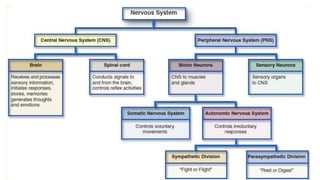
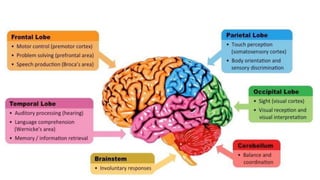
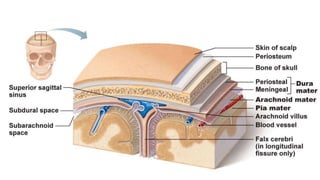
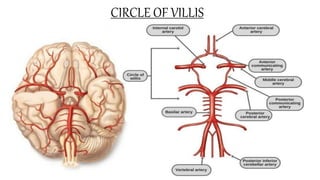
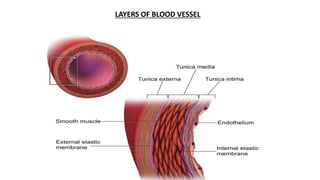
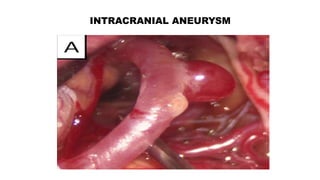
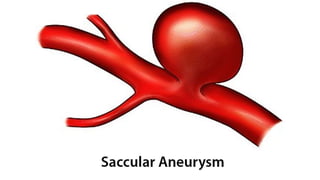
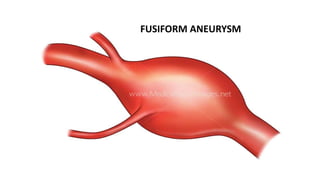
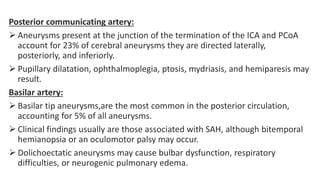
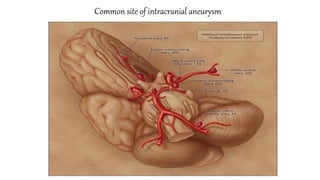
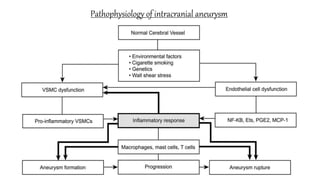
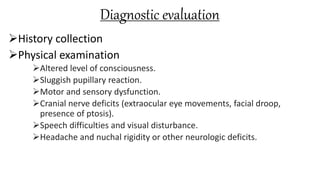
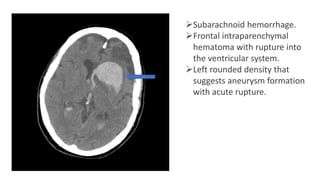
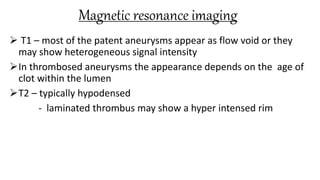
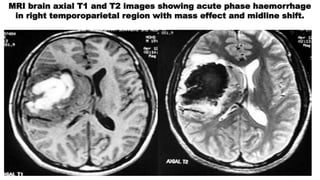
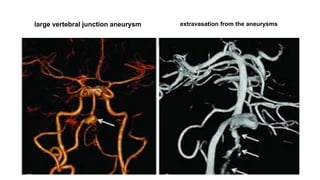
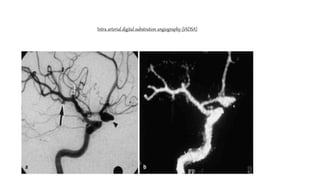
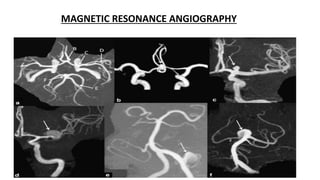
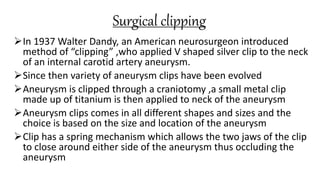
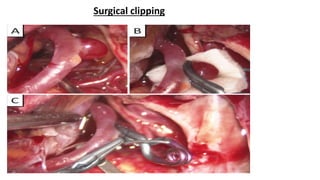
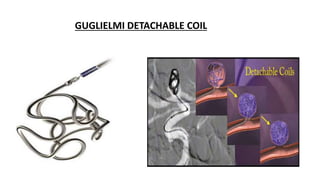
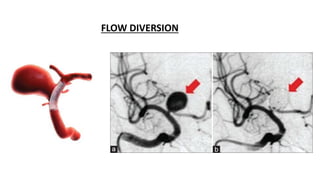
The document discusses intracranial aneurysms, which are abnormal dilations of arteries in the brain. It describes the anatomy of the circle of Willis where most aneurysms occur. Common types are saccular, fusiform, and dissecting aneurysms. Risk factors include hypertension, smoking, genetics and connective tissue disorders. Signs and symptoms depend on the location and whether the aneurysm has ruptured. Diagnostic tests include CT, MRI, cerebral angiography and lumbar puncture. Complications of rupture include rebleeding, vasospasm and hydrocephalus. Management involves treating risk factors medically for unruptured aneurysms and surgery or endovascular coiling for ruptured aneurysms to prevent re