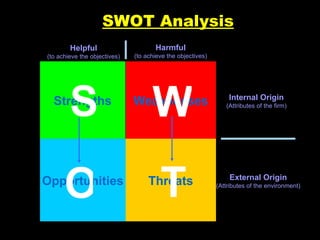
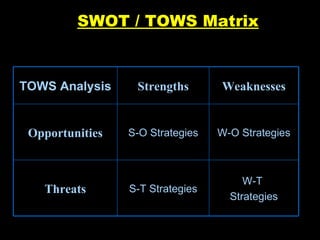
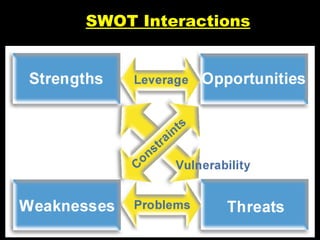
The document outlines the concept of SWOT analysis, which assesses internal strengths and weaknesses as well as external opportunities and threats for a business. It emphasizes the importance of this analysis in marketing management and strategy formulation to develop competitive advantages. Additionally, it provides guidelines on how to effectively conduct a SWOT analysis and avoid common pitfalls.














![Thanks, Kindly send me your comments on [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swotanalysisshow-12824097476665-phpapp01/85/SWOT-Analysis-18-320.jpg)