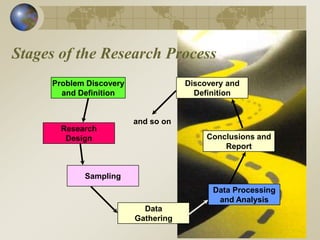
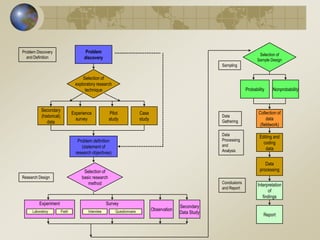
The document outlines the stages of the research process, including problem discovery, research design, sampling, data gathering, processing, analysis, and reporting. It emphasizes the significance of defining research problems and objectives, distinguishing between management decision problems and research problems, and formulating research questions and hypotheses. Examples are provided to illustrate how to compare demographic profiles and test statistical relationships.