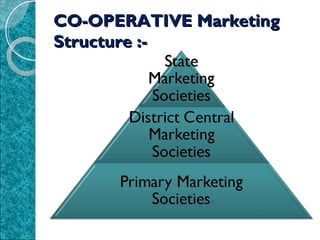
This document outlines the functions and structure of cooperative marketing in India. It discusses how cooperative marketing societies work at the national, state, district, and primary levels to market agricultural products. The societies grade, process, store and transport members' products to obtain the best prices while educating members on fair trading practices. Cooperative marketing also provides agricultural inputs, credit, and helps implement government price support policies.