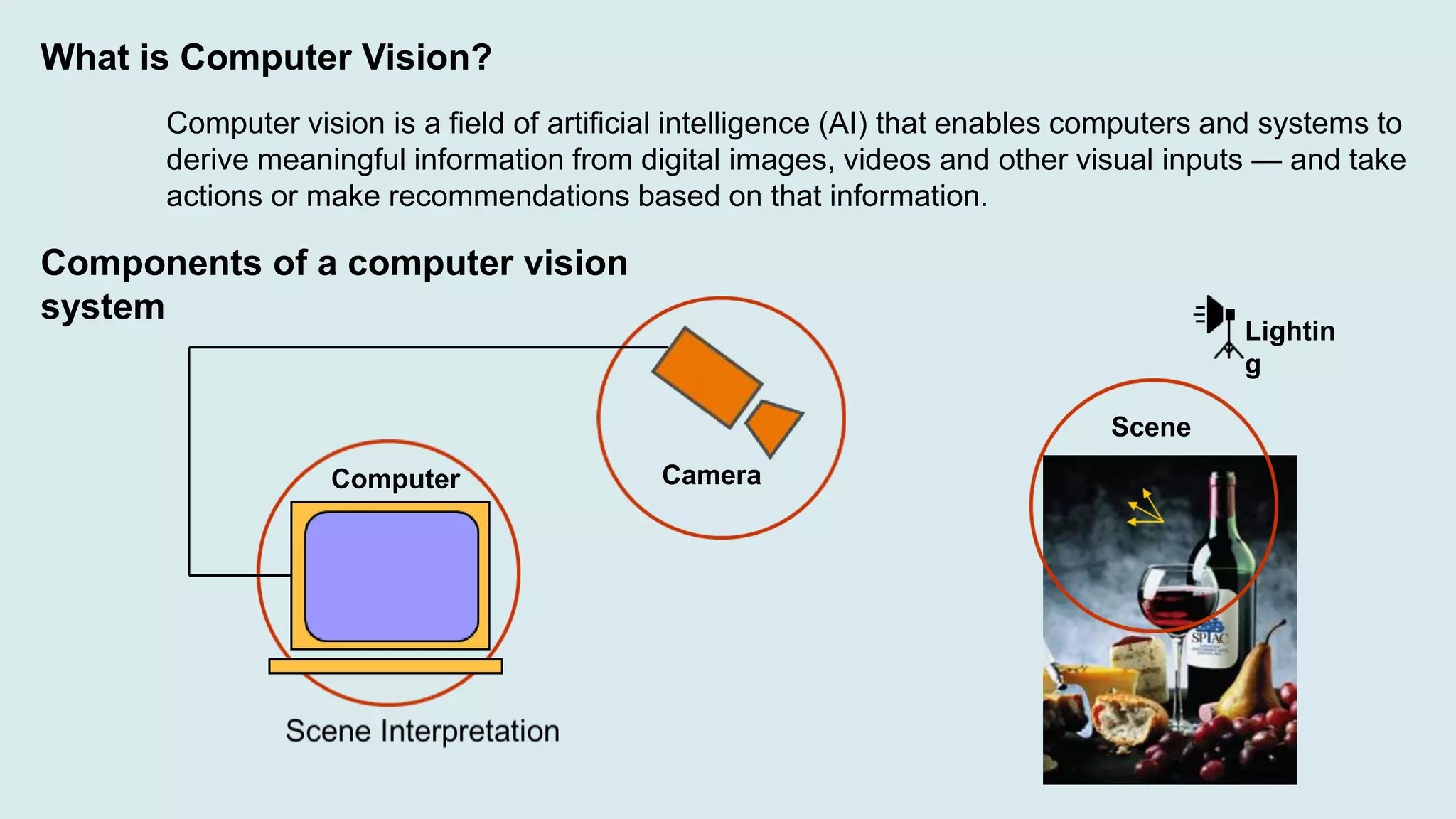
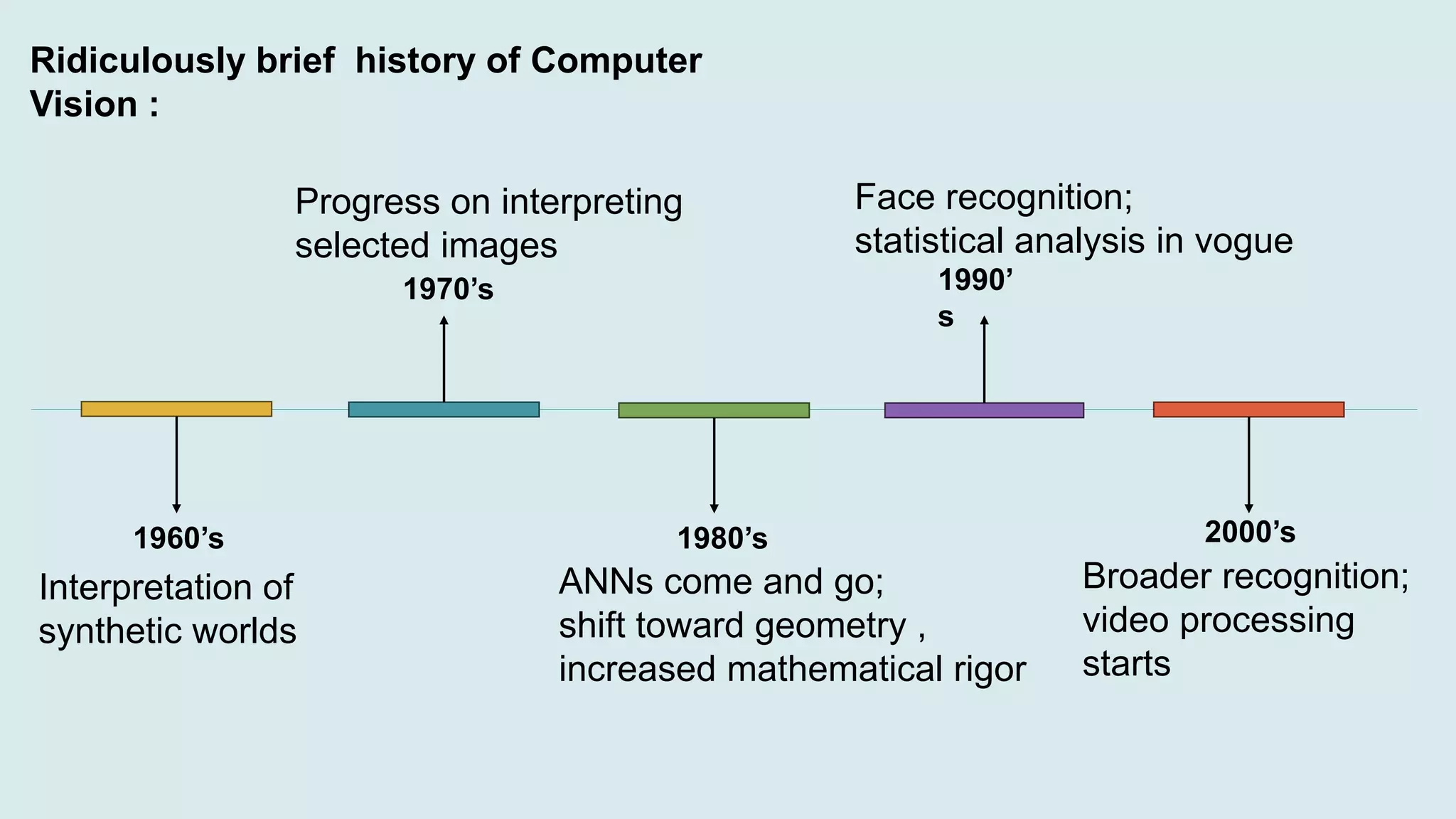
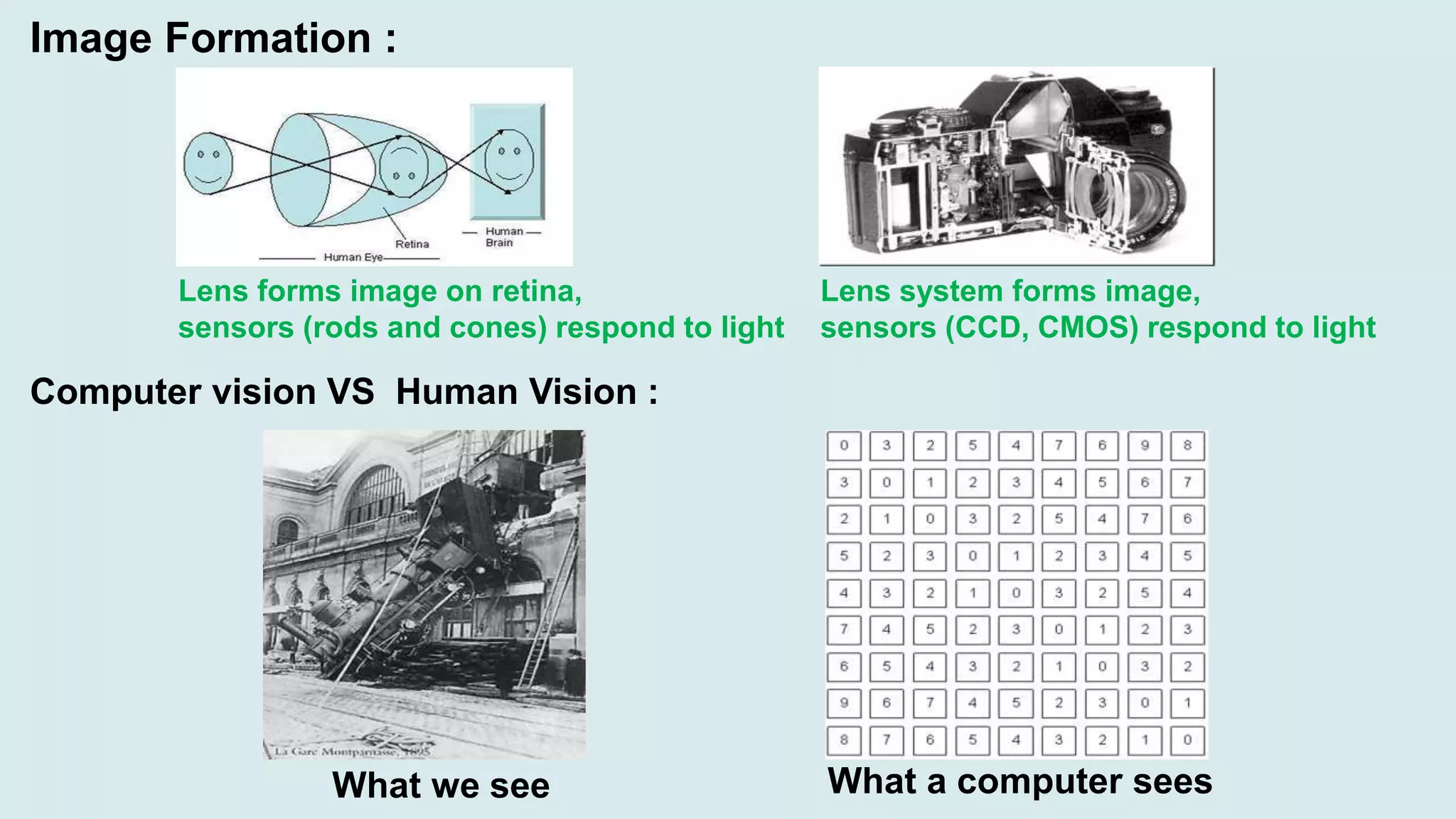
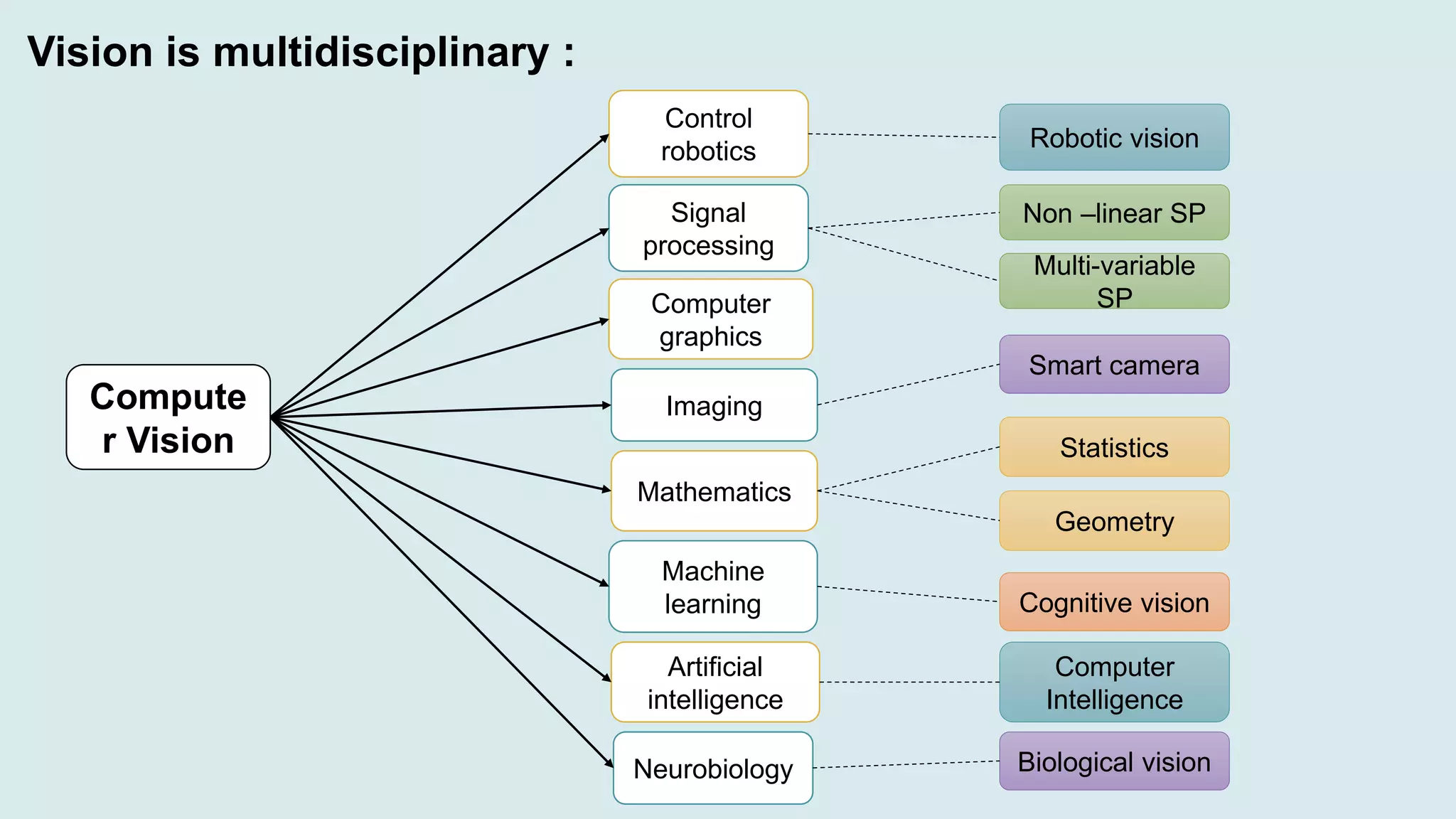
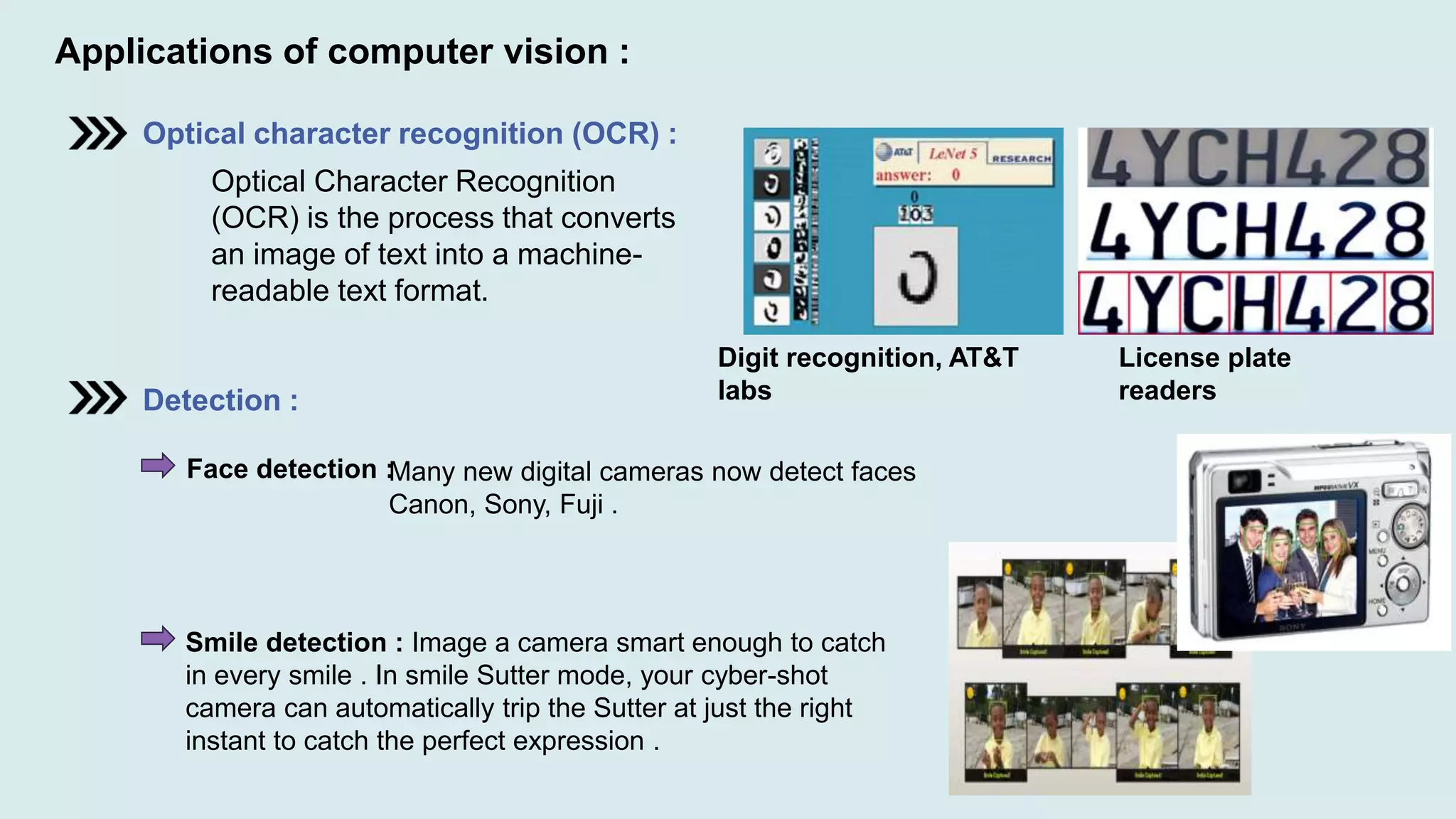
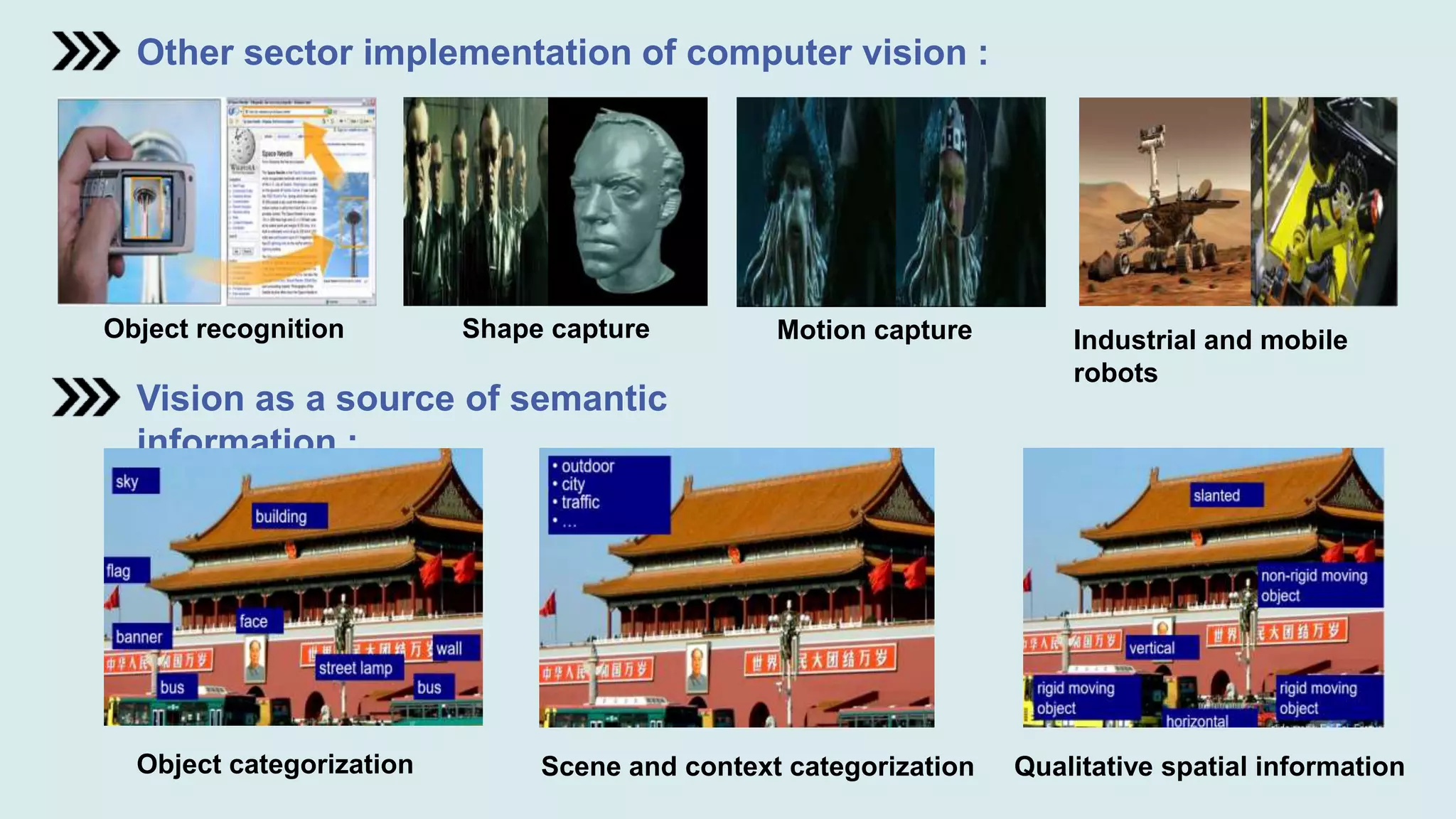
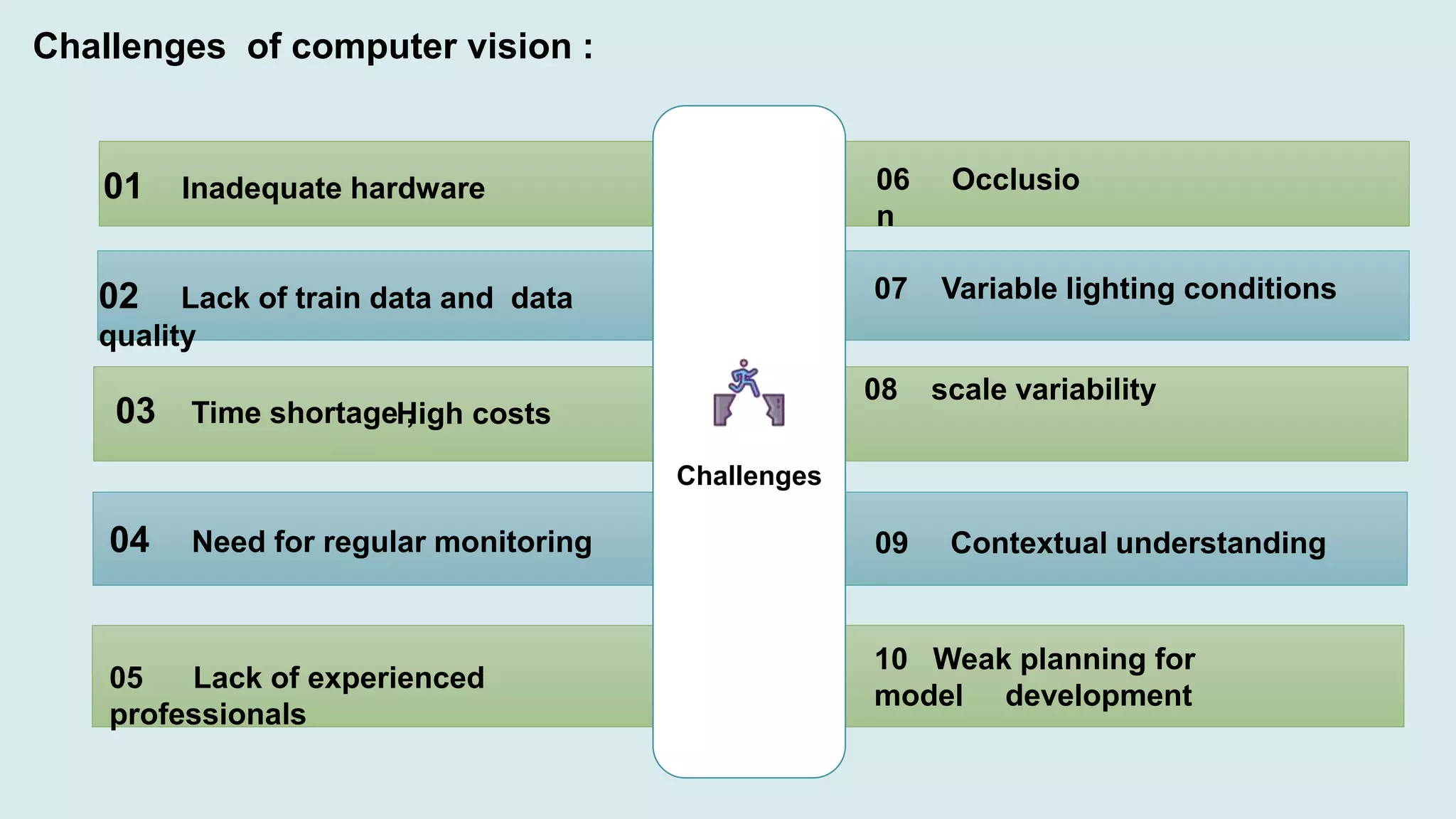
Computer vision is a field of artificial intelligence that enables computers to derive meaningful information from visual inputs like images and videos. It has various applications including optical character recognition, face detection, pedestrian detection, disease detection, self-driving cars, and medical imaging. Some challenges of computer vision include inadequate hardware, lack of training data, variable lighting conditions, occlusion, scale variability, and contextual understanding.