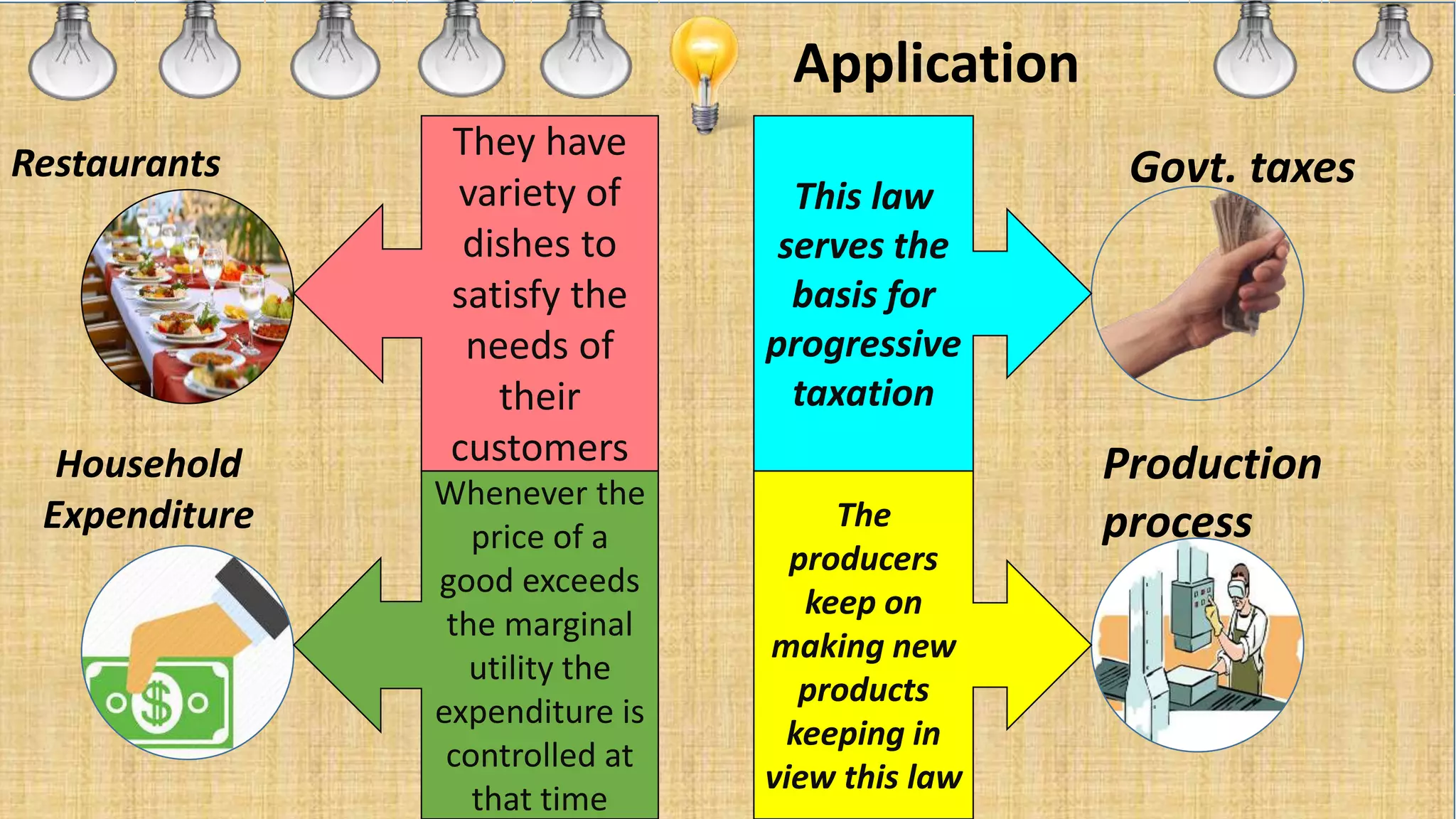
This document discusses the law of diminishing marginal utility. It defines the law as stating that as a consumer consumes more of a commodity, the satisfaction derived from each additional unit decreases. The law is based on assumptions like consumption being continuous and utility being measurable. It is explained using an example where a person's utility from hamburgers decreases from 10 to 0 over 6 units. Diagrams are used to represent it. Applications include production, taxation, and household expenditure. Exceptions include rare collections, money, and liquor consumption where utility may not diminish. The conclusion restates that the law forms the basis of other economic principles.