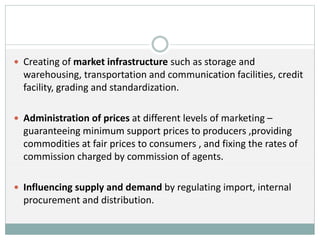
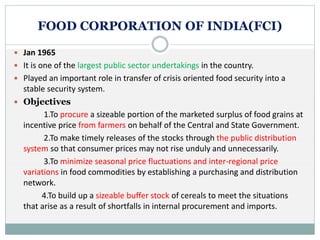
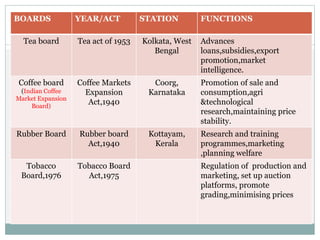
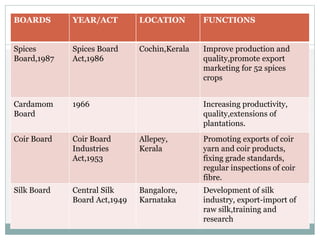
This document discusses various marketing institutions involved in agricultural development in India. It outlines the role of these institutions in framing rules and regulations, establishing organizations to provide services to farmers, promoting cooperatives, and creating market infrastructure. Some key public sector institutions discussed are the Food Corporation of India, Directorate of Marketing and Inspection, and Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices. Major cooperative sector institutions mentioned are the National Cooperative Development Corporation and National Agricultural Cooperative Marketing Federation. The document also provides details on specific institutions like the Tamil Nadu Co-op Milk Producers Federation and Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority.