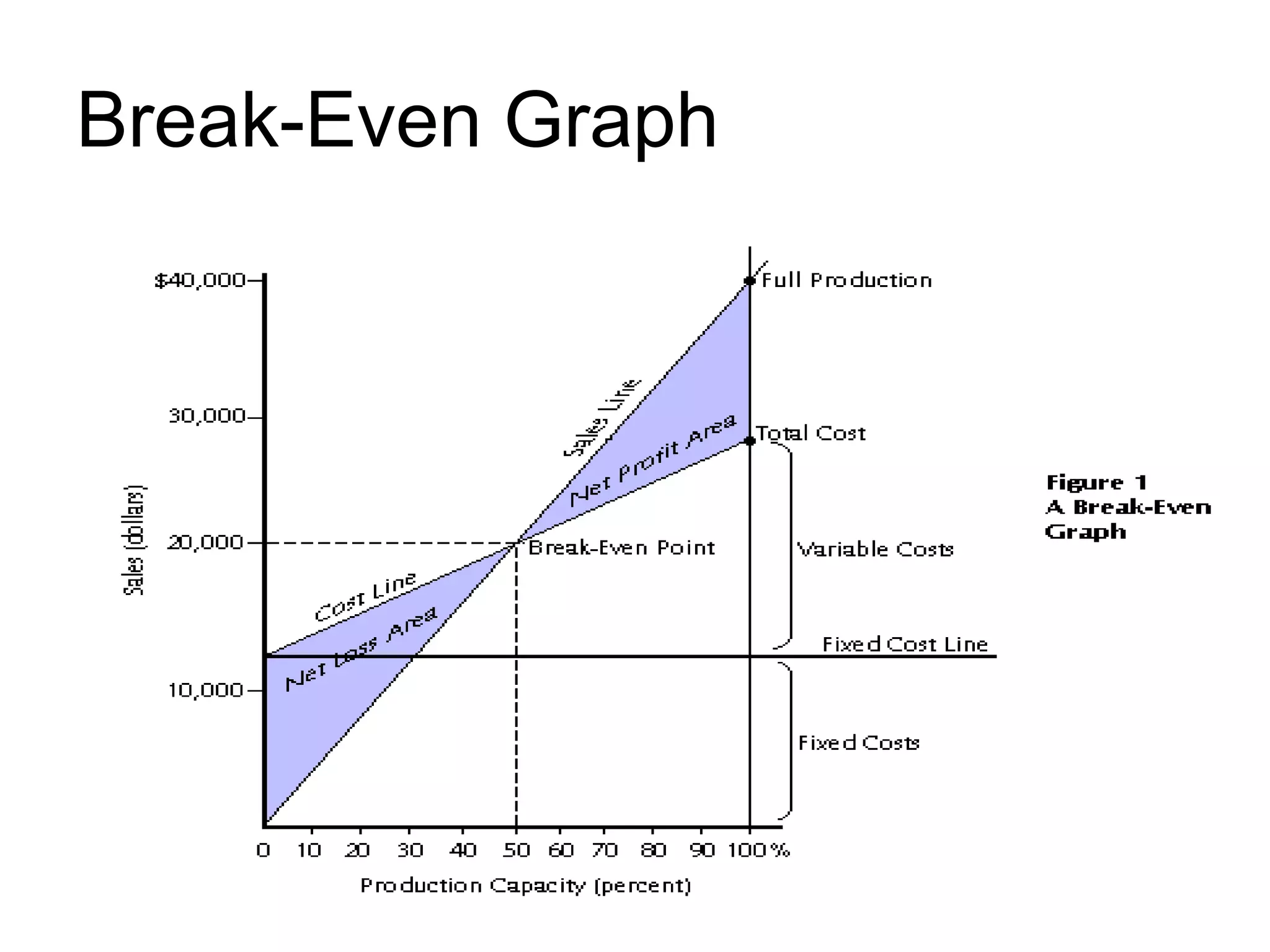
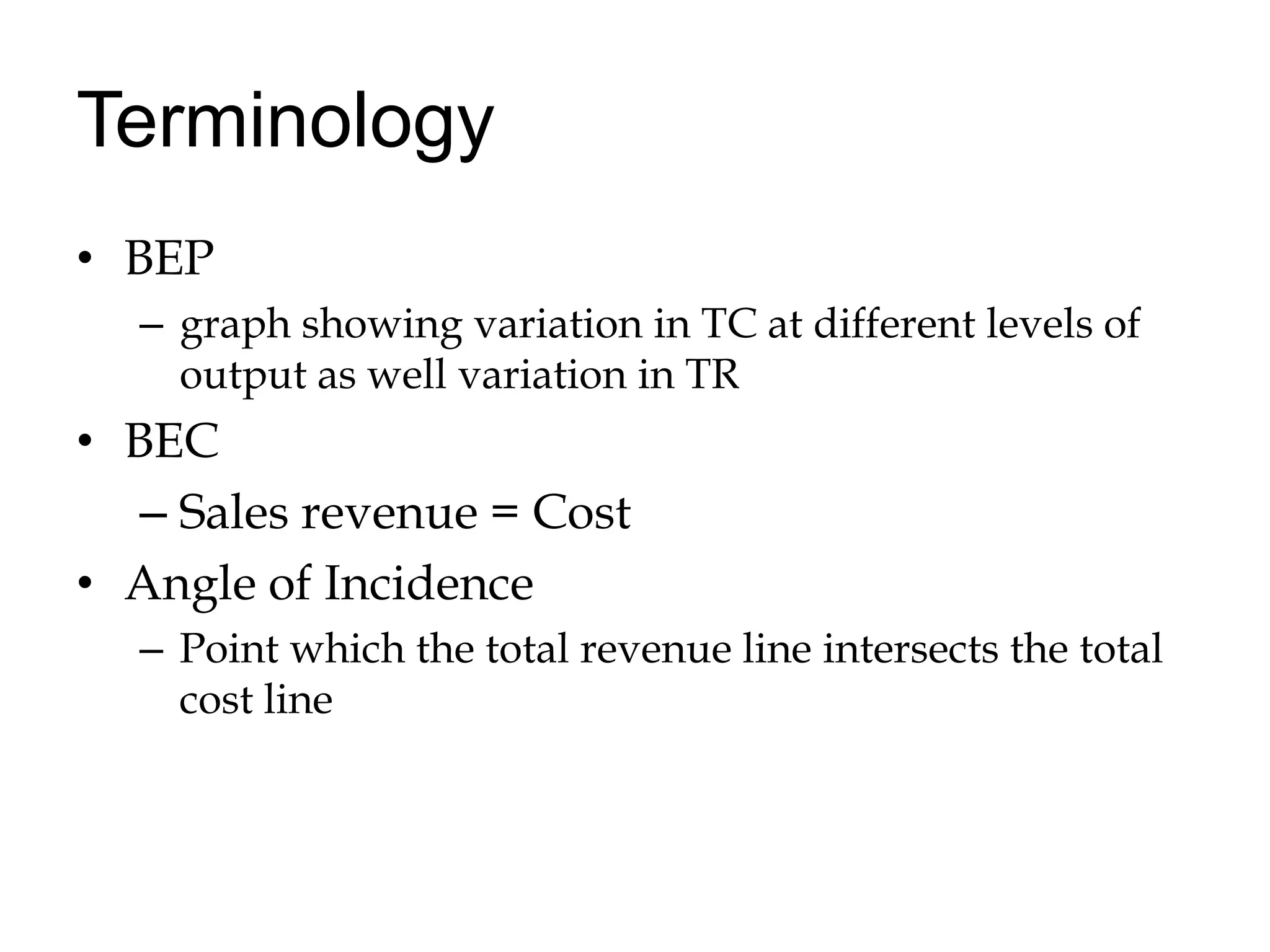
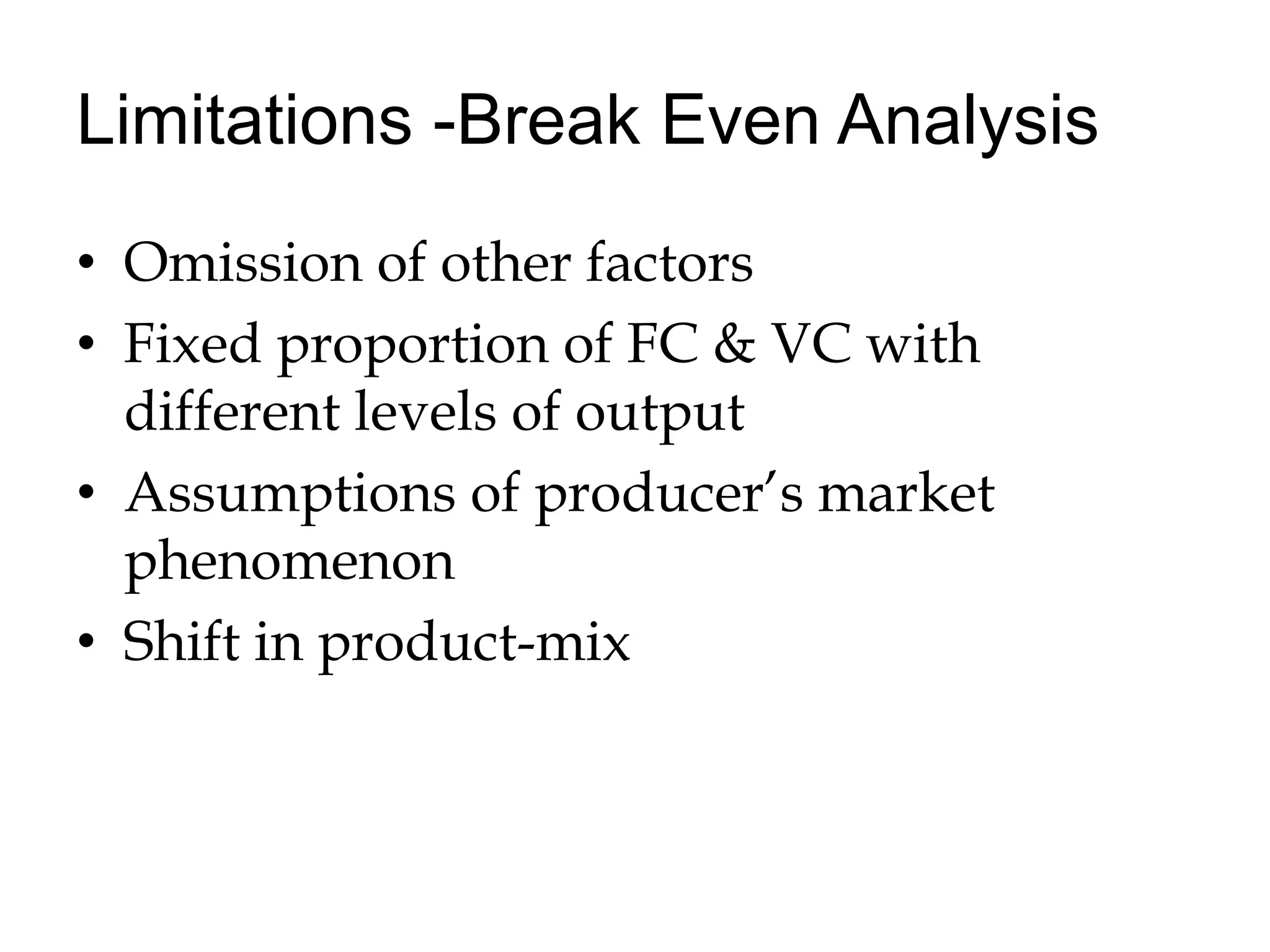
Break-even analysis determines the level of output where costs and revenues are equal. It makes assumptions like constant prices and linear cost relationships. The break-even point is where total revenue equals total cost. The margin of safety is the difference between actual/budgeted sales and break-even sales. The profit-volume ratio measures contribution and is used to determine the most profitable areas. Break-even analysis can be shown graphically and is used for profit and cost analysis, determining the break-even point, and setting production levels.