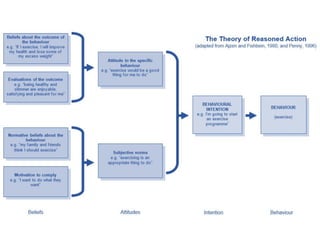
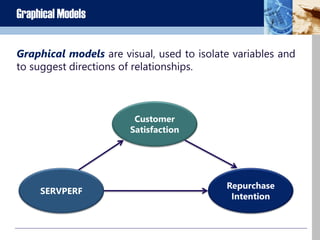
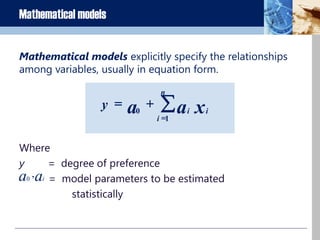
The document discusses business research methods. It defines business research as determining, analyzing, and disseminating relevant data and information to decision makers to maximize business performance. The primary purpose of research is to reduce risk in business decisions. There are two main categories of research: applied and basic/pure research. Good research has a clearly defined purpose, detailed process, thorough planning, high ethics, addresses limitations, adequate analysis, and conclusions justified by evidence. The scientific method and various types of models, including verbal, analytical, graphical and mathematical, are discussed as frameworks for business research.