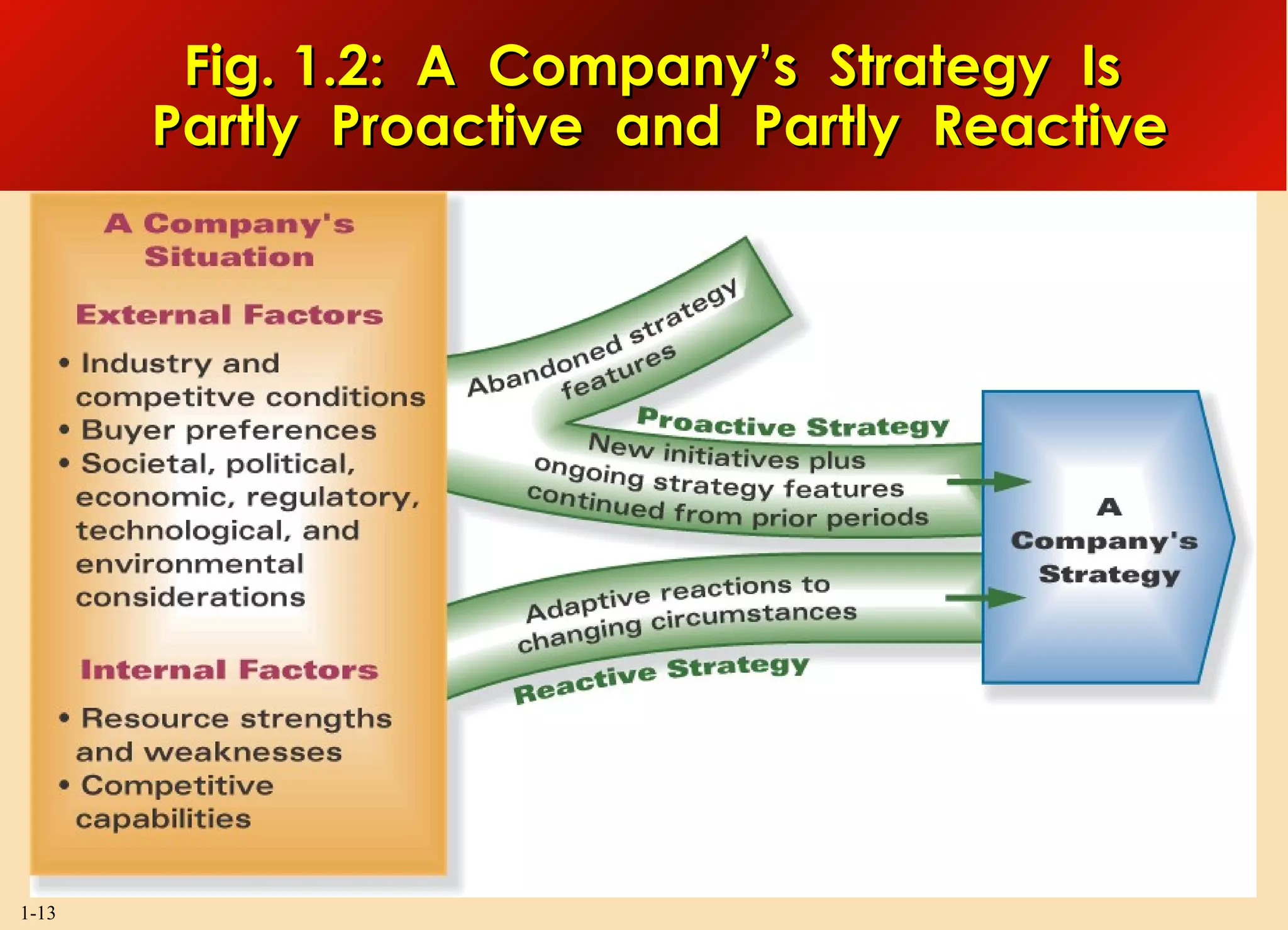
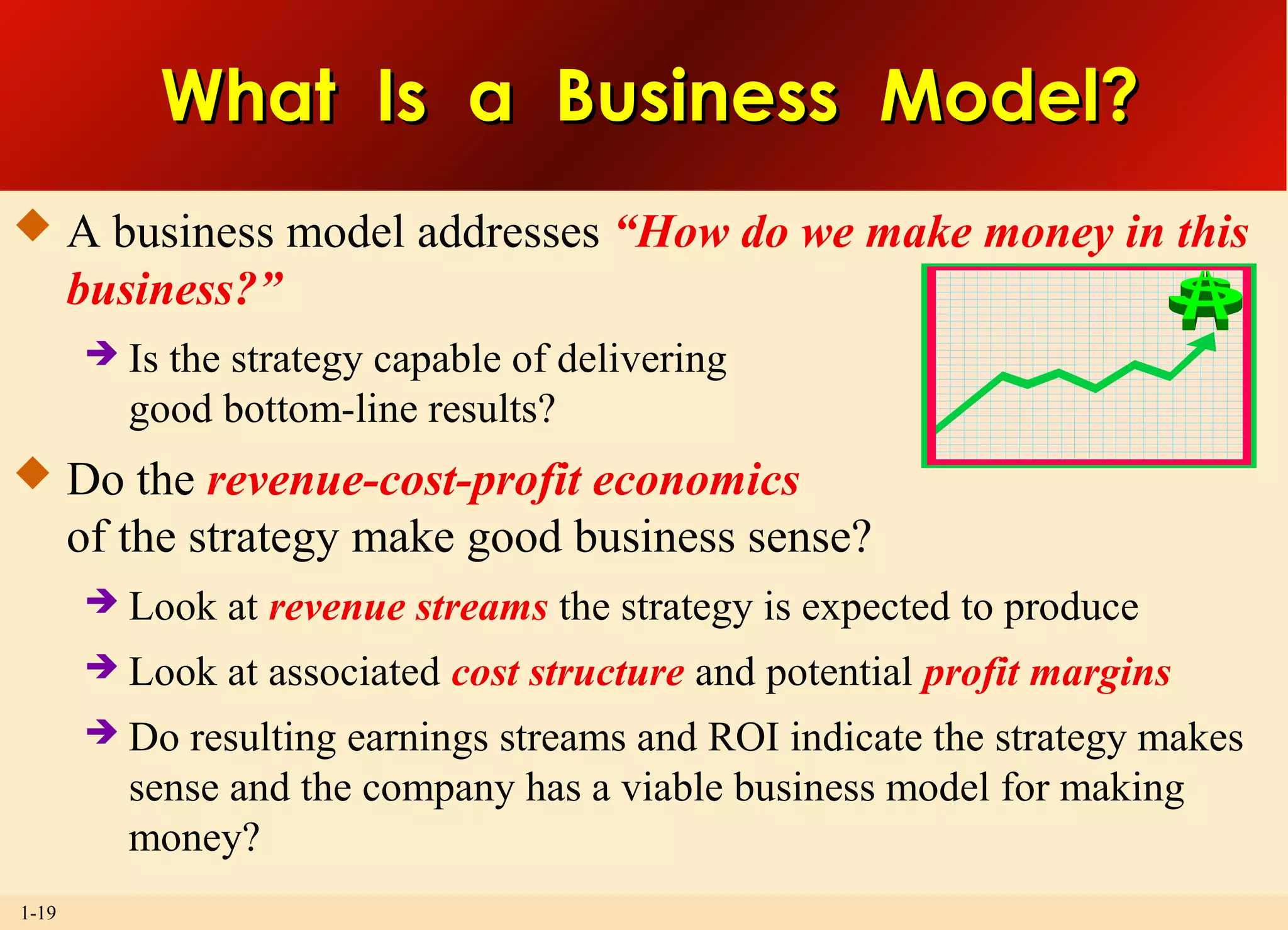
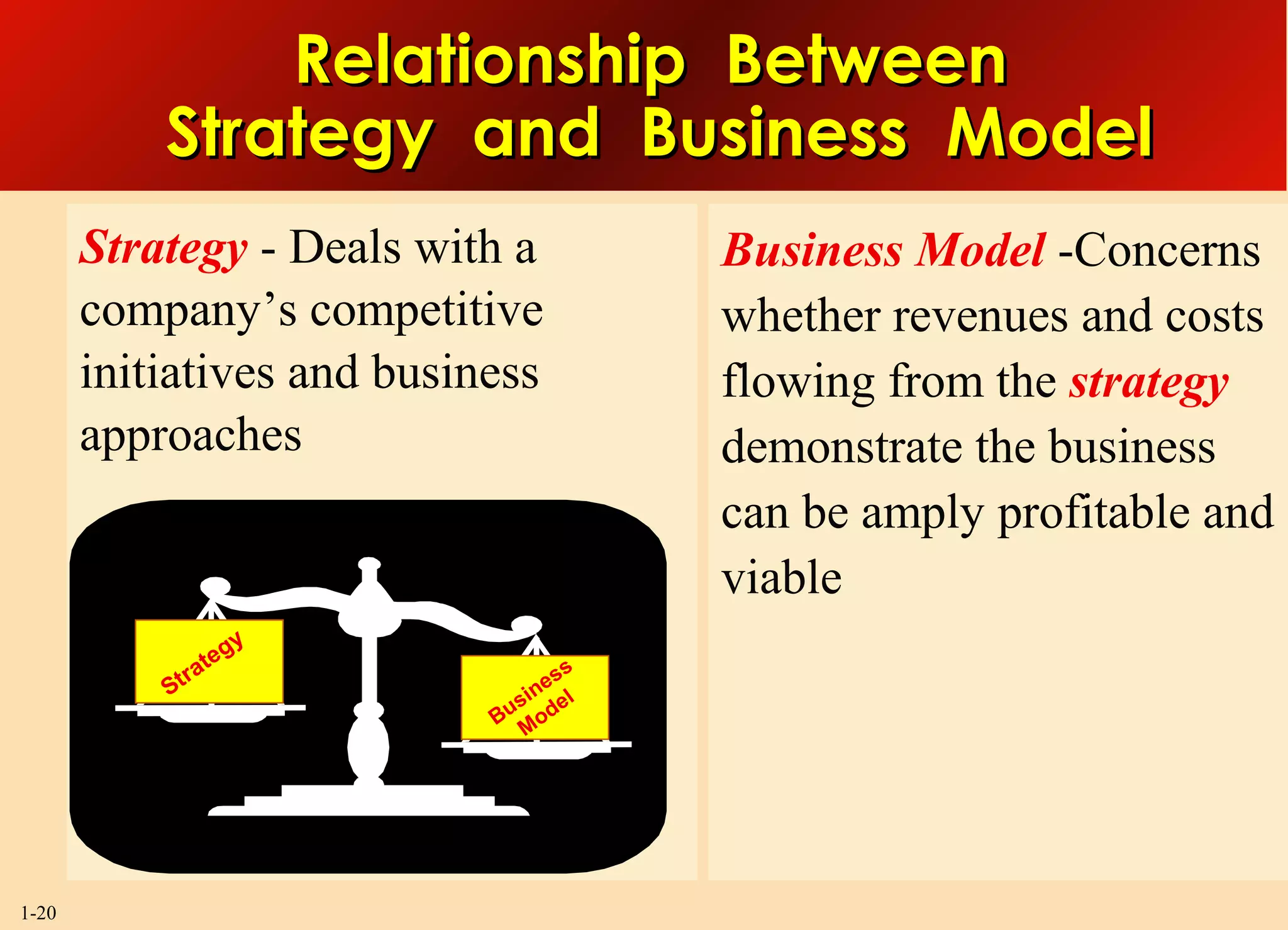
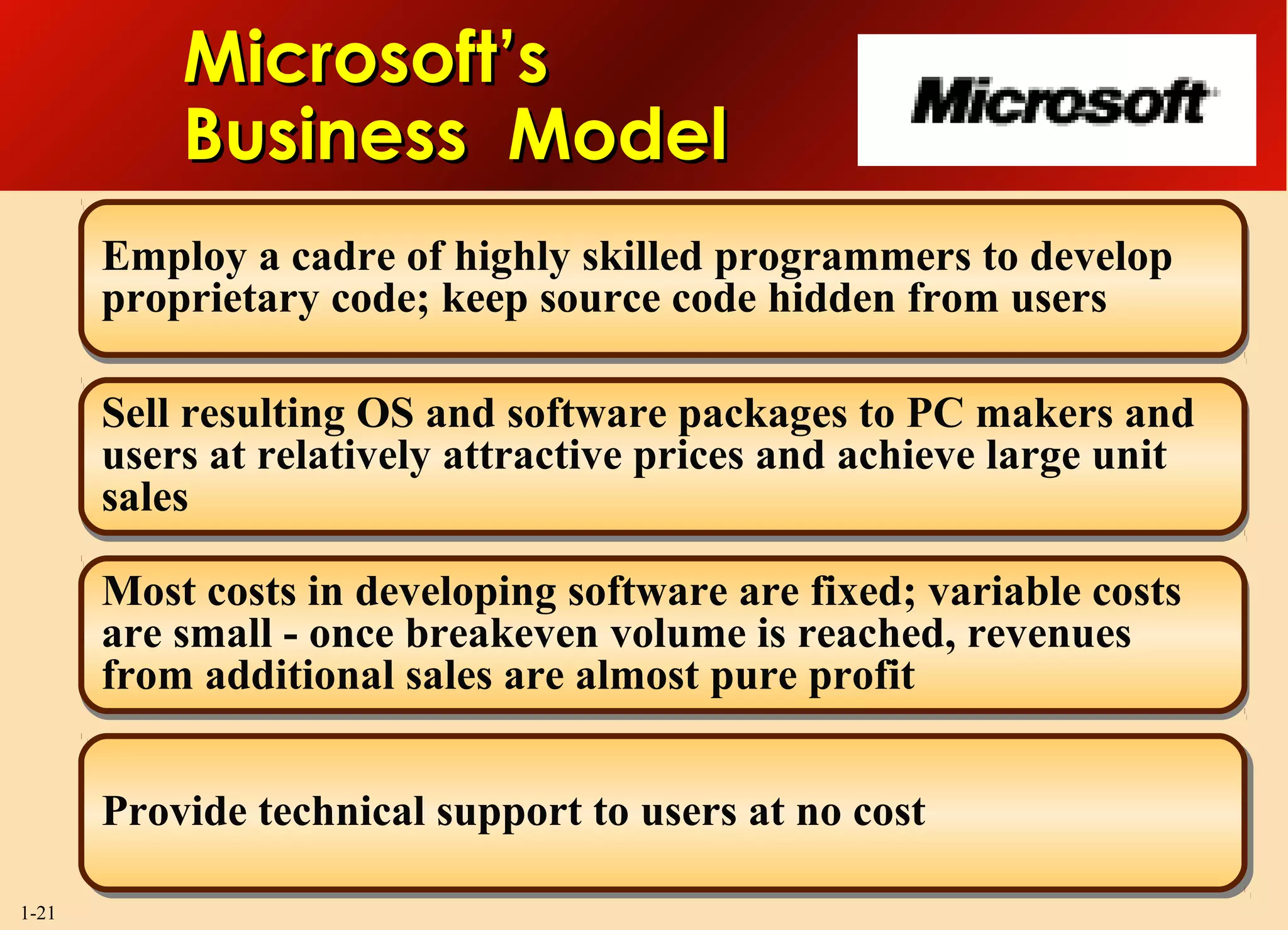
This document discusses the importance of strategy and provides an overview of key strategic concepts. It defines strategy as a company's "game plan" to attract customers, compete successfully, and achieve objectives. A good strategy fits the company's situation, provides competitive advantage, and boosts performance. Crafting and executing strategy are core management functions because they shape the company's direction and impact its long-term success.