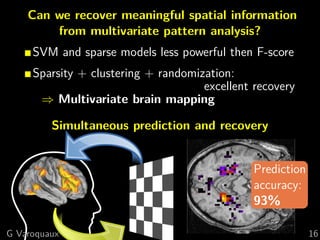
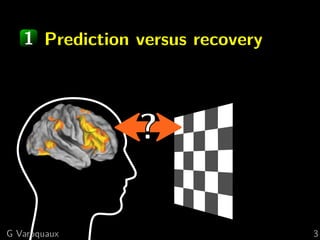
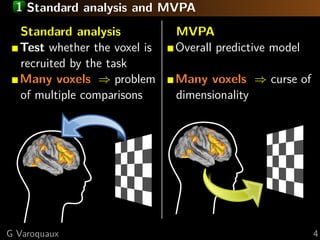
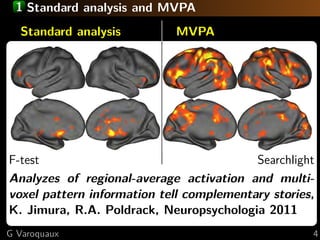
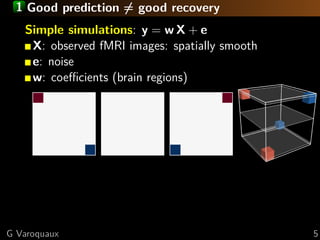
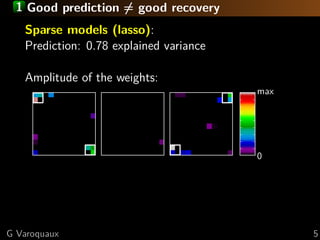
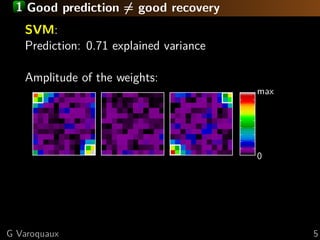
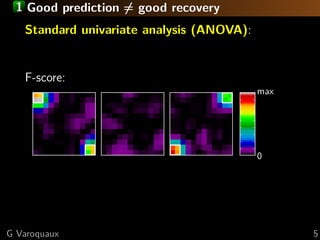
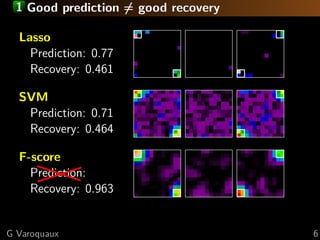
The document discusses the potential of recovering meaningful spatial information using multivariate pattern analysis (MVPA) techniques in fMRI studies. It compares various methods, including sparse models and standard univariate analysis, to highlight the effectiveness of combining clustering and randomization for feature recovery. The findings suggest that with appropriate modeling, high prediction accuracy can be achieved in brain mapping tasks.



![1 Sparse models
Compressive sensing:
detection of k signals out of p (voxels)
with only n observations ∝ k
Iterpretable
Selects random subsets in correlated signals
Face vs house
discrimination
Data from [Haxby 2001]
G Varoquaux 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-120611112403-phpapp01/85/Can-we-recover-meaning-full-spatial-information-from-multivariate-pattern-analysis-15-320.jpg)
![1 Sparse models
Compressive sensing:
detection of k signals out of p (voxels)
with only n observations ∝ k
Iterpretable
Selects random subsets in correlated signals
Stability selection:
Face vsrandom perturbations to the data
Apply house
discrimination that are selected often
Keep voxels
Data from [Haxby 2001] [Meinhausen 2010]
G Varoquaux 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-120611112403-phpapp01/85/Can-we-recover-meaning-full-spatial-information-from-multivariate-pattern-analysis-16-320.jpg)
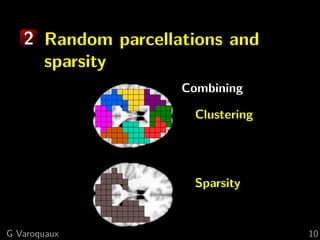
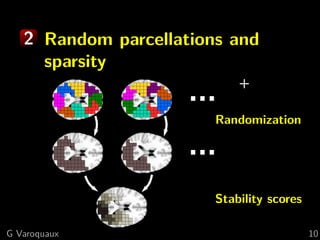
![1 Spatial models
Brain parcellations:
Ward clustering to reduce voxel numbers
Supervised clustering [Michel 2011]
... ... ...
... ...
Clustering blind to experimental conditions
G Varoquaux 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-120611112403-phpapp01/85/Can-we-recover-meaning-full-spatial-information-from-multivariate-pattern-analysis-17-320.jpg)
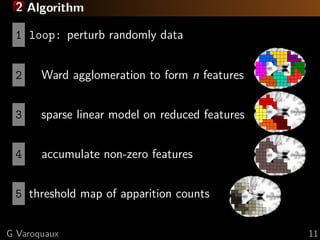
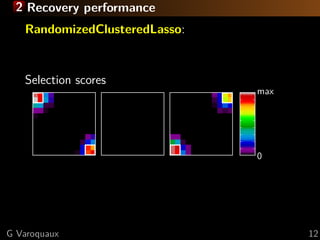
![2 What is the best method for feature recovery?
For small brain regions: elastic net
For large brain regions: randomized-clustered sparsity
Large regions and very smooth images: F-tests
[Varoquaux 2012] ICML
G Varoquaux 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-120611112403-phpapp01/85/Can-we-recover-meaning-full-spatial-information-from-multivariate-pattern-analysis-22-320.jpg)
![2 fMRI: face vs house discrimination [Haxby 2001]
F-scores
L R
L R
y=-31 x=17
z=-17
G Varoquaux 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-120611112403-phpapp01/85/Can-we-recover-meaning-full-spatial-information-from-multivariate-pattern-analysis-23-320.jpg)
![2 fMRI: face vs house discrimination [Haxby 2001]
Randomized Clustered Sparsity
L R
L R
y=-31 x=17
z=-17
Less background noise
(source of false positive)
G Varoquaux 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-120611112403-phpapp01/85/Can-we-recover-meaning-full-spatial-information-from-multivariate-pattern-analysis-24-320.jpg)
![2 Predictive power of selected voxels
Object recognition [Haxby 2001]
Using recovered voxels improves prediction
G Varoquaux 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-120611112403-phpapp01/85/Can-we-recover-meaning-full-spatial-information-from-multivariate-pattern-analysis-25-320.jpg)