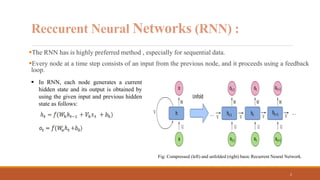
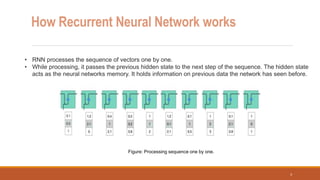
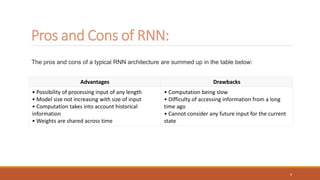
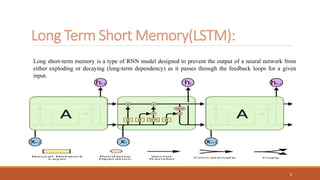
Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) are useful for processing sequential data like text or time series. RNNs have shortcomings like vanishing gradients when processing long sequences. Long short-term memory (LSTM) networks address this by using forget, input, and output gates to regulate the flow of information through the network. The forget gate determines what old information to discard, the input gate determines what new information to add to the cell state, and the output gate determines what information from the cell state to output as the hidden state. LSTMs are widely used for applications involving sequential data like machine translation, speech recognition, and text generation.









![Input Gate
• The goal of this gate is to determine what new
information should be added to the networks
long-term memory (cell state), given the
previous hidden state and new input data.
• The input gate is a sigmoid activated network
which acts as a filter, identifying which
components of the ‘new memory vector’ are
worth retaining. This network will output a vector
of values in [0,1].
• It is also passed the hidden state and current
input into the tanh function to squish values
between -1 and 1 to help regulate the network.
Cont…
Figure: Input Gate.
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rnn-lstm-230705151553-8ba61622/85/RNN-LSTM-pptx-14-320.jpg)




