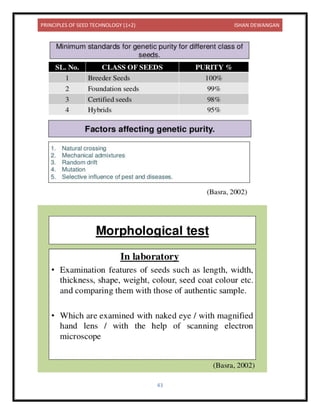
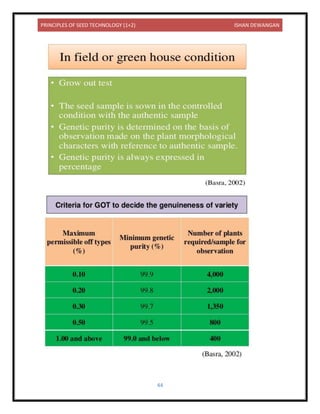
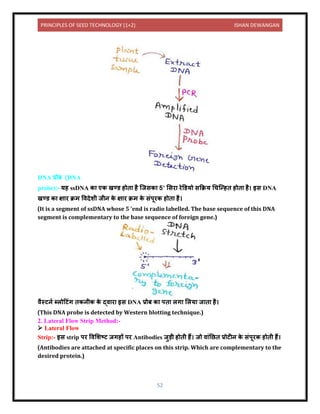
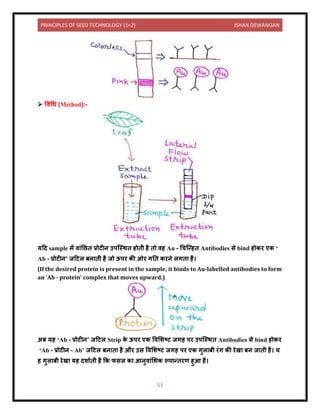
This document provides information on seed technology and seed production of various crops. It begins with definitions of seed and seed technology. It then discusses causes of variety deterioration and methods to control deterioration. Principles of foundation and certified seed production are outlined. Detailed information is provided on seed production methods for various crops including wheat, rice, maize, sorghum, bajra, potato, tomato, chilies, berseem and lucerne. Key steps discussed include source of seed, field selection, isolation distances, sowing methods, fertilizer use, irrigation, plant protection, rouging, and harvesting.














































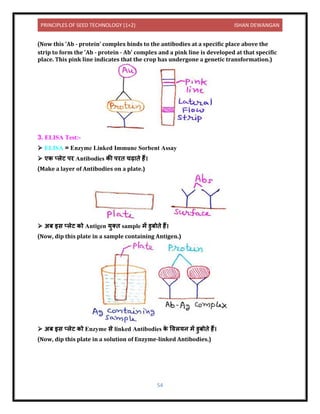
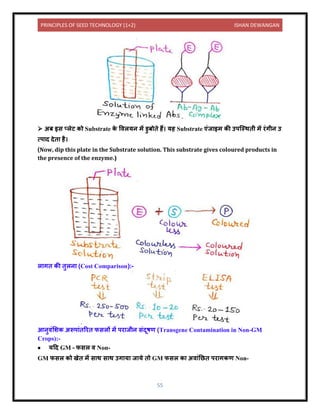

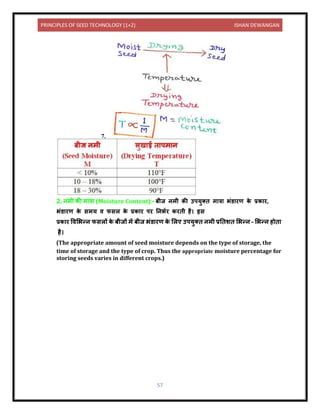
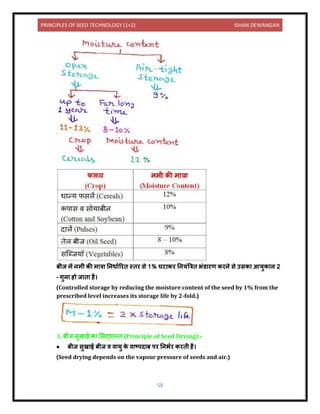


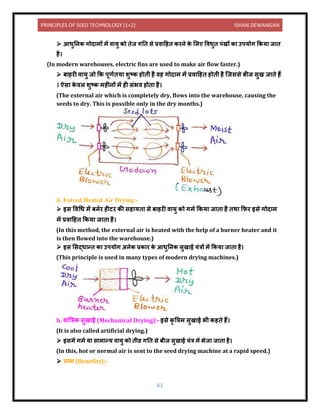
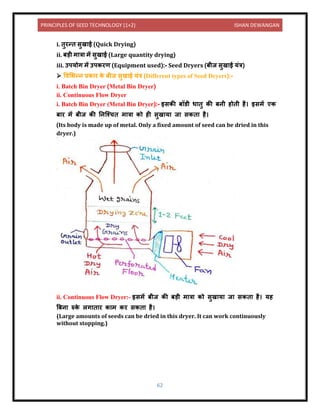
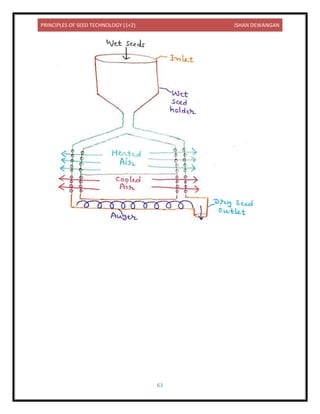



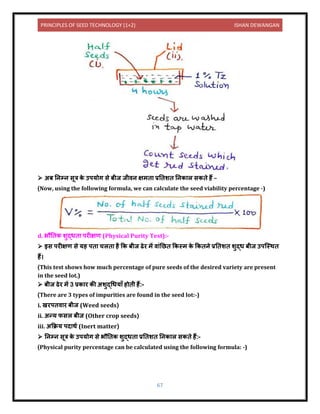



![PRINCIPLES OF SEED TECHNOLOGY (1+2) ISHAN DEWANGAN
73
iv. भंर् रण कीटों से सुरक्ष प्रि ि करि है।
(Provides protection from storage insects.)
v. मृि कीटों को नियंबत्रि करि है।
(Controls soil insects.)
2. प्रक र (Types):-
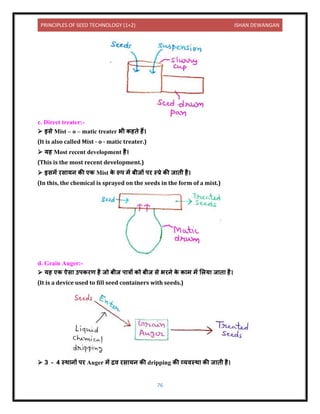
a. बीज कीट णुशोधि (Seed disinfection):- यह किकीय बीज णुओं क
े उन्मूलि को प्रिलशयि करि है
जो बीज चोल क
े भीिर य और अधधक गहरे क्स्थि ऊिकों स्थ वपि हो गए हैं। प्रभ िी नियंत्रण क
े
ललए, किकि शी उपच र को ि स्िि में उपक्स्थि किक को म रिे क
े ललए बीज क
े अंिर घुसि
च दहए।
(It refers to the eradication of fungal spores that have become established within the seed coat,
or in more deep-seated tissues. For effective control, the fungicidal treatment must actually
penetrate the seed in order to kill the fungus that is present.)
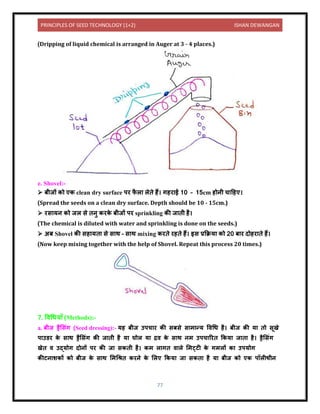
b. बीज ककट णुि शि (Seed disinfestation):- यह सिह जनिि सूक्ष्मजीिों क
े विि श को प्रिलशयि
करि है क्जन्होंिे बीज की सिह को संिूवषि ककय है परन्िु बीज की सिह को संक्रलमि िहीं ककय
है। रस यि में र्ुबोि , लभगोि , किकि शी क धूल, ग र य िरल क
े रूप में उपयोग सफल प य गय
है।
(It refers to the destruction of surface-borne organisms that have contaminated the seed
surface but not infected the seed surface. Chemical dips, soaks, fungicides applied as dust,
slurry or liquid have been found successful.)
c. बीज संरक्षण (Seed Protection):- बीज संरक्षण क उद्िेश्य मृि में उपक्स्थि सूक्ष्मजीिों से बीज
और िरुण अंक
ु र की सुरक्ष करि है, जो अन्यथ अंक
ु रण से पहले बीज क क्षय कर सकिे हैं।
(The purpose of seed protection is to protect the seed and young seedling from organisms in the
soil which might otherwise cause decay of the seed before germination.)
िोट
(Note):- कीटि शी य किकि शी से उपच ररि बीज म िि उपभोग क
े अयोग्य होिे हैं जबकक Protectan
ts (Malathion, Reldan) से उपच ररि बीज म िि उपभोग क
े योग्य होिे हैं।
[Seeds treated with insecticides or fungicides are unfit for human consumption while
seeds treated with Protectants (Malathion, Reldan) are fit for human consumption.]
3. पररक्स्थनिय ाँ क्जिमें बीज को उपच ररि करि च दहए (Conditions under which seed must be
treated):-
a. क्षनिग्रस्ि बीज (Injured Seeds):- एक बीज क
े बीज चोल में कोई भी क्षनि, किक को बीज में
प्रिेश करिे और उसे म रिे क उत्कृ टट अिसर िेि है, य उससे उत्पन्ि होिे ि ले अंक
ु र को जग
िेि है। बीज संयोजि और थ्रेलशंग ऑपरेशि क
े िौर ि य अत्यधधक ऊ
ं च ई से धगर ए ज िे क
े िौर ि
बीज को य ंबत्रक क्षनि होिी है। िे मौसम य अिुधचि भंर् रण से भी क्षनिग्रस्ि हो सकिे हैं।
(Any break in the seed coat of a seed affords an excellent opportunity for fungi to enter the
seed and either kill it, or awaken the seedling that will be produced from it. Seeds suffer
mechanical injury during combining and threshing operations, or from being dropped from
excessive heights. They may also be injured by weather or improper storage.)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cmpltnotes-230317071515-45cd9685/85/principles-of-seed-technology-5221-notes-73-320.jpg)