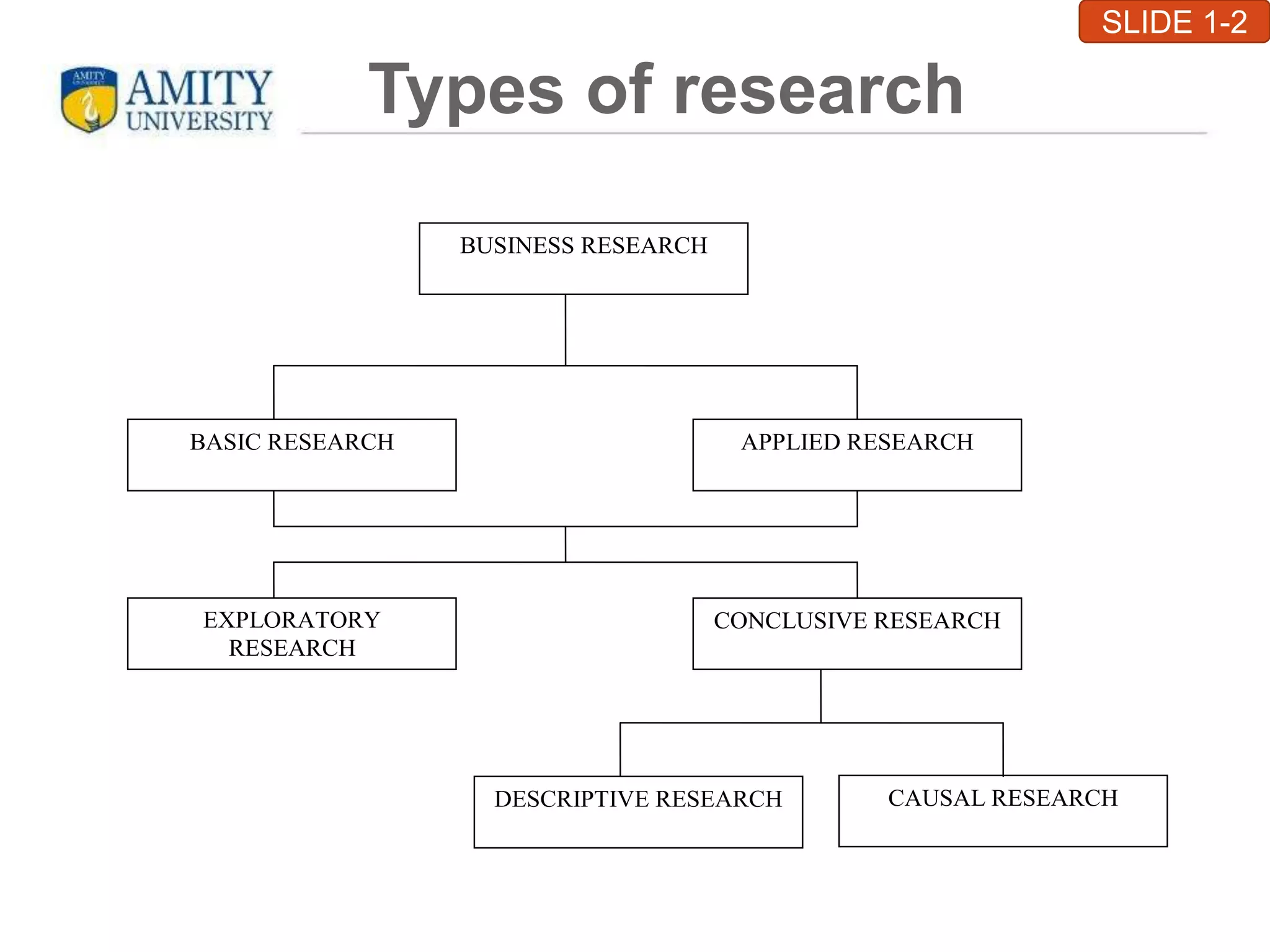
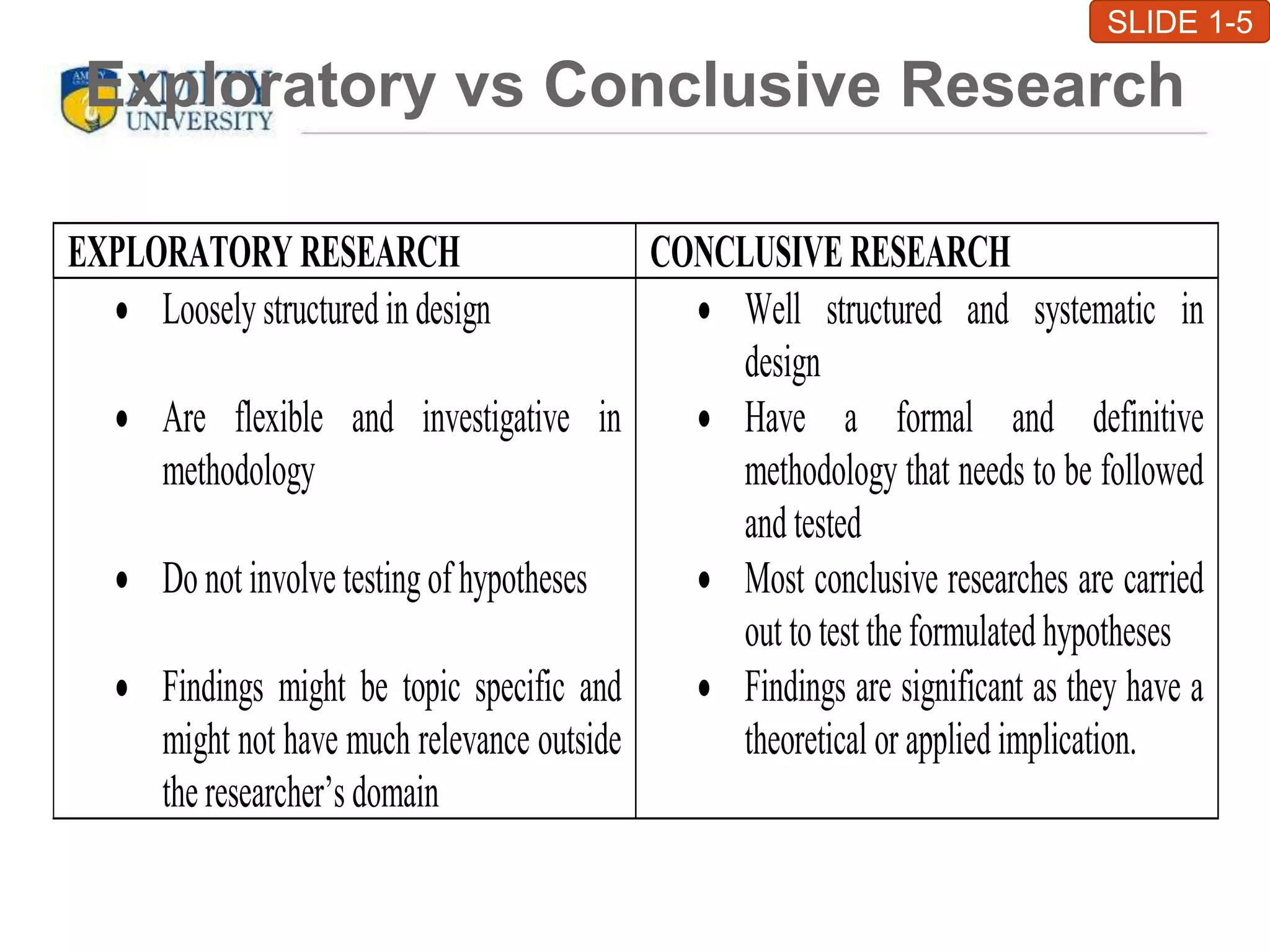
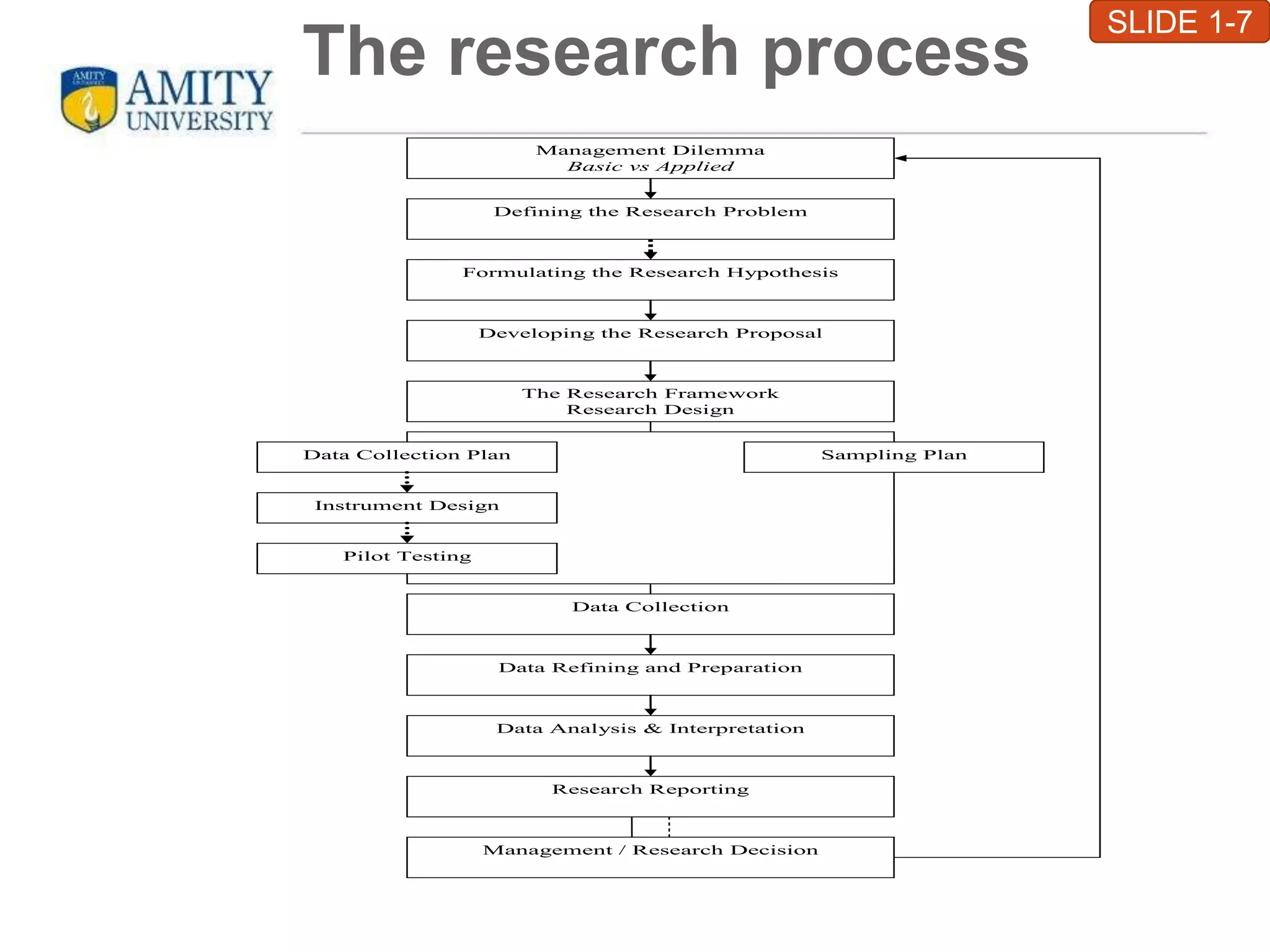
This chapter introduces business research and its various types. It defines research as a structured, sequential method to achieve business objectives by validating existing theories or developing new ones. The main types of research discussed are basic, applied, exploratory, conclusive, descriptive, and causal research. Exploratory research is loosely structured to provide direction, while conclusive research is well-structured and tests hypotheses. Descriptive research describes data characteristics, and causal research explores the effect of variables. The chapter outlines the research process and applications in various business areas like marketing, finance, human resources, and production management. It concludes with criteria for valid research like a clear purpose, sequential plan, justified methods, unbiased conduct, and reliability.