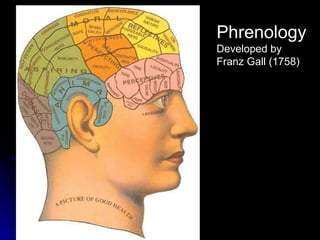
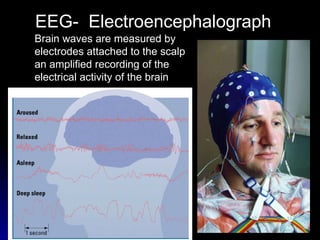
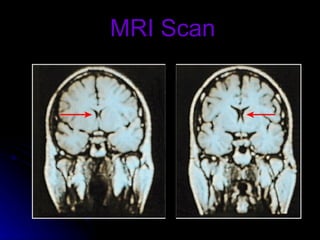
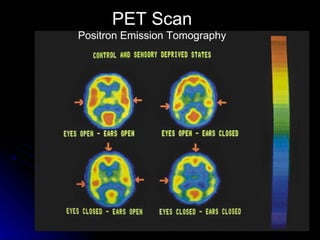
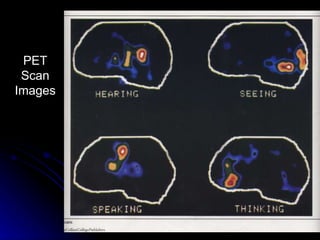
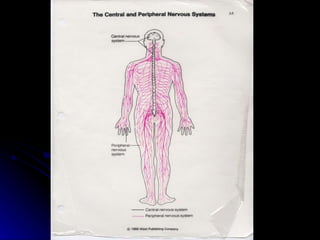
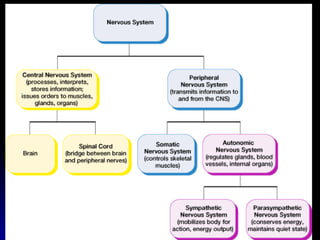
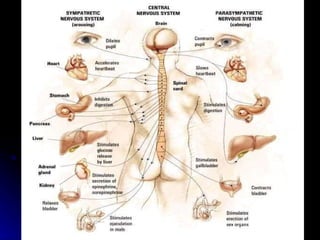
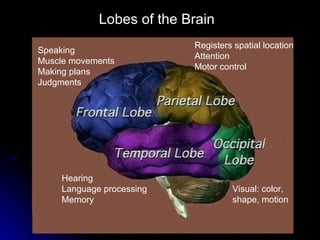
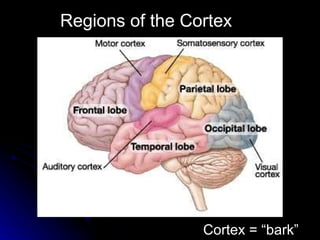
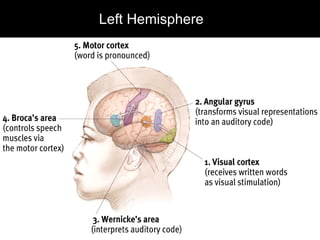
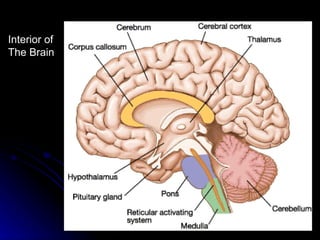
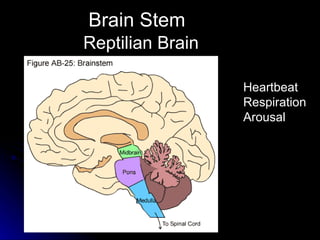
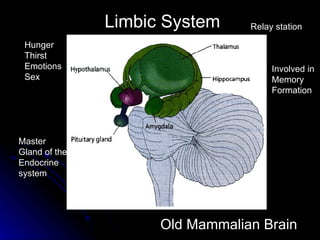
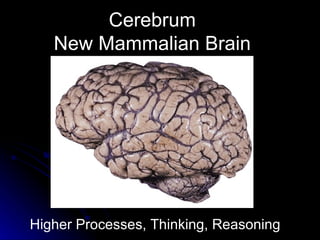
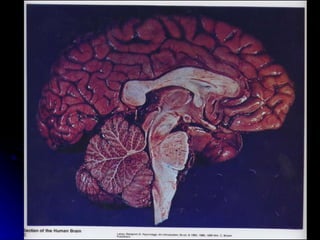
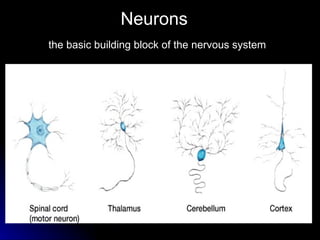
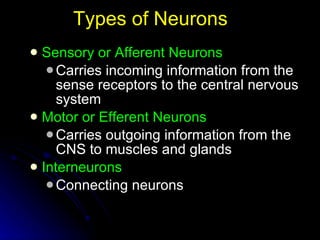
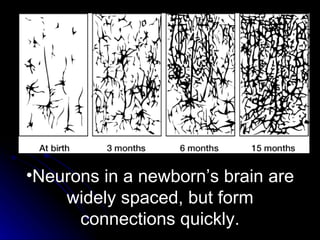
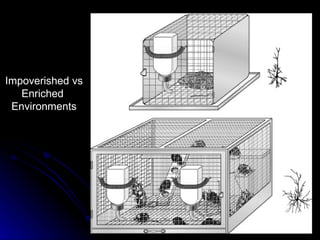
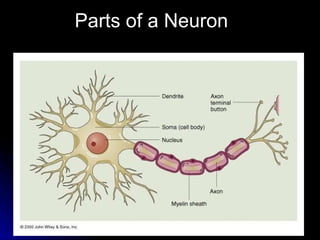
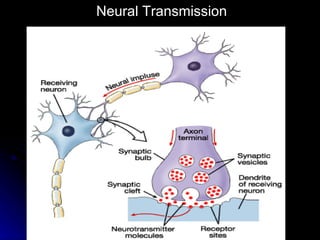
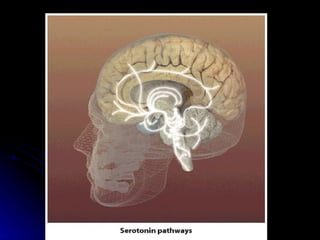
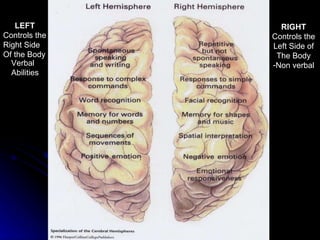
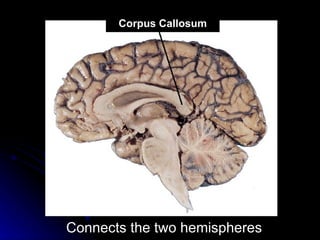
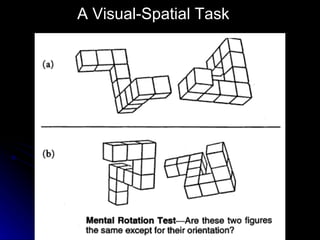
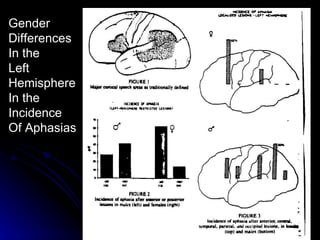
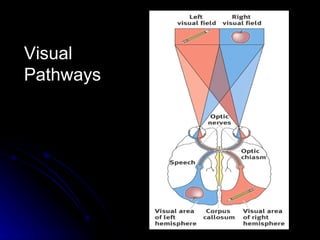
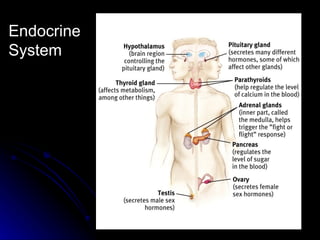
The document discusses the structure and function of the nervous system. It describes key parts of the brain including the lobes, cortex, and interior structures like the brain stem, limbic system, and cerebrum. It also discusses neurons, the basic unit of the nervous system, and how they transmit signals via neurotransmitters and electrical impulses. Imaging techniques like EEG, MRI, and PET scans are used to study the living brain.