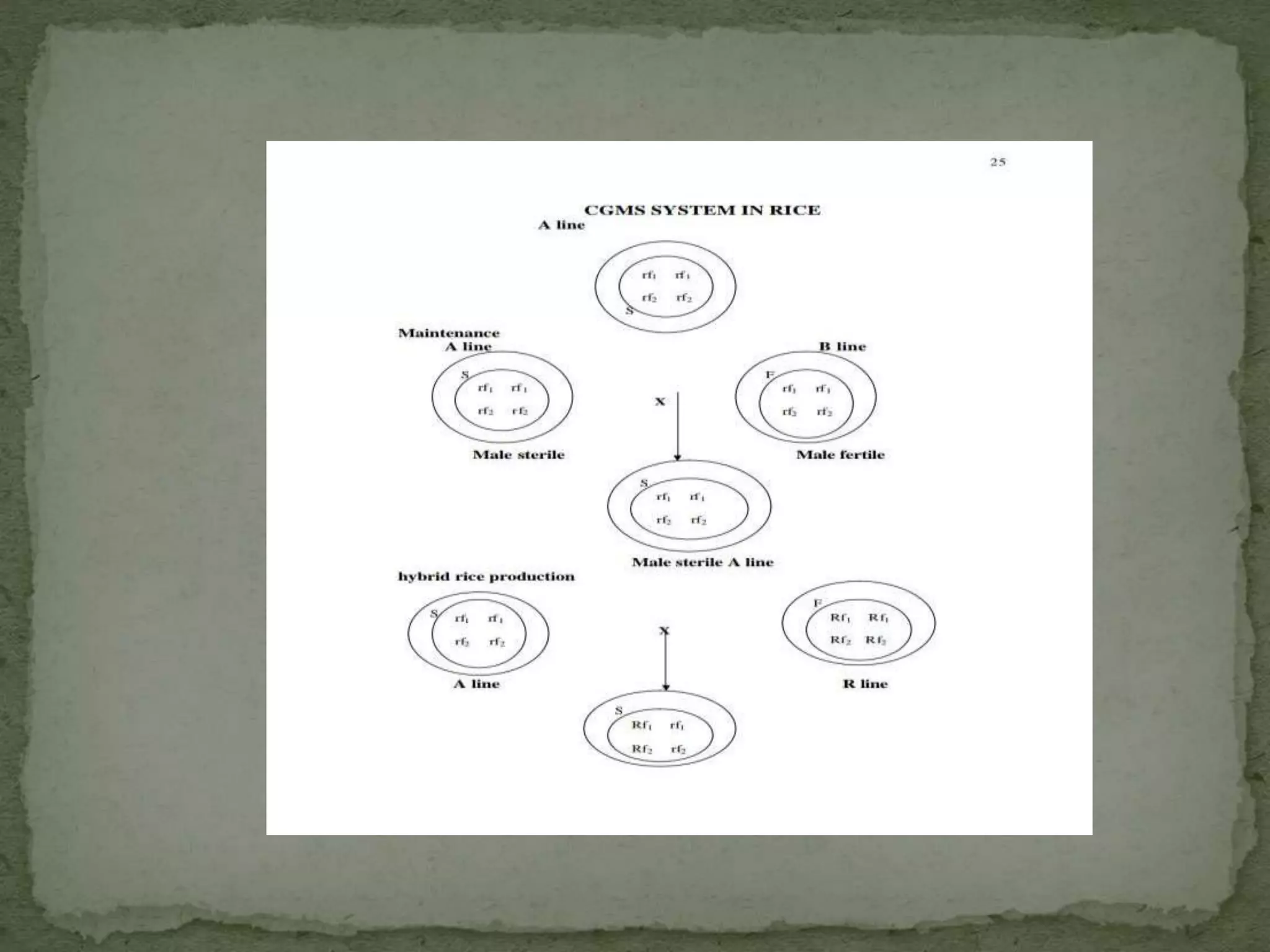
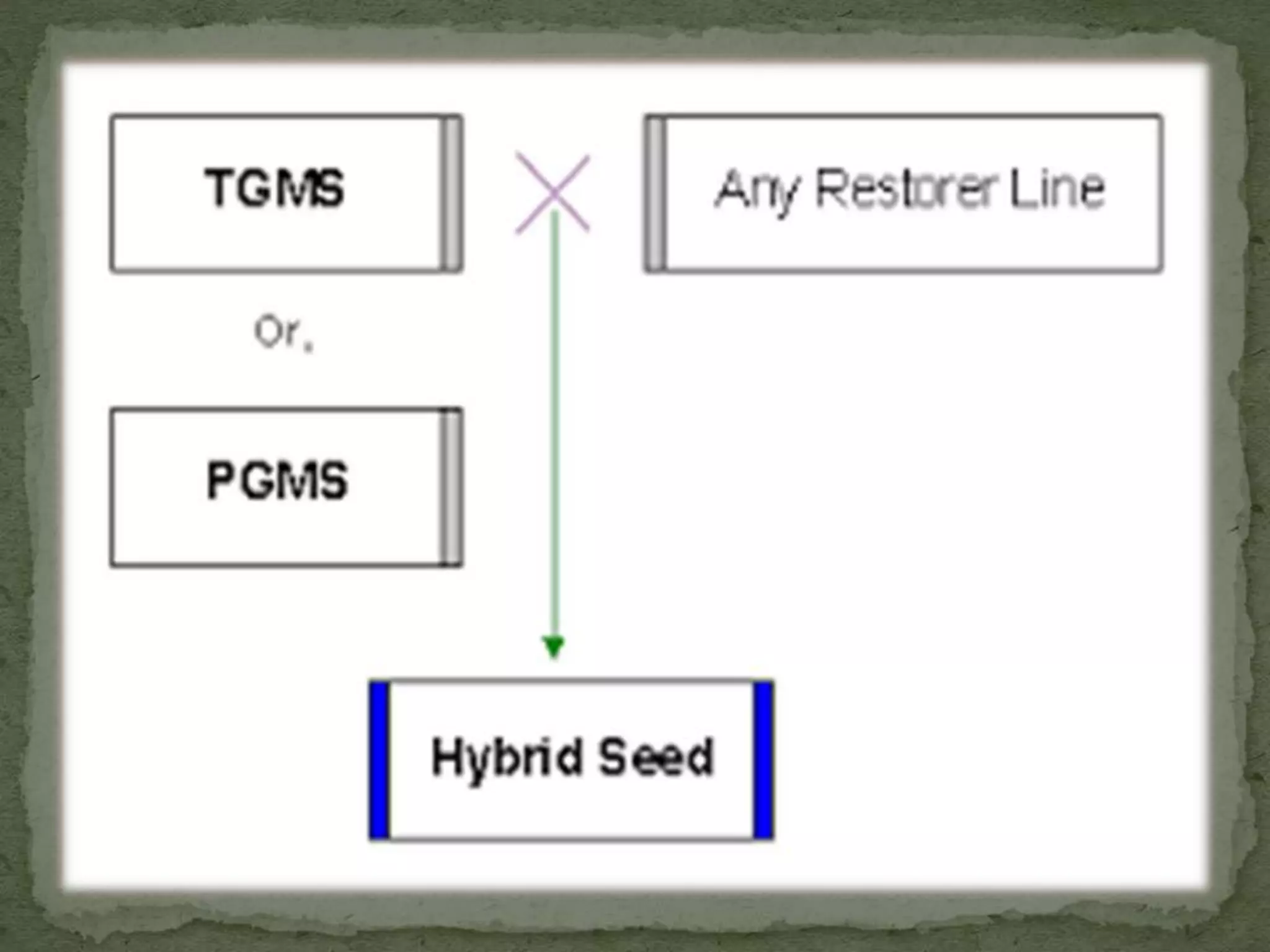
The document discusses hybrid rice production methods, primarily focusing on the CGMS system and the multiple approaches used for seed production, including the use of chemical emasculants. It highlights key practices for maintaining parental lines, planting ratios, field inspections, and techniques to improve cross-pollination. Additionally, it outlines cultural practices and precautions during harvesting and threshing to ensure high seed yield.