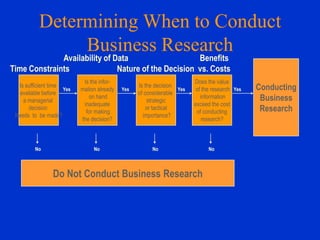
This document provides an overview of business research. It defines business research as the systematic process of generating objective information to aid decision making. Business research includes areas like marketing, operations, and motivational research. It must be objective and detached to facilitate managerial decisions. The two main types are basic research, which expands knowledge without solving specific problems, and applied research, which addresses real-life business problems. Factors considered in deciding whether to conduct research include time, data availability, resources, the nature of the decision, and the costs and benefits of the research. Major topics of business research are also outlined.