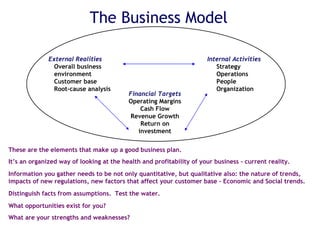
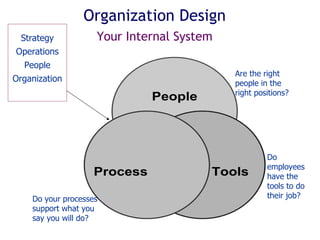
The document outlines a structured approach for business planning, emphasizing the importance of establishing a vision, mission, and strategic framework for success. It includes a SWOT analysis to identify organizational strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, and encourages the development of action goals to achieve the business's vision. Ultimately, the document underscores that effective planning directs organizational efforts and enhances performance.

![Jacqueline Collins, President Partnering for Performance 98 Temple Street, Abington, MA 02351 Phone: 781-982-8812 Email: [email_address] Website: www.pfpconsult.com Proprietary Statement Partnering for Performance All Rights Reserved. This document embodies information that is proprietary. It may not be copied or reproduced in whole or in part or used for other purposes without written permission.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01-jc-utilizingyourresources-110331075422-phpapp02/85/Utilizing-Your-Resources-by-Jacqueline-Collins-2-320.jpg)