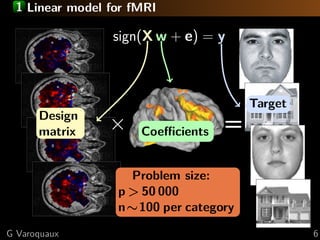
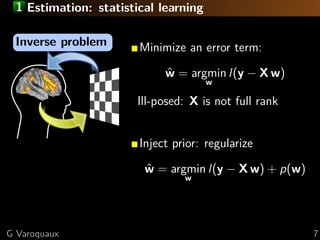
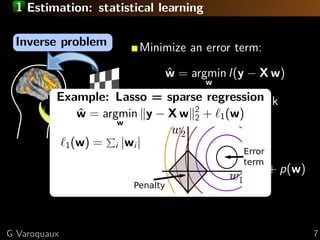
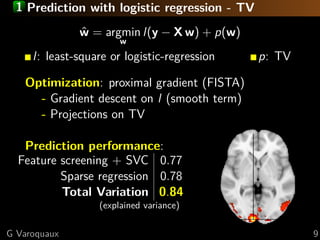
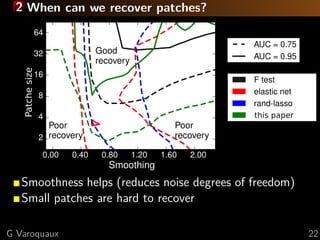
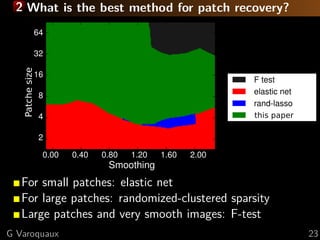
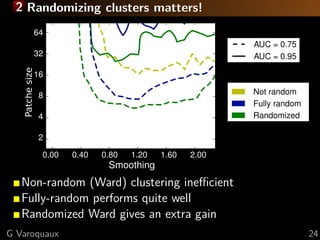
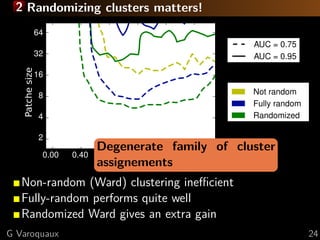
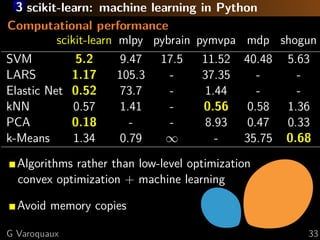
This document discusses techniques for predictive modeling of brain imaging data using statistical learning methods. It presents an approach that combines sparse recovery, randomized clustering, and total variation regularization to predict stimuli from fMRI data with over 50,000 voxels and around 100 samples. The key steps are clustering spatially correlated voxels, running sparse models on the reduced feature set, and accumulating selected features over multiple runs. Simulations show this approach outperforms other methods at recovering brain patches. The document also discusses disseminating research through open source Python libraries like scikit-learn, which has helped popularize machine learning techniques.

![1 Brain reading
Predicting the object category viewed
[Haxby 2001, Distributed and Overlapping
Representations of Faces and Objects in Ventral
Temporal Cortex ]
Supervised learning task
G Varoquaux 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-121201102552-phpapp02/85/Brain-reading-compressive-sensing-fMRI-and-statistical-learning-in-Python-6-320.jpg)
![1 Brain reading
Predicting the object category viewed
[Haxby 2001, Distributed and Overlapping
Representations of Faces and Objects in Ventral
Temporal Cortex ]combinations of voxels to
Find
predict the stimuli
Supervised learning task
Multi-variate statistics
G Varoquaux 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-121201102552-phpapp02/85/Brain-reading-compressive-sensing-fMRI-and-statistical-learning-in-Python-7-320.jpg)
![1 TV-penalization to promote regions
[Haxby 2001]
Neuroscientists think in
terms of brain regions
Total-variation penalization
Impose sparsity on the gradient
of the image:
p(w) = 1( w)
[Michel TMI 2011]
G Varoquaux 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-121201102552-phpapp02/85/Brain-reading-compressive-sensing-fMRI-and-statistical-learning-in-Python-11-320.jpg)
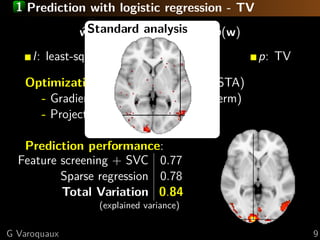
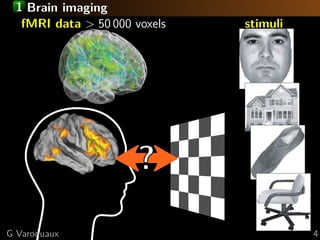
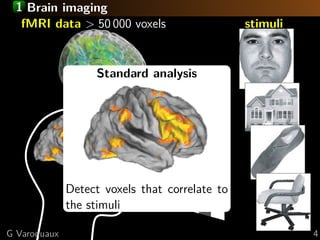
![1 Standard analysis or predictive modeling?
Predicting the object category viewed
[Haxby 2001, Distributed and Overlapping
Representations of Faces and Objects in Ventral
Temporal Cortex ]
Take home message:
brain regions, not prediction
G Varoquaux 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-121201102552-phpapp02/85/Brain-reading-compressive-sensing-fMRI-and-statistical-learning-in-Python-14-320.jpg)
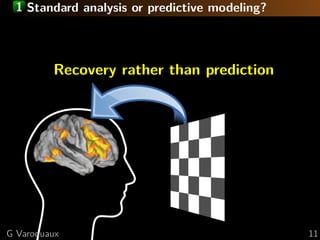
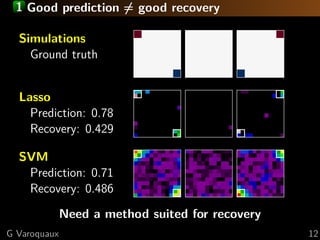
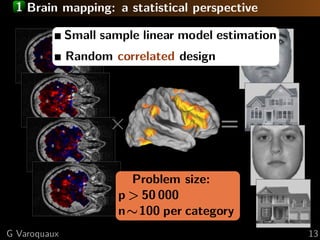
![1 Brain mapping: a statistical perspective
Small sample linear model estimation
Random correlated design
Estimation strategy
Standard approach: univariate statistics
×
Multiple comparisons problem
⇒ statistical power ∝ 1/p
=
We want sub-linear sample complexity
⇒ non-rotationally-invariant estimators
e.g. 1 penalization
[ Ng, 2004 Feature selection, 1 vs. 2 regularization,
and rotational invariance ]
G Varoquaux 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-121201102552-phpapp02/85/Brain-reading-compressive-sensing-fMRI-and-statistical-learning-in-Python-18-320.jpg)
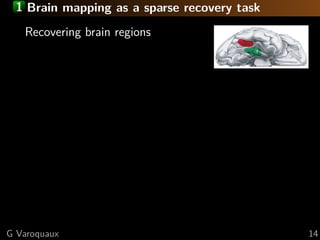
![1 Brain mapping as a sparse recovery task
Recovering k non-zero coefficients
nmin ∼ 2 k log p
Restricted-isometry-like property:
The design matrix is well-conditioned [Candes 2006]
on sub-matrices of size > k [Tropp 2004]
[Wainwright 2009]
Mutual incoherence:
Relevant features S and irrelevant
ones S are not too correlated
Violated by spatial
correlations in our design
lasso: 23 non-zeros
G Varoquaux 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-121201102552-phpapp02/85/Brain-reading-compressive-sensing-fMRI-and-statistical-learning-in-Python-20-320.jpg)
![1 Randomized sparsity
[Meinshausen and Buhlmann 2010, Bach 2008]
Perturb the design matrix:
Subsample the data
Randomly rescale features
+ Run sparse estimator
Keep features that are often selected
⇒ Good recovery without mutual incoherence
But RIP-like condition
Cannot recover large
correlated groups
For m correlated features,
selection frequency divided by m
G Varoquaux 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-121201102552-phpapp02/85/Brain-reading-compressive-sensing-fMRI-and-statistical-learning-in-Python-21-320.jpg)

![2 Sparse recovery with
correlated designs
Combining
Clustering
Sparsity
[Varoquaux ICML 2012]
G Varoquaux 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-121201102552-phpapp02/85/Brain-reading-compressive-sensing-fMRI-and-statistical-learning-in-Python-23-320.jpg)
![2 Brain parcellations
Spatially-connected hierarchical clustering
⇒ reduces voxel numbers [Michel Pat Rec 2011]
Replace features by corresponding cluster average
+ Use a supervised learner on reduced problem
Cluster choice sub-optimal for regression
G Varoquaux 17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-121201102552-phpapp02/85/Brain-reading-compressive-sensing-fMRI-and-statistical-learning-in-Python-24-320.jpg)

![2 fMRI: face vs house discrimination [Haxby 2001]
F-scores
L R
L R
y=-31 x=17
z=-17
G Varoquaux 25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-121201102552-phpapp02/85/Brain-reading-compressive-sensing-fMRI-and-statistical-learning-in-Python-33-320.jpg)
![2 fMRI: face vs house discrimination [Haxby 2001]
1 Logistic
L R
L R
y=-31 x=17
z=-17
G Varoquaux 25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-121201102552-phpapp02/85/Brain-reading-compressive-sensing-fMRI-and-statistical-learning-in-Python-34-320.jpg)
![2 fMRI: face vs house discrimination [Haxby 2001]
Randomized 1 Logistic
L R
L R
y=-31 x=17
z=-17
G Varoquaux 25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-121201102552-phpapp02/85/Brain-reading-compressive-sensing-fMRI-and-statistical-learning-in-Python-35-320.jpg)
![2 fMRI: face vs house discrimination [Haxby 2001]
Randomized Clustered 1 Logistic
L R
L R
y=-31 x=17
z=-17
G Varoquaux 25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-121201102552-phpapp02/85/Brain-reading-compressive-sensing-fMRI-and-statistical-learning-in-Python-36-320.jpg)
![2 fMRI: face vs house discrimination [Haxby 2001]
F-scores
L R
L R
y=-31 x=17
z=-17
G Varoquaux 25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-121201102552-phpapp02/85/Brain-reading-compressive-sensing-fMRI-and-statistical-learning-in-Python-37-320.jpg)
![2 Predictive model on selected features
Object recognition [Haxby 2001]
Using recovered features improves prediction
G Varoquaux 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-121201102552-phpapp02/85/Brain-reading-compressive-sensing-fMRI-and-statistical-learning-in-Python-38-320.jpg)





![Bibliography
[Michel TMI 2011] V. Michel, et al., Total variation regularization for
fMRI-based prediction of behaviour, IEEE Transactions in medical
imaging (2011)
http://hal.inria.fr/inria-00563468/en
[Varoquaux ICML 2012] G. Varoquaux, A. Gramfort, B. Thirion
Small-sample brain mapping: sparse recovery on spatially correlated
designs with randomization and clustering, ICML (2012)
http://hal.inria.fr/hal-00705192/en
[Michel Pat Rec 2011] V. Michel, et al., A supervised clustering approach
for fMRI-based inference of brain states, Pattern Recognition (2011)
http://hal.inria.fr/inria-00589201/en
[Pedregosa ICML 2011] F. Pedregosa, el al., Scikit-learn: machine
learning in Python, JMRL (2011)
http://hal.inria.fr/hal-00650905/en
G Varoquaux 37](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-121201102552-phpapp02/85/Brain-reading-compressive-sensing-fMRI-and-statistical-learning-in-Python-50-320.jpg)