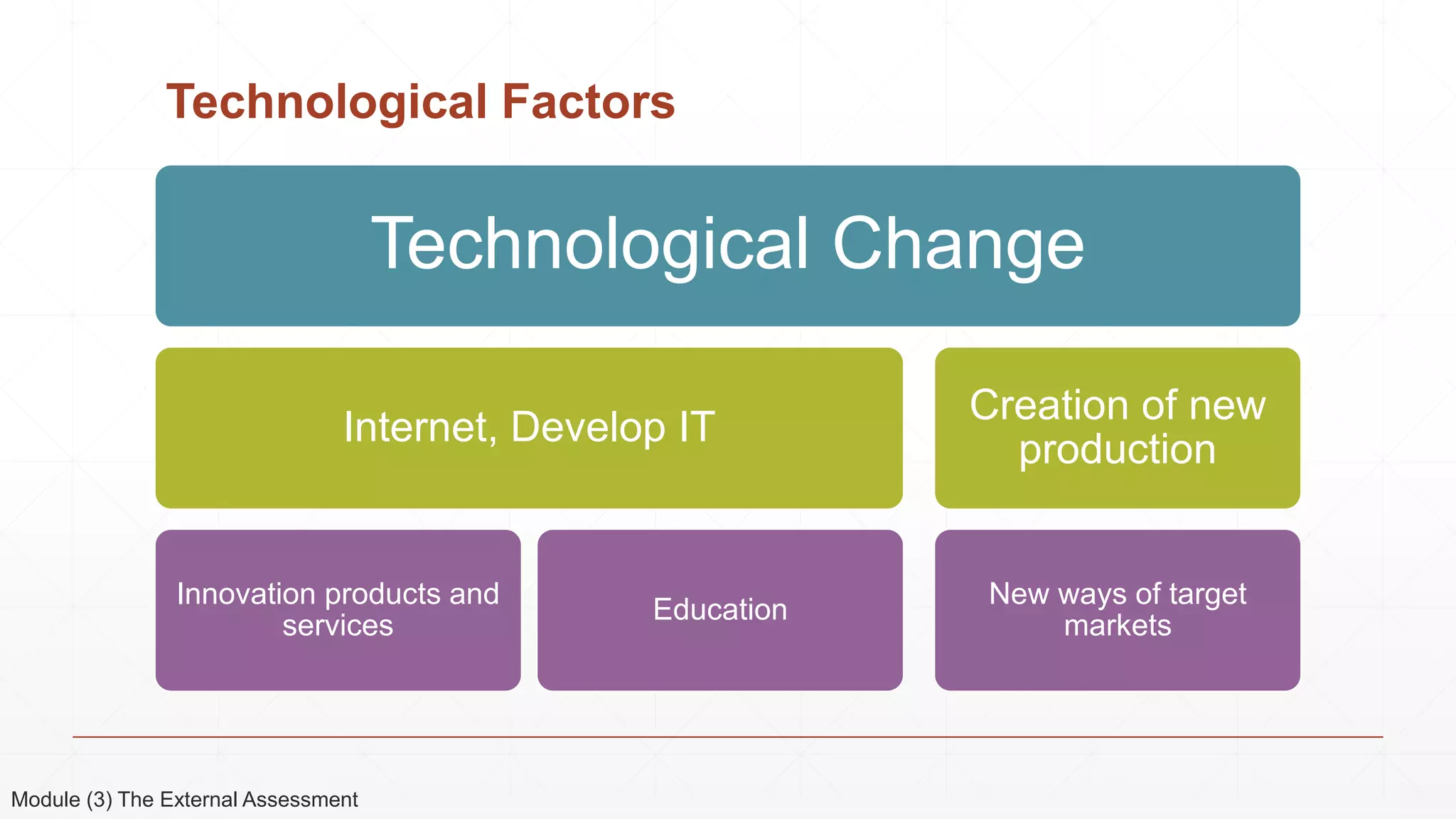
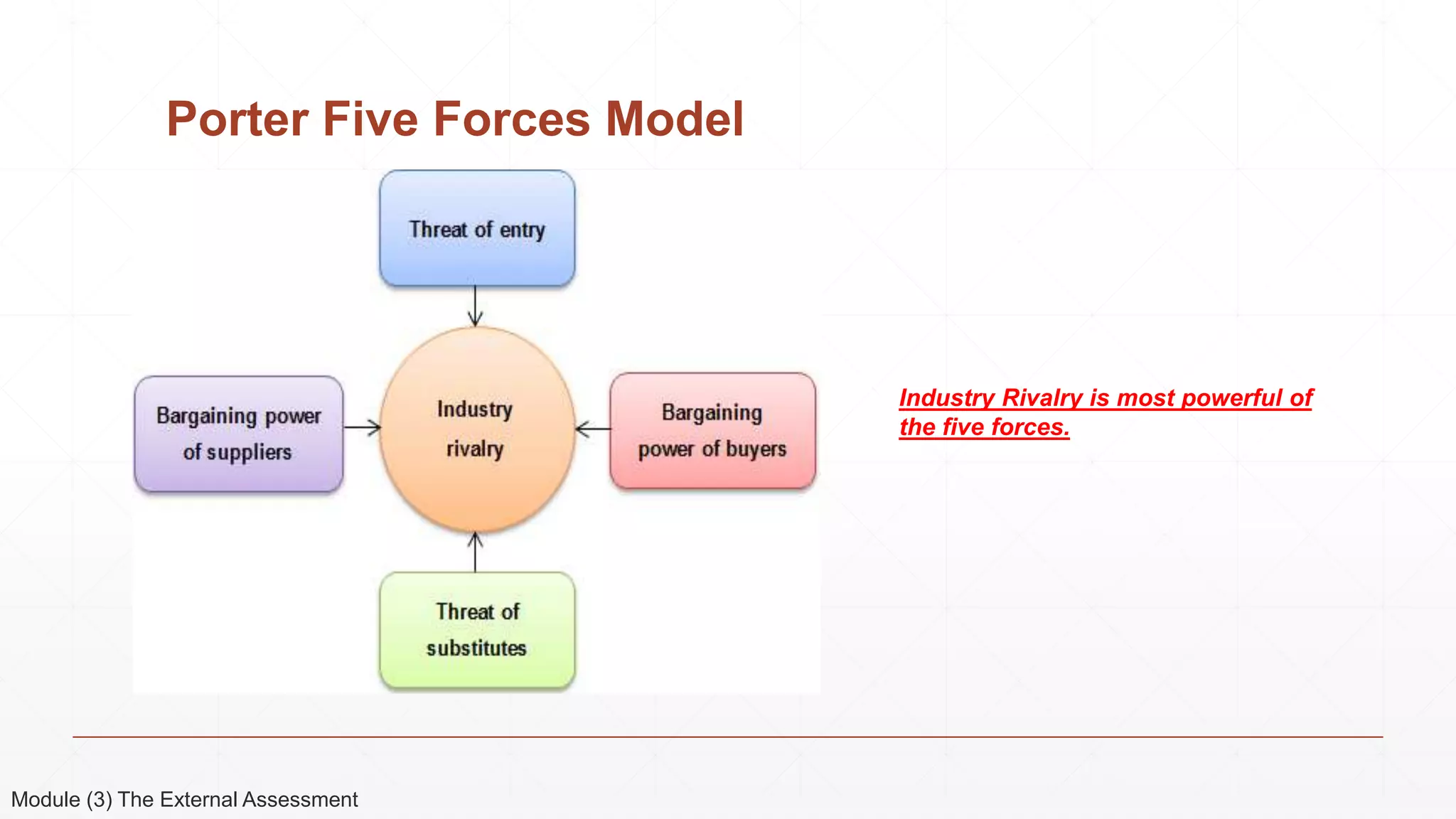
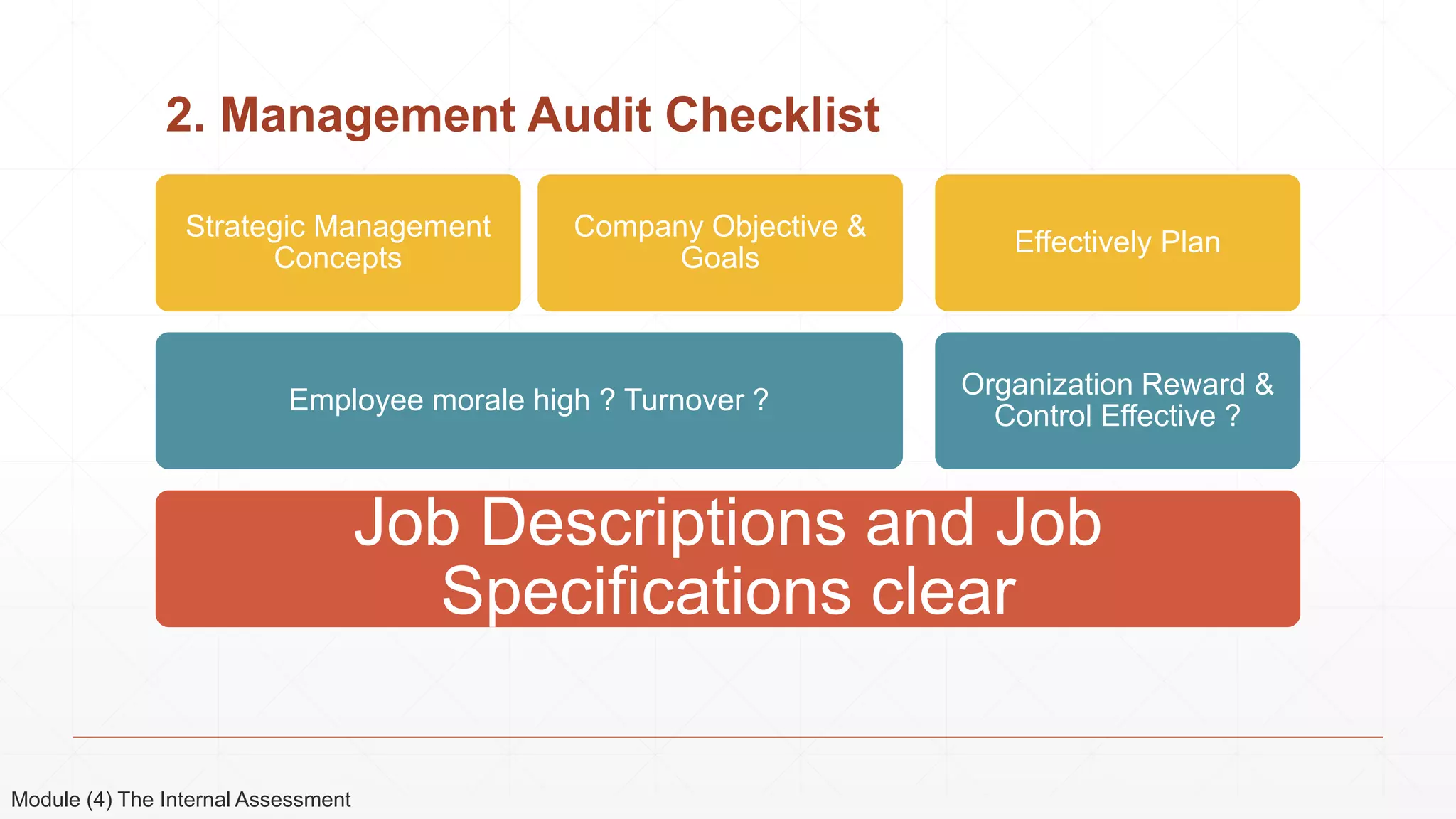
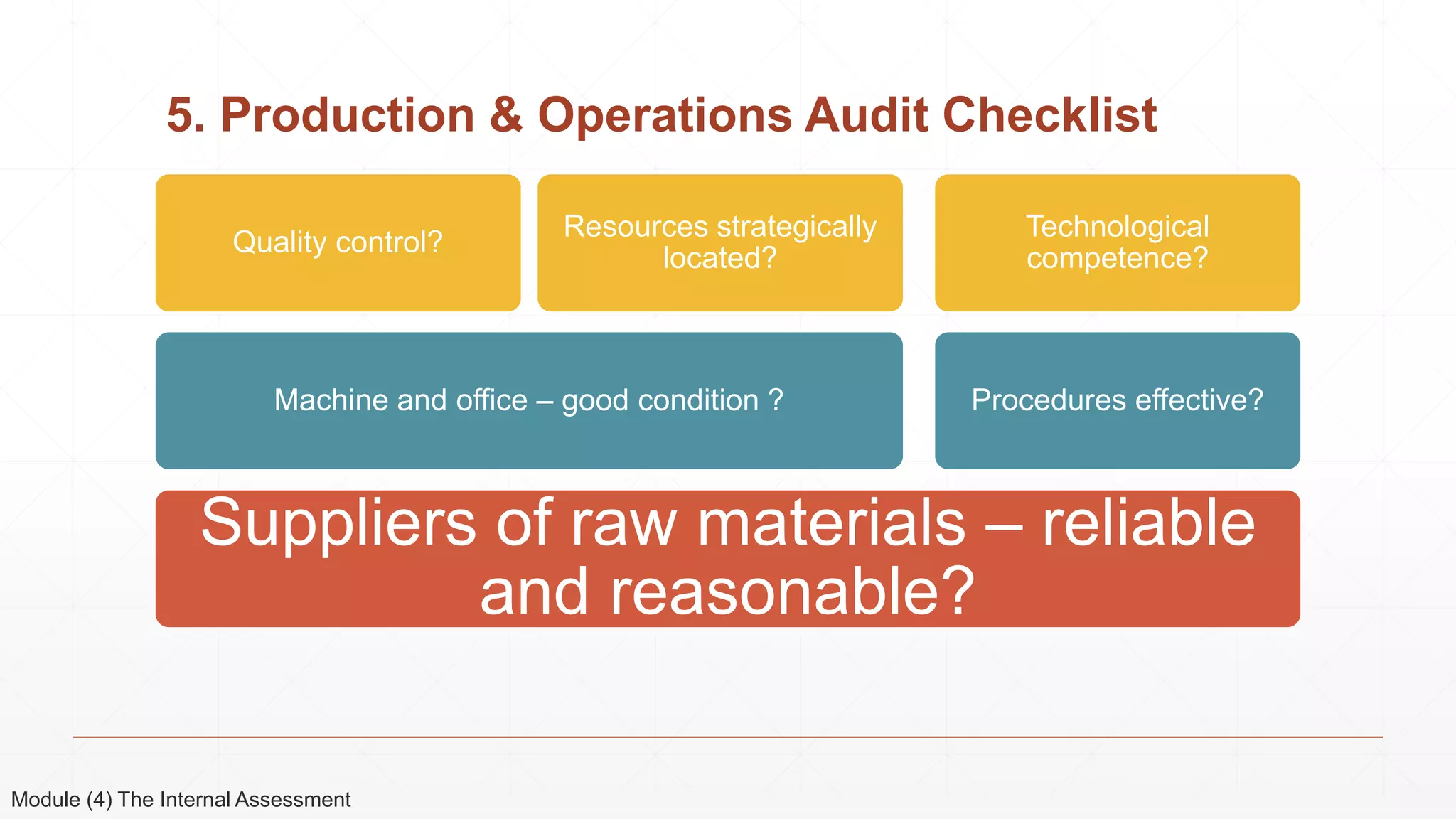
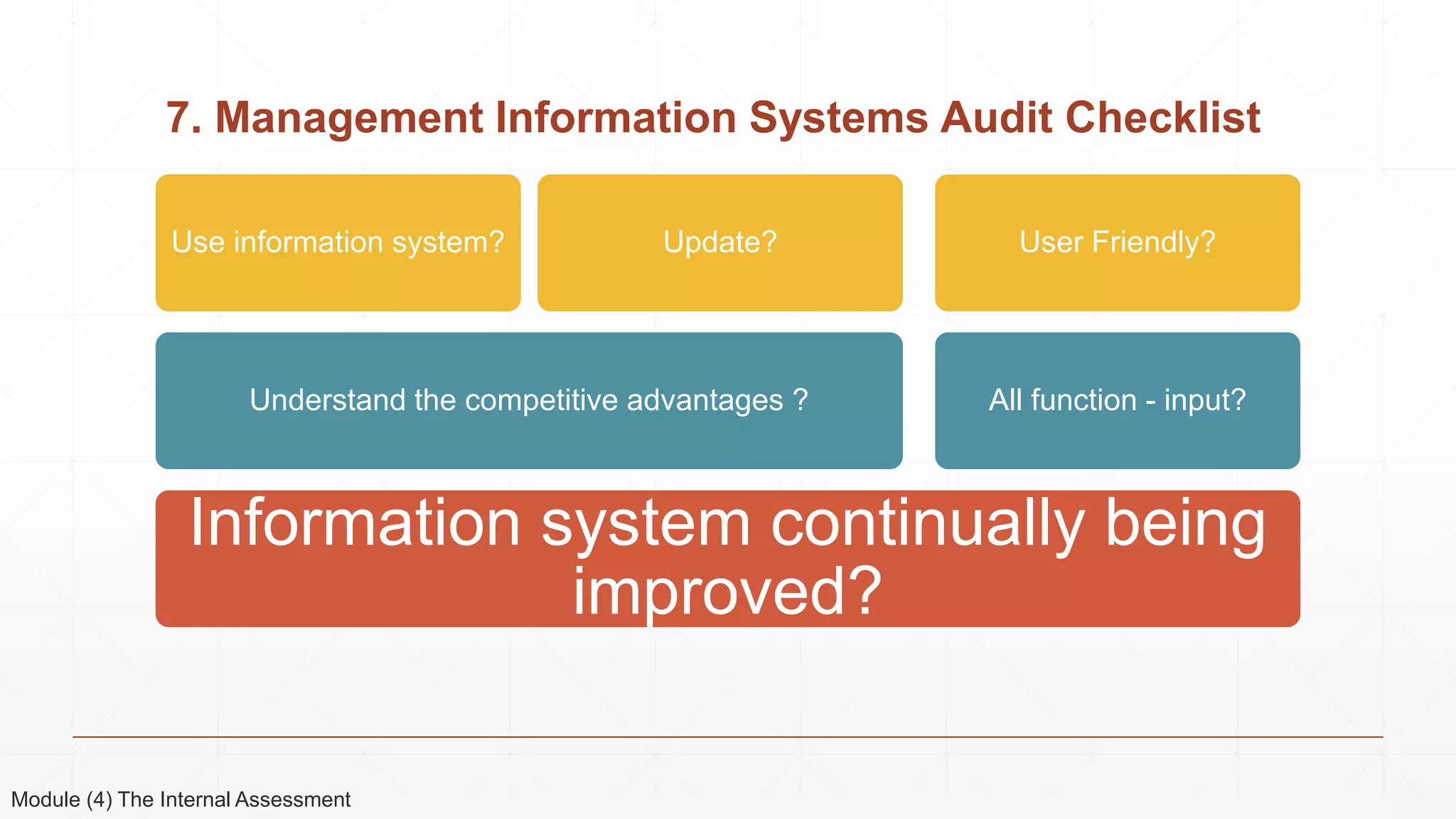
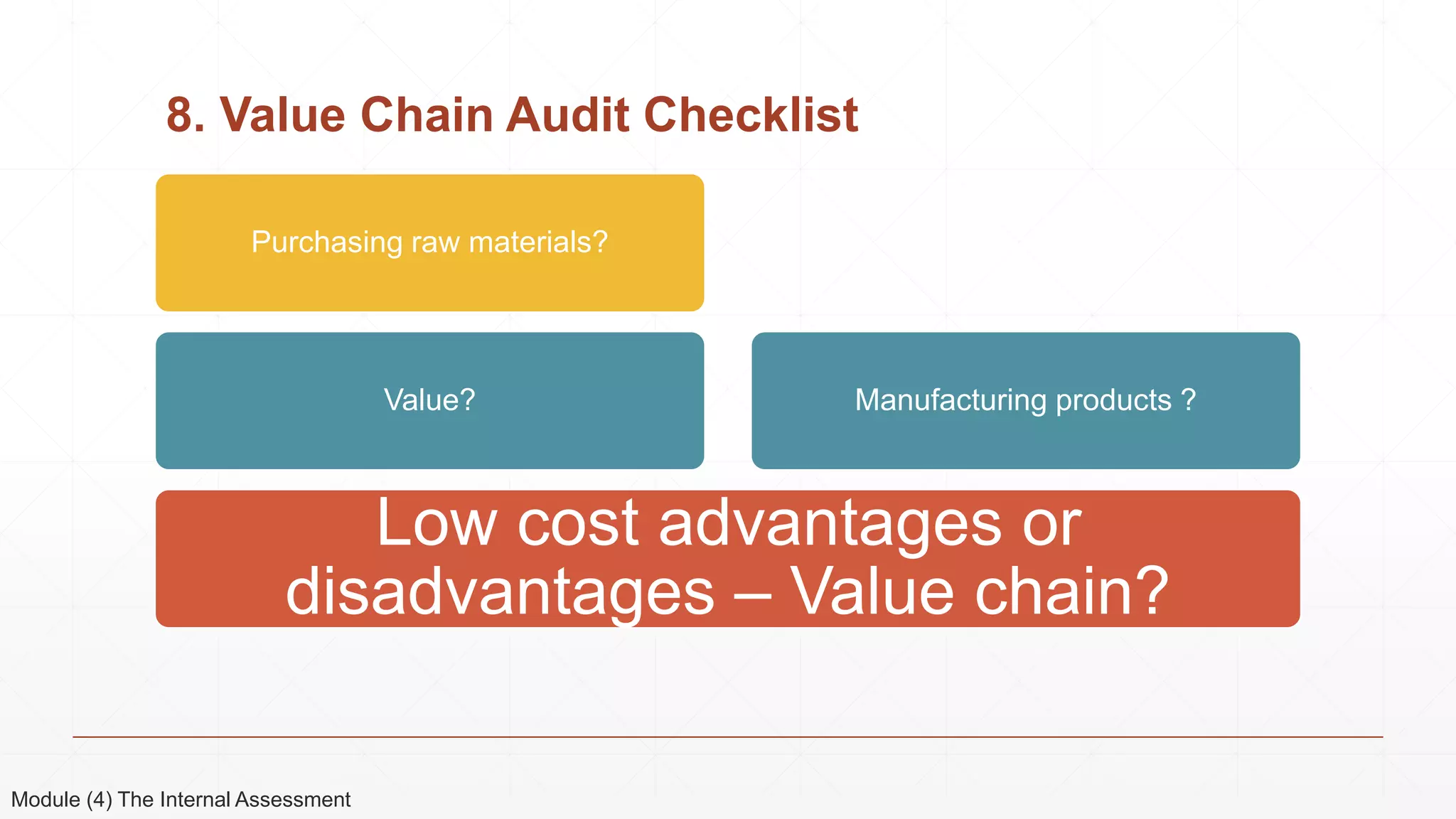
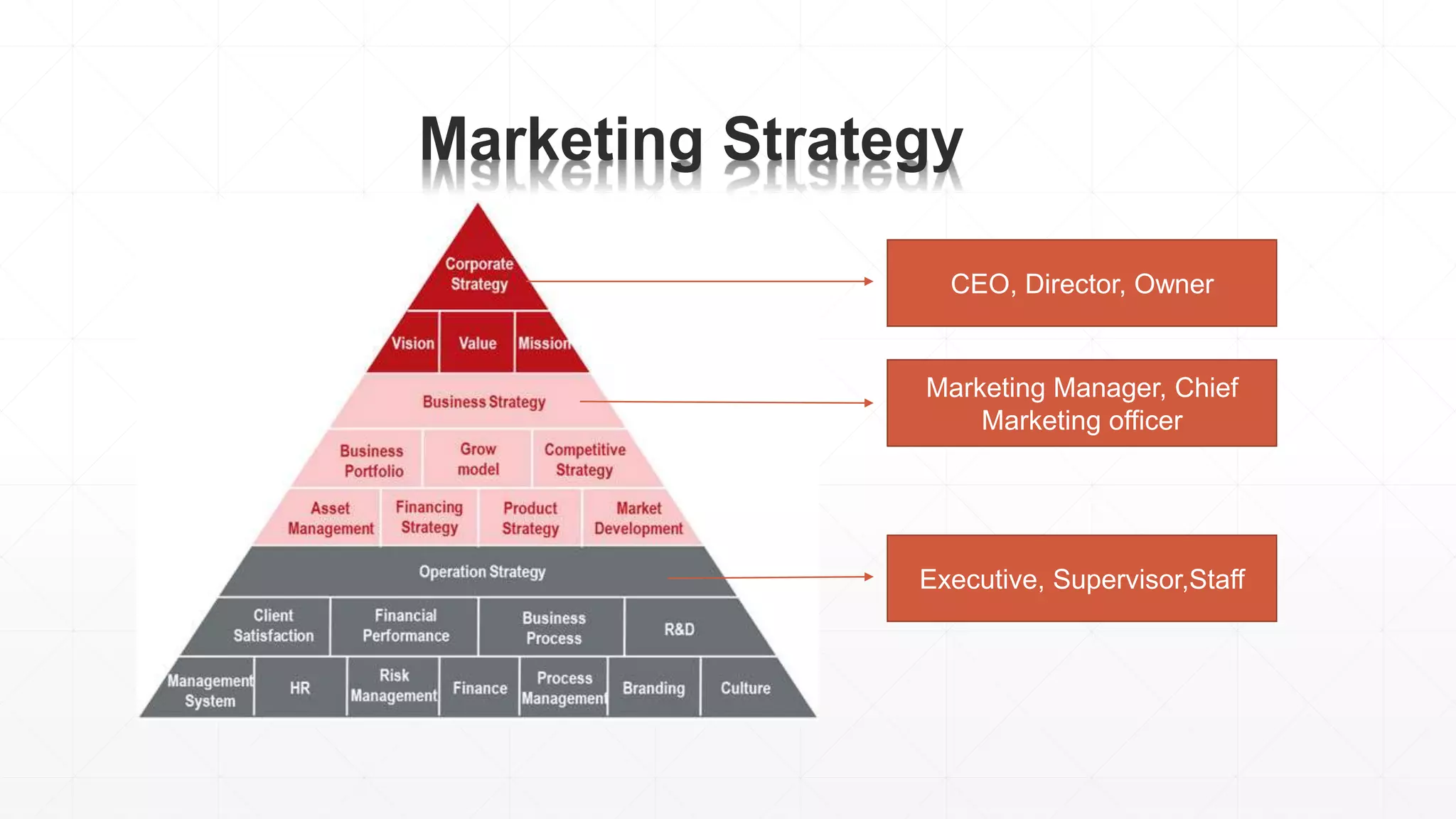
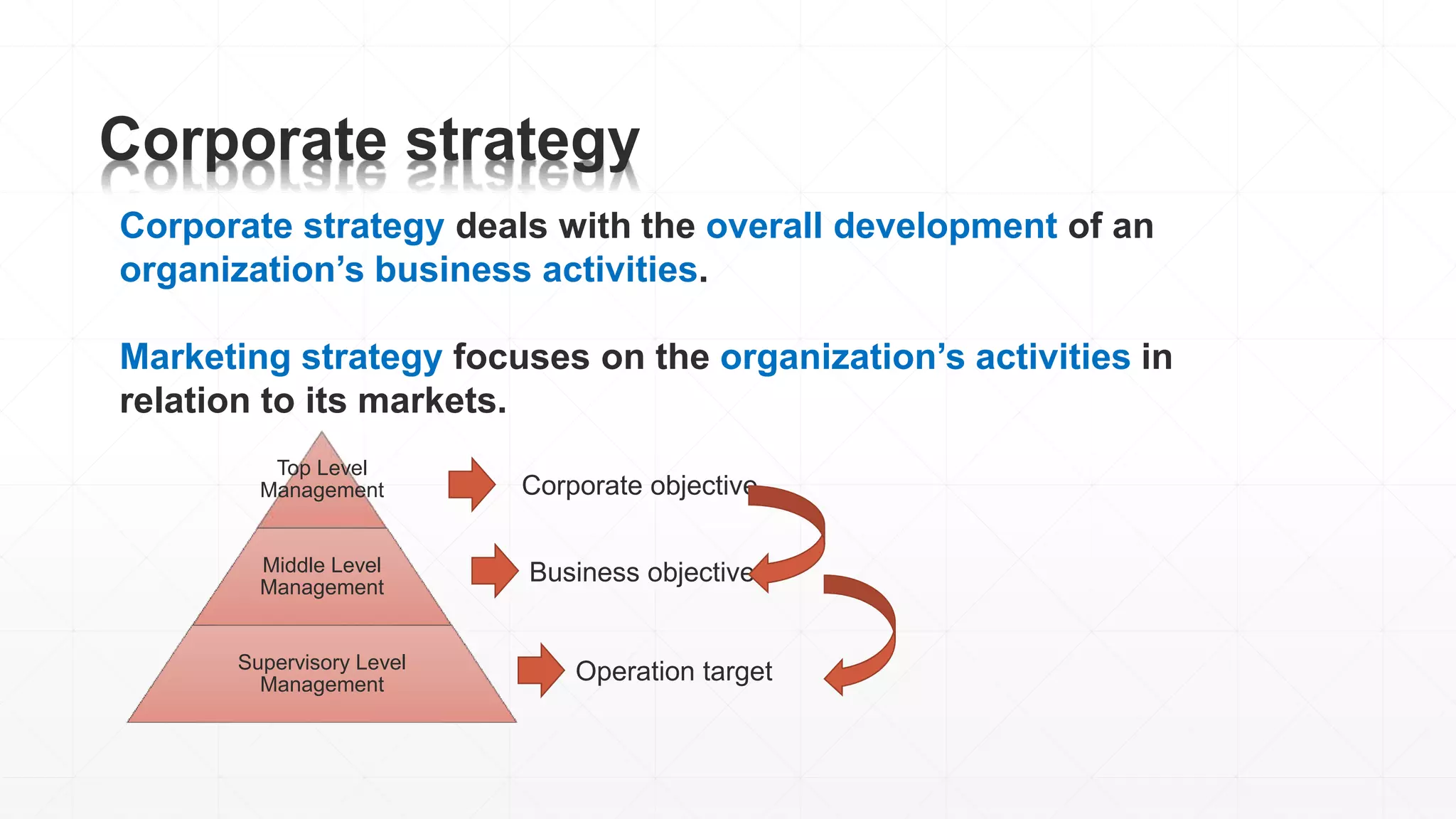
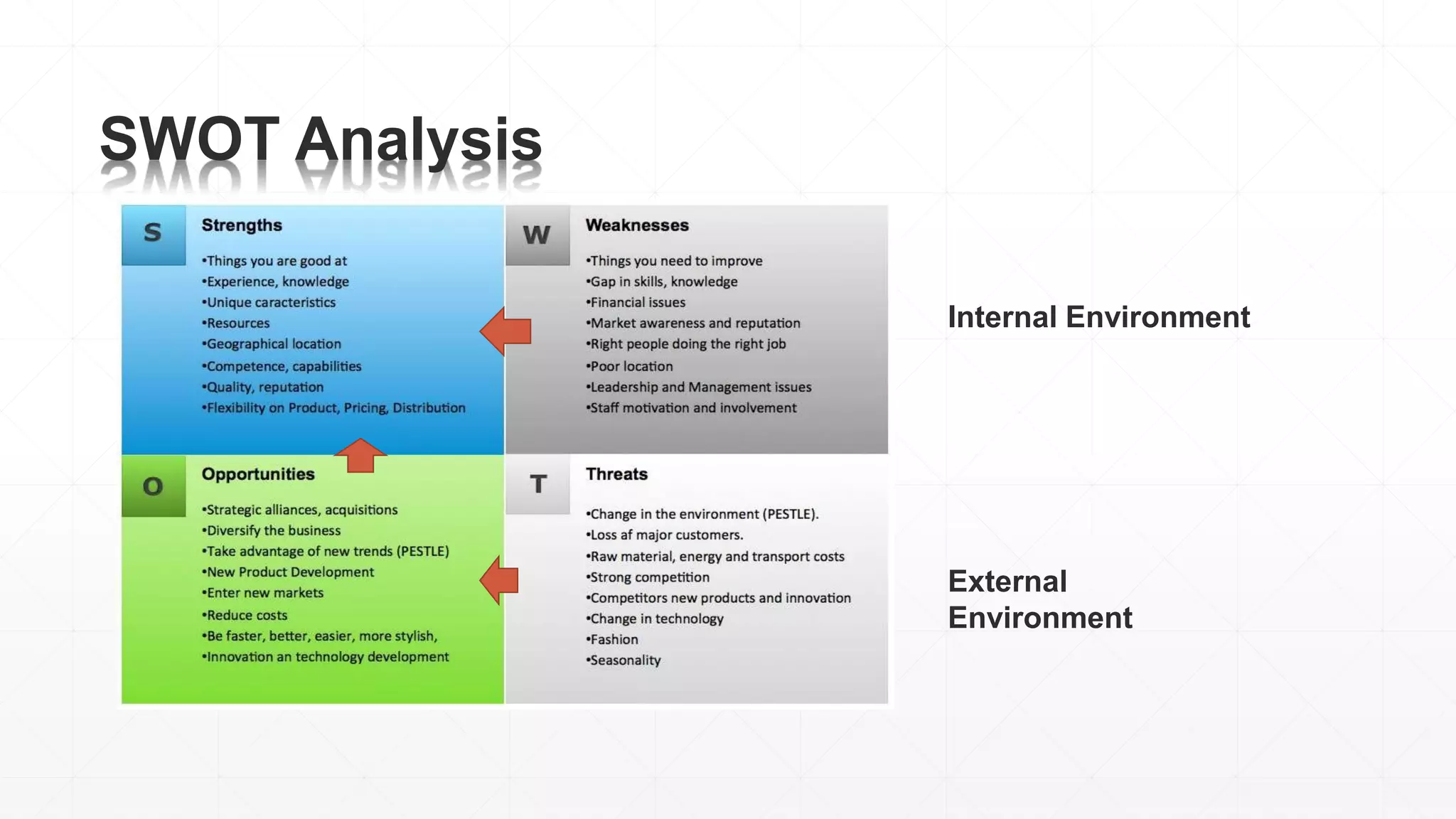
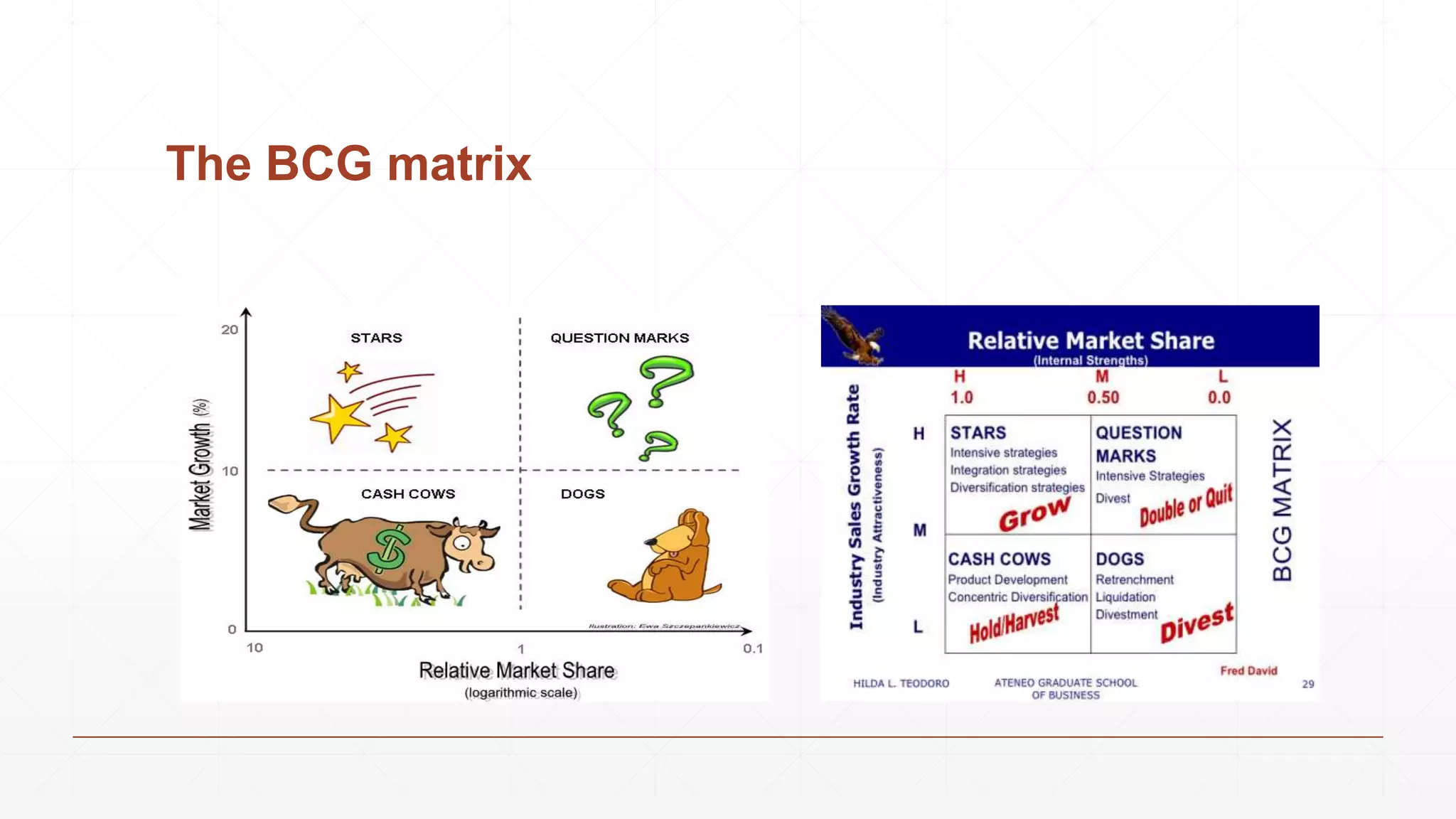
The document outlines the agenda and content for a 3-day seminar on building and sustaining competitive advantage. Day 1 covers an introduction to strategic management, including definitions of key concepts like strategy, competitive advantage, and the importance of strategic planning. It also discusses vision and mission statements. Day 2 focuses on external assessments using PEST and Porter's Five Forces analyses. Day 3 addresses internal assessments, including the McKinsey 7S framework and different types of business strategies. The seminar aims to help participants understand how to develop and maintain a competitive edge over competitors.