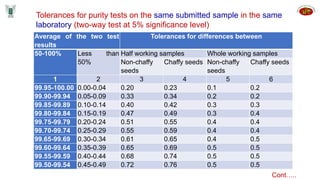
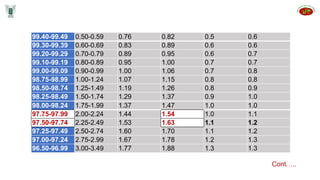
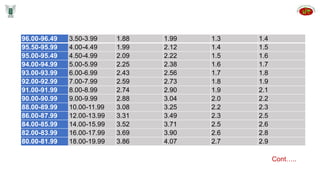
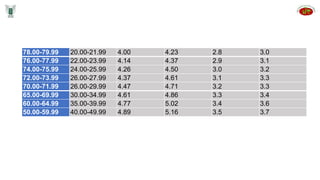
Seed inspectors are appointed by state governments to enforce seed quality control laws. They have various qualifications and duties including integrity, knowledge of seed standards, sampling procedures, and enforcement powers. Inspectors are responsible for drawing representative samples, sending them for analysis, investigating potential offenses, and taking actions like stop sale orders or seizures if standards are not met. They aim to educate industry and ensure compliance with laws to protect seed quality and the industry.